Overlock stitching secures fabric edges with multiple threads to prevent fraying, ideal for durable seams and stretchy materials, while flatlock stitching joins two fabric pieces edge-to-edge, creating a flat, smooth seam that enhances comfort and reduces bulk, perfect for activewear and garments meant to minimize irritation against Your skin. Choosing between overlock and flatlock depends on the seam strength, stretch, and comfort required for Your project.
Table of Comparison
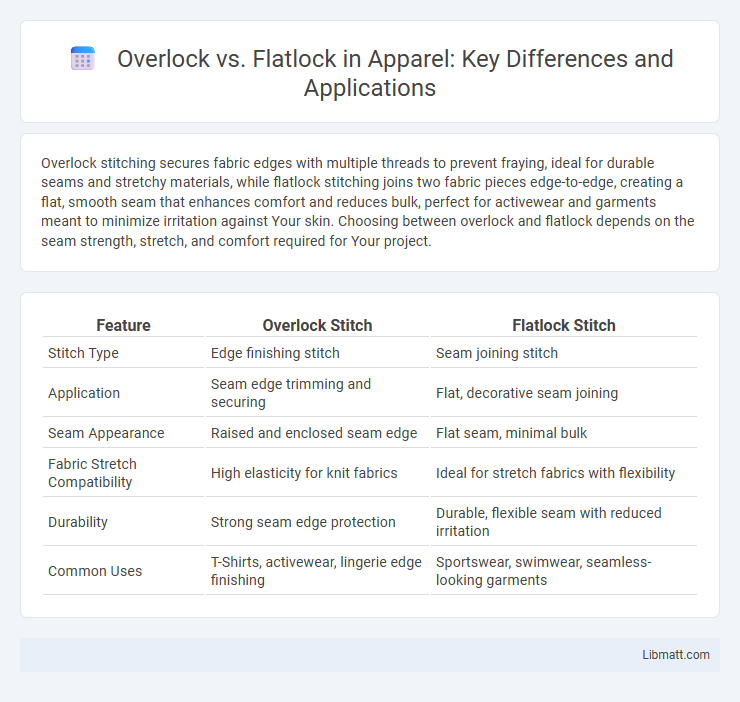
| Feature | Overlock Stitch | Flatlock Stitch |
|---|---|---|
| Stitch Type | Edge finishing stitch | Seam joining stitch |
| Application | Seam edge trimming and securing | Flat, decorative seam joining |
| Seam Appearance | Raised and enclosed seam edge | Flat seam, minimal bulk |
| Fabric Stretch Compatibility | High elasticity for knit fabrics | Ideal for stretch fabrics with flexibility |
| Durability | Strong seam edge protection | Durable, flexible seam with reduced irritation |
| Common Uses | T-Shirts, activewear, lingerie edge finishing | Sportswear, swimwear, seamless-looking garments |
Introduction to Overlock and Flatlock Stitches
Overlock stitches use multiple threads to encase fabric edges, preventing fraying while providing durable seam finishes ideal for knit and stretch fabrics. Flatlock stitches join fabric pieces edge-to-edge, creating flat, seam-reducing joins commonly found in activewear and swimwear for enhanced comfort. Both stitches offer specialized seam solutions, with overlock focusing on edge finishing and flatlock emphasizing flat, stretchable seams.
How Overlock Stitching Works
Overlock stitching uses multiple threads looped together to encase the edge of fabric, preventing fraying while providing stretch and durability. This method involves a specialized overlock machine that trims excess fabric as it sews, creating a clean, secure seam ideal for knitwear and stretchy materials. Understanding how overlock stitching works can help you achieve professional-quality finishes in garment construction and fabric edge management.
How Flatlock Stitching Works
Flatlock stitching joins two fabric edges by overlapping them and sewing through both layers, creating a flat seam that minimizes bulk and enhances comfort. This technique uses a specialized sewing machine with multiple needles and loopers to interlock threads, producing a strong, flexible seam ideal for activewear and stretch fabrics. Your garments benefit from the flatlock stitch's ability to reduce chafing and improve durability compared to traditional overlock seams.
Key Differences Between Overlock and Flatlock
Overlock stitching uses multiple threads to trim and sew edges simultaneously, creating a secure seam ideal for preventing fabric fraying, often found in garment construction. Flatlock stitching joins two pieces of fabric edge-to-edge without overlapping, resulting in a flat, decorative seam that reduces bulk and enhances comfort, commonly used in activewear and sportswear. The primary distinction lies in overlock's edge-finishing and seam-strengthening capability versus flatlock's flat, flexible seam appearance optimized for stretch fabrics.
Applications of Overlock Stitching
Overlock stitching is primarily used in garment manufacturing for finishing seams and preventing fabric fraying in knitwear, activewear, and stretch fabrics. It provides a strong, flexible edge ideal for hems, cuffs, and side seams in T-shirts, leggings, and underwear. The stitch's durability and elasticity make it essential for mass production of apparel requiring clean, professional seam finishes.
Applications of Flatlock Stitching
Flatlock stitching is widely used in activewear and sportswear due to its smooth, flat seams that reduce chafing and enhance comfort during physical activities. This technique is common in swimwear, leggings, and compression garments where flexibility and skin-friendly seams are essential. Flatlock stitching also appears in casual clothing and upholstery, providing durable seams with a distinctive decorative finish.
Pros and Cons of Overlock Stitches
Overlock stitches provide excellent edge finishing and seam durability, preventing fabric fraying while allowing stretch compatible with knit materials, making them ideal for activewear and stretchy fabrics. However, overlock machines can be complex and costly, with limited stitch variety compared to flatlock, and the dense stitching may cause fabric puckering on delicate materials. The rapid sewing speed and ability to trim fabric edges simultaneously enhance production efficiency but require skilled operation to avoid thread tension issues.
Pros and Cons of Flatlock Stitches
Flatlock stitches provide a smooth, flat seam ideal for activewear and swimwear, offering comfort with minimal chafing and effective stretchability. However, flatlock seams tend to be less durable than overlock seams and may allow increased water or wind penetration. The stitch's exposed thread can also lead to quicker wear in heavy-duty applications, limiting its use in rugged or high-friction garments.
Choosing the Right Stitch: Overlock vs Flatlock
Overlock stitches provide strong, durable seams with a professional finish ideal for edge trimming and preventing fabric fraying, commonly used in garment construction. Flatlock stitches create flat, flexible seams perfect for activewear and stretch fabrics, reducing bulk and enhancing comfort against the skin. Selecting between overlock and flatlock depends on fabric type, desired seam strength, and the garment's intended use for optimal performance and appearance.
Overlock vs Flatlock: Final Comparison and Verdict
Overlock stitching provides strong, durable seams ideal for preventing fabric fraying, making it perfect for garment construction requiring high stretch and resilience. Flatlock stitching, however, offers a smooth, flat seam that enhances comfort by reducing bulk and chafing, commonly used in activewear and seamless apparel. For Your project, choose overlock for durability and reinforcement, while flatlock is preferable when comfort and an aesthetically flat seam are priorities.
overlock vs flatlock Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com