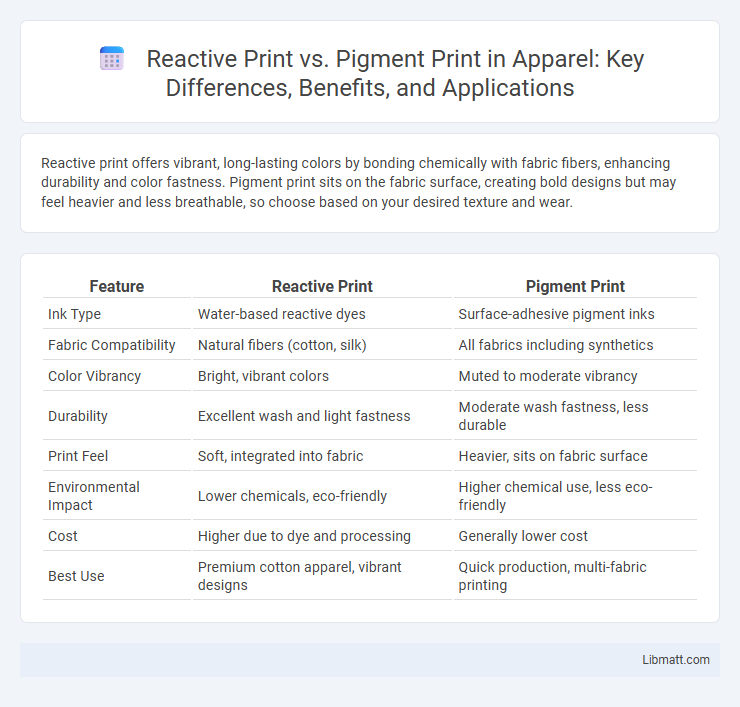
Reactive print offers vibrant, long-lasting colors by bonding chemically with fabric fibers, enhancing durability and color fastness. Pigment print sits on the fabric surface, creating bold designs but may feel heavier and less breathable, so choose based on your desired texture and wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reactive Print | Pigment Print |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Type | Water-based reactive dyes | Surface-adhesive pigment inks |
| Fabric Compatibility | Natural fibers (cotton, silk) | All fabrics including synthetics |
| Color Vibrancy | Bright, vibrant colors | Muted to moderate vibrancy |
| Durability | Excellent wash and light fastness | Moderate wash fastness, less durable |
| Print Feel | Soft, integrated into fabric | Heavier, sits on fabric surface |
| Environmental Impact | Lower chemicals, eco-friendly | Higher chemical use, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher due to dye and processing | Generally lower cost |
| Best Use | Premium cotton apparel, vibrant designs | Quick production, multi-fabric printing |
Introduction to Textile Printing Methods
Reactive print uses reactive dyes that chemically bond with cotton fibers, resulting in vibrant, durable colors ideal for natural fabrics. Pigment print applies color pigments that sit on the fabric surface, suitable for a wide range of textiles and offering versatility with less water usage. Both methods are essential in textile printing, with reactive printing favored for softness and wash-fastness, while pigment printing excels in cost-effectiveness and fabric compatibility.
What is Reactive Printing?
Reactive printing is a textile dyeing process where reactive dyes form a covalent bond with the fabric fibers, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors. This method is primarily used on cotton and other cellulose fibers and offers excellent wash and light fastness compared to pigment printing. Unlike pigment printing, reactive printing penetrates the fiber, ensuring deeper color saturation and a softer hand feel on the finished textile.
What is Pigment Printing?
Pigment printing involves applying colored pigments onto the fabric's surface without significant chemical bonding, resulting in vibrant and durable designs suitable for various textiles. Unlike reactive printing, which forms a chemical bond with natural fibers, pigment printing relies on a binder to adhere the color, making it versatile across both natural and synthetic materials. Your choice between pigment and reactive printing should consider fabric type, desired durability, and the vibrancy of the final print.
Key Differences Between Reactive and Pigment Print
Reactive print uses dyes that chemically bond with fabric fibers, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors with excellent wash durability, while pigment print applies color as a surface coating that sits on top of the fabric, offering less vibrancy and shorter lifespan. Reactive prints are ideal for cotton and natural fibers due to their deep penetration and softer feel, whereas pigment prints are versatile across various materials but may feel stiffer. Your choice between these methods impacts colorfastness, fabric feel, and durability, with reactive prints typically providing superior quality for textile applications.
Color Vibrancy and Fastness Comparison
Reactive print offers superior color vibrancy due to its chemical bonding with fabric fibers, resulting in brighter and more vivid hues compared to pigment print, which sits on the fabric surface and may appear duller. Reactive dyes exhibit excellent color fastness, maintaining brightness and resisting fading through multiple washes and exposure to sunlight, whereas pigment prints tend to have lower wash and light fastness, often fading or cracking over time. This fundamental difference makes reactive printing ideal for high-quality textile applications requiring long-lasting, vibrant colors.
Fabric Compatibility: Reactive vs Pigment
Reactive prints are best suited for natural fibers like cotton, linen, and silk, where the dye chemically bonds with the fabric for vibrant, long-lasting colors. Pigment prints are compatible with a wider range of textiles, including synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, as they coat the fabric surface rather than penetrating it. The choice between reactive and pigment printing often depends on the specific fabric composition and desired durability of the print.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reactive print offers superior environmental sustainability due to its water-based dyes, which bond chemically with cotton fibers, reducing harmful chemical runoff and water consumption compared to pigment print. Pigment printing, relying on surface adhesion of pigments, often requires higher levels of binders and thickening agents, increasing the environmental footprint through additional wastewater treatment challenges and less biodegradability. Choosing reactive printing methods supports eco-friendly textile production by minimizing toxic effluents and enhancing fabric longevity, aligning with sustainable industry standards.
Cost Efficiency and Production Process
Pigment printing generally offers lower upfront costs since it uses color pigments that stay on the fabric surface, reducing the need for extensive water and energy consumption during production. Reactive printing, while often more expensive due to the chemical bonding process between dye and fiber, delivers more vibrant and long-lasting colors, making it cost-efficient over large-volume or high-quality textile runs. You can optimize production by choosing pigment printing for faster turnaround and lower initial investment, whereas reactive printing suits projects demanding superior color durability and softness.
Applications and Popular Uses
Reactive print is widely used for dyeing natural fibers like cotton and silk, making it popular in fashion and home textiles due to its vibrant colors and excellent wash fastness. Pigment print applies to a broader range of fabric types, including synthetics and blends, favored for producing bold, durable designs on sportswear, upholstery, and promotional textiles. You'll find reactive prints dominating high-quality apparel, while pigment prints suit cost-effective, versatile applications where colorfastness to washing is less critical.
Choosing the Right Printing Method
Reactive print offers vibrant colors and excellent durability on natural fibers like cotton, making it ideal for high-quality apparel and textiles requiring soft hand feel and colorfastness. Pigment print provides versatility across various fabric types and quicker production with a slightly raised texture but offers less wash durability compared to reactive printing. Choosing the right printing method depends on fabric type, desired print longevity, color vibrancy, and production speed requirements.
Reactive print vs pigment print Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com