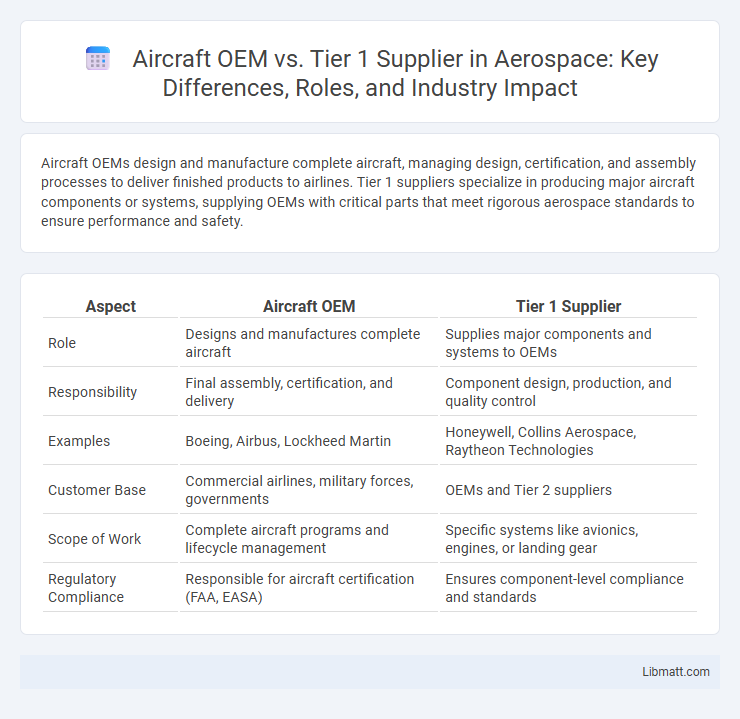
Aircraft OEMs design and manufacture complete aircraft, managing design, certification, and assembly processes to deliver finished products to airlines. Tier 1 suppliers specialize in producing major aircraft components or systems, supplying OEMs with critical parts that meet rigorous aerospace standards to ensure performance and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aircraft OEM | Tier 1 Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Designs and manufactures complete aircraft | Supplies major components and systems to OEMs |
| Responsibility | Final assembly, certification, and delivery | Component design, production, and quality control |
| Examples | Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin | Honeywell, Collins Aerospace, Raytheon Technologies |
| Customer Base | Commercial airlines, military forces, governments | OEMs and Tier 2 suppliers |
| Scope of Work | Complete aircraft programs and lifecycle management | Specific systems like avionics, engines, or landing gear |
| Regulatory Compliance | Responsible for aircraft certification (FAA, EASA) | Ensures component-level compliance and standards |
Introduction to Aircraft OEMs and Tier 1 Suppliers
Aircraft OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) design, engineer, and assemble entire aircraft, holding primary responsibility for the final product delivered to airlines or military clients. Tier 1 suppliers provide critical subsystems and major components, such as avionics, engines, or landing gear, directly to OEMs, playing a key role in aircraft production and quality assurance. Understanding your role within this supply chain can optimize collaboration and innovation between manufacturers and suppliers.
Defining the Roles: OEMs vs Tier 1 Suppliers
Aircraft OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) are responsible for designing, engineering, and assembling the complete aircraft, integrating systems and ensuring regulatory compliance. Tier 1 suppliers specialize in producing large, complex components or systems such as engines, avionics, or fuselage sections, delivering these fully integrated assemblies directly to OEMs. The distinct roles emphasize OEMs' system-level accountability while Tier 1 suppliers focus on high-value module manufacturing and subsystem integration within the aerospace supply chain.
Key Differences in Responsibilities and Deliverables
Aircraft OEMs are responsible for the overall design, integration, and certification of the entire aircraft, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and meeting market demands. Tier 1 suppliers deliver complex systems or major components such as avionics, landing gear, or propulsion units, providing specialized engineering, manufacturing, and testing services directly to OEMs. While OEMs oversee the final product and maintain system-level accountability, Tier 1 suppliers focus on the development and supply of critical subsystems that meet OEM specifications and quality requirements.
The Supply Chain Structure in Aerospace
The aerospace supply chain structure is characterized by a hierarchical relationship where Aircraft OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) design and assemble the final aircraft, relying on Tier 1 Suppliers to deliver major subsystems and components meeting strict quality and certification standards. Tier 1 Suppliers manage complex supply networks themselves, sourcing parts from Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers while ensuring integration, compliance, and timely delivery to the OEMs. This structured collaboration streamlines production, enhances innovation, and mitigates risks in the aerospace manufacturing process.
Collaboration Models Between OEMs and Tier 1 Suppliers
Collaboration models between aircraft OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers often involve integrated product teams that facilitate joint development and real-time problem solving. These partnerships rely on synchronized engineering processes and shared digital platforms to streamline supply chain management and enhance quality control. Your role in this ecosystem can benefit from clear communication channels and aligned objectives that support innovation and timely delivery.
Innovation and Technology Development: Who Leads?
Aircraft OEMs lead innovation by driving comprehensive technology development from conceptual design to system integration, leveraging their deep expertise and vast R&D resources. Tier 1 suppliers excel in specialized innovation, focusing on advancing component-level technologies and manufacturing processes to meet OEM specifications. Collaborative partnerships between OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers accelerate the adoption of cutting-edge materials, digitalization, and propulsion advancements in aerospace.
Quality Control and Certification Standards
Aircraft OEMs implement rigorous quality control processes aligned with stringent certification standards such as FAA and EASA to ensure the overall safety and airworthiness of the aircraft. Tier 1 suppliers must adhere to these OEM requirements while maintaining their own quality management systems, often certified under AS9100 and NADCAP, to deliver components that meet precise aerospace specifications. Your collaboration with Tier 1 suppliers demands strict oversight to guarantee that every part complies with industry regulations and contributes to the aircraft's certified performance.
Challenges Faced by OEMs and Tier 1 Suppliers
Aircraft OEMs face challenges such as managing complex global supply chains, ensuring regulatory compliance, and meeting stringent safety and performance standards. Tier 1 suppliers encounter difficulties in maintaining quality control, adhering to OEM specifications, and balancing cost pressures while innovating advanced components. Both entities must collaborate closely to address delivery schedules and integrate cutting-edge technologies efficiently.
Future Trends in OEM-Tier 1 Relationships
Future trends in aircraft OEM-Tier 1 relationships emphasize enhanced collaboration through digital integration and advanced data sharing technologies. OEMs increasingly rely on Tier 1 suppliers for innovation in lightweight materials and systems integration to meet sustainability targets and regulatory requirements. This evolving partnership fosters joint development initiatives and supply chain transparency, driving efficiency and agility in aircraft production.
Conclusion: Impact on the Aerospace Industry
Aircraft OEMs drive innovation and brand value by designing and assembling complete aircraft, while Tier 1 suppliers specialize in manufacturing critical systems and components, ensuring quality and efficiency. The collaboration between OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers enhances supply chain resilience, reduces production costs, and accelerates time-to-market for new aerospace technologies. This dynamic partnership significantly advances industry standards, fosters technological breakthroughs, and strengthens global aerospace competitiveness.
Aircraft OEM vs Tier 1 Supplier Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com