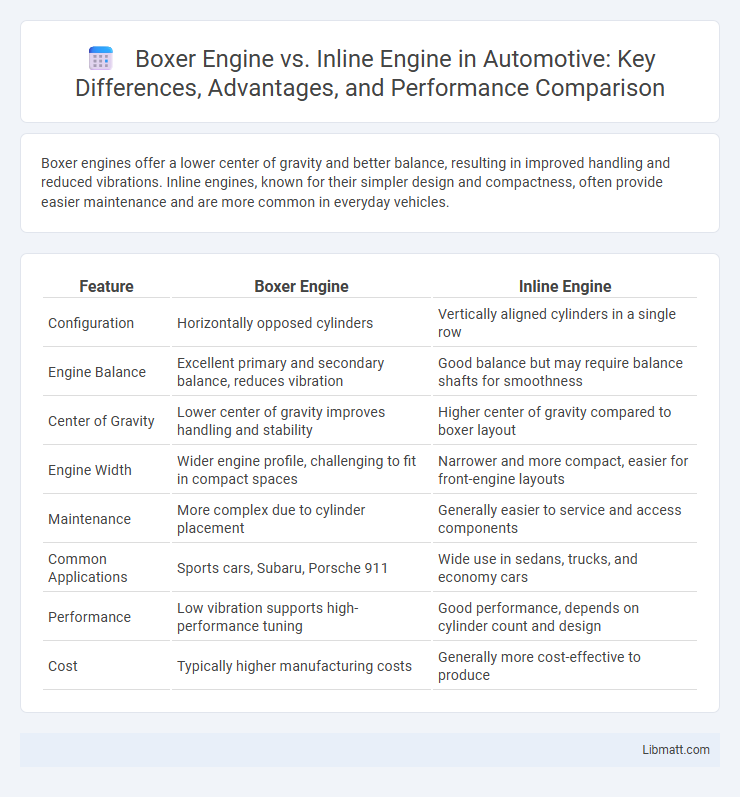
Boxer engines offer a lower center of gravity and better balance, resulting in improved handling and reduced vibrations. Inline engines, known for their simpler design and compactness, often provide easier maintenance and are more common in everyday vehicles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Boxer Engine | Inline Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Horizontally opposed cylinders | Vertically aligned cylinders in a single row |
| Engine Balance | Excellent primary and secondary balance, reduces vibration | Good balance but may require balance shafts for smoothness |
| Center of Gravity | Lower center of gravity improves handling and stability | Higher center of gravity compared to boxer layout |
| Engine Width | Wider engine profile, challenging to fit in compact spaces | Narrower and more compact, easier for front-engine layouts |
| Maintenance | More complex due to cylinder placement | Generally easier to service and access components |
| Common Applications | Sports cars, Subaru, Porsche 911 | Wide use in sedans, trucks, and economy cars |
| Performance | Low vibration supports high-performance tuning | Good performance, depends on cylinder count and design |
| Cost | Typically higher manufacturing costs | Generally more cost-effective to produce |
Overview of Boxer and Inline Engines
Boxer engines feature horizontally opposed cylinders, providing a low center of gravity and improved balance, which enhances vehicle stability and handling. Inline engines arrange cylinders in a single row, offering compact design, easier maintenance, and typically smoother power delivery for everyday driving. Your choice between these engine types depends on priorities like performance, space, and vehicle dynamics.
Design Differences: Boxer vs Inline Engines
Boxer engines feature horizontally opposed cylinders that lie flat in pairs on either side of the crankshaft, promoting a lower center of gravity and improved balance. Inline engines arrange cylinders in a single straight line, simplifying design and often resulting in a narrower engine profile suitable for compact engine bays. Your choice between boxer and inline engines depends on vehicle packaging needs and desired performance characteristics.
Performance Comparison: Power and Torque
Boxer engines deliver a lower center of gravity and enhanced balance, resulting in smoother power delivery and improved handling dynamics. Inline engines typically produce higher peak power due to their simpler design and ability to accommodate more cylinders in a straight configuration. Torque characteristics in boxer engines often favor mid-range responsiveness, while inline engines provide strong torque across a wider RPM range, optimizing acceleration and overall performance.
Handling and Vehicle Dynamics
Boxer engines contribute to superior handling and vehicle dynamics due to their low center of gravity, which enhances stability and reduces body roll during cornering. Inline engines, typically taller and narrower, result in a higher engine mounting position, potentially raising the vehicle's center of gravity and affecting agility. Subaru and Porsche models with boxer engines are renowned for their balanced weight distribution, offering improved traction and precise steering response compared to many inline engine configurations.
Engine Size and Packaging
Boxer engines feature a horizontally opposed cylinder layout that allows for a lower center of gravity and a more compact engine height, making them ideal for vehicles with tight engine bays and improved handling dynamics. Inline engines, characterized by cylinders arranged in a straight line, typically take up more vertical space but offer easier packaging in engines' lengthwise orientation, which can benefit vehicles designed with longitudinal engine mounts. Understanding how engine size and packaging affect your vehicle's balance and space can guide you in choosing the optimal engine configuration for performance and design constraints.
Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
Boxer engines typically offer better fuel efficiency due to their lower center of gravity and smoother operation, which reduces internal friction and energy loss. Inline engines often produce higher emissions because their design can lead to less efficient combustion and greater heat buildup. Advances in fuel injection and exhaust treatment technologies have narrowed these differences, but boxer engines generally maintain an edge in both fuel economy and lower emissions.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Boxer engines offer lower vibration due to their horizontally opposed pistons, which translates to reduced wear on engine components and improved long-term reliability compared to inline engines. Inline engines generally have fewer moving parts and a simpler design, making maintenance tasks quicker and more cost-effective. Your choice between these engine types should consider the balance between smoother operation in boxer engines and the easier serviceability of inline engines.
Cost of Production and Ownership
Boxer engines typically have higher production costs due to their complex design and wider engine block, which also increases manufacturing material requirements. Inline engines, with their simpler and more compact structure, generally offer lower production expenses, contributing to reduced initial vehicle costs. Maintenance and repair for inline engines tend to be less costly and simpler, resulting in lower overall ownership expenses compared to the often more labor-intensive servicing needed for boxer engines.
Common Applications and Popular Models
Boxer engines, characterized by their horizontally opposed cylinders, are commonly found in Subaru and Porsche vehicles, with popular models including the Subaru Impreza and Porsche 911. Inline engines, noted for their straightforward design and smooth operation, dominate in compact and midsize cars, featuring prominently in models like the Toyota Corolla and BMW 3 Series. Both engine types cater to different performance and packaging preferences, influencing their application across various automotive segments.
Pros and Cons: Boxer Engine vs Inline Engine
Boxer engines offer a lower center of gravity and smoother balance due to their horizontally opposed cylinders, enhancing vehicle stability and handling, but they tend to be wider and more complex to manufacture. Inline engines provide a more compact, simpler design that is easier to maintain and often more fuel-efficient, yet they can generate more vibration and heat due to the cylinder arrangement. The choice between boxer and inline engines depends on priorities like performance, packaging constraints, and maintenance preferences.
Boxer engine vs Inline engine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com