Premium gas contains a higher octane rating than regular gas, which improves engine performance and reduces knocking in high-compression engines. Your vehicle's manufacturer guidelines determine whether premium fuel is necessary for optimal efficiency and engine health.
Table of Comparison
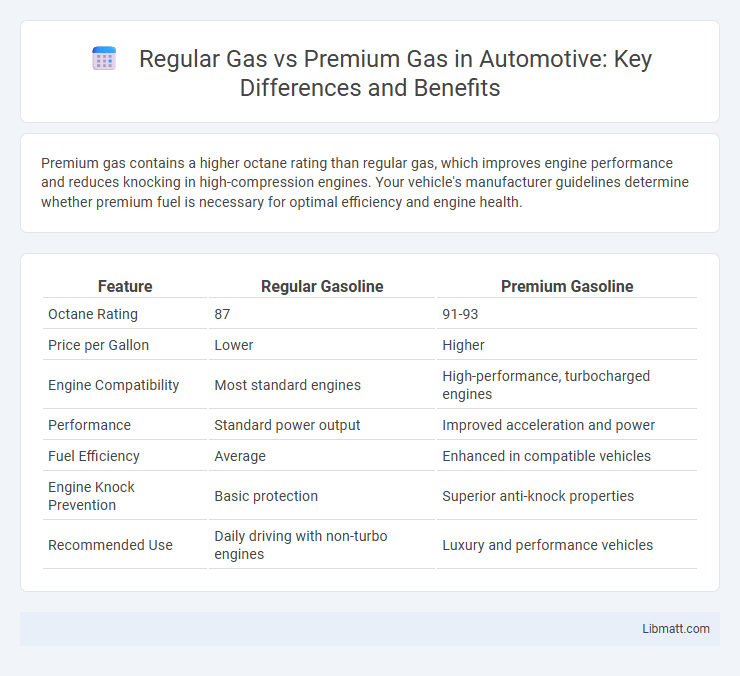
| Feature | Regular Gasoline | Premium Gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Octane Rating | 87 | 91-93 |
| Price per Gallon | Lower | Higher |
| Engine Compatibility | Most standard engines | High-performance, turbocharged engines |
| Performance | Standard power output | Improved acceleration and power |
| Fuel Efficiency | Average | Enhanced in compatible vehicles |
| Engine Knock Prevention | Basic protection | Superior anti-knock properties |
| Recommended Use | Daily driving with non-turbo engines | Luxury and performance vehicles |
Understanding Regular Gas and Premium Gas
Regular gas typically contains an octane rating of 87, suitable for most standard engines and promoting efficient combustion. Premium gas, with an octane rating usually 91 or higher, is designed for high-performance or luxury vehicles requiring greater resistance to engine knocking. Understanding the octane rating helps drivers choose the appropriate fuel to optimize engine performance and prevent damage.
Key Differences Between Regular and Premium Gas
Regular gas typically contains an octane rating of 87, while premium gas has a higher octane rating, usually 91 to 93, which helps prevent engine knocking in high-performance engines. Premium fuel is designed to withstand higher compression ratios found in luxury or sports cars, improving performance and efficiency. Using premium gas in vehicles not requiring it generally does not provide significant benefits and can result in unnecessary expenses.
Octane Ratings: What Do They Mean?
Octane ratings measure a fuel's ability to resist engine knocking during combustion, with regular gas typically rated at 87 and premium gas at 91 or higher. Higher octane fuels like premium are designed to prevent knocking in high-performance or turbocharged engines, optimizing efficiency and power. Using the appropriate octane rating for your vehicle ensures smooth operation and protects your engine from potential damage.
Engine Performance: Regular vs Premium Gas
Regular gas typically contains an octane rating of 87, while premium gas ranges from 91 to 93, impacting engine performance significantly. High-performance or turbocharged engines often require premium gas to prevent knocking and ensure optimal combustion, resulting in smoother acceleration and better power output. Choosing the correct fuel for your vehicle maintains engine efficiency and prolongs its lifespan, avoiding potential damage from premature ignition.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Premium gas typically contains a higher octane rating, which can improve engine performance in vehicles designed for it, potentially enhancing fuel efficiency. Regular gas, with a lower octane rating, is generally sufficient for most standard engines and does not usually impact fuel efficiency negatively in such vehicles. Using premium gas in an engine not optimized for higher octane often results in no significant gains in fuel efficiency or engine performance.
Cost Analysis: Is Premium Worth the Price?
Regular gasoline typically costs 30-50 cents less per gallon than premium gas, making it a more budget-friendly option for most drivers. Cars designed for regular gas do not experience significant performance gains or improved fuel efficiency when using premium, resulting in minimal added value. Premium gas is only worth the extra cost for vehicles requiring higher octane to prevent engine knocking and maintain optimal performance.
Manufacturer Recommendations for Fuel Types
Vehicle manufacturers specify fuel types based on engine design to optimize performance and fuel efficiency; most modern cars are designed to run efficiently on regular gasoline with an octane rating of 87. Premium gas, typically with an octane rating of 91 or higher, is recommended for high-compression engines or performance vehicles to prevent knocking and ensure smooth operation. Using the manufacturer-recommended fuel type preserves engine longevity, maintains warranty coverage, and can prevent costly repairs from improper fuel use.
Impact on Engine Longevity
Using premium gas in engines designed for regular fuel generally does not enhance engine longevity and provides minimal benefits in performance or engine health. Regular gasoline meets the required octane rating for most standard engines, ensuring efficient combustion that prevents knocking and minimizes wear. Your engine's longevity depends more on proper maintenance and using the manufacturer-recommended fuel type than on choosing premium over regular gasoline.
Environmental Considerations
Regular gas produces fewer emissions than premium gas due to its lower octane rating, which typically results in more complete combustion in standard engines. Premium gas often contains additional additives that can reduce engine deposits but doesn't significantly reduce overall environmental impact unless used in high-performance vehicles designed for it. Your choice between regular and premium gas should consider the environmental benefits of efficient engine performance matched with fuel type to minimize pollution.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gas Choices
Regular gas typically has an octane rating of 87, while premium gas ranges from 91 to 93, influencing engine performance and efficiency. Your vehicle's owner's manual usually indicates the recommended fuel type to prevent knocking and maintain optimal function. Choosing the correct gas type can impact your car's engine longevity, fuel economy, and overall performance.
Regular gas vs Premium gas Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com