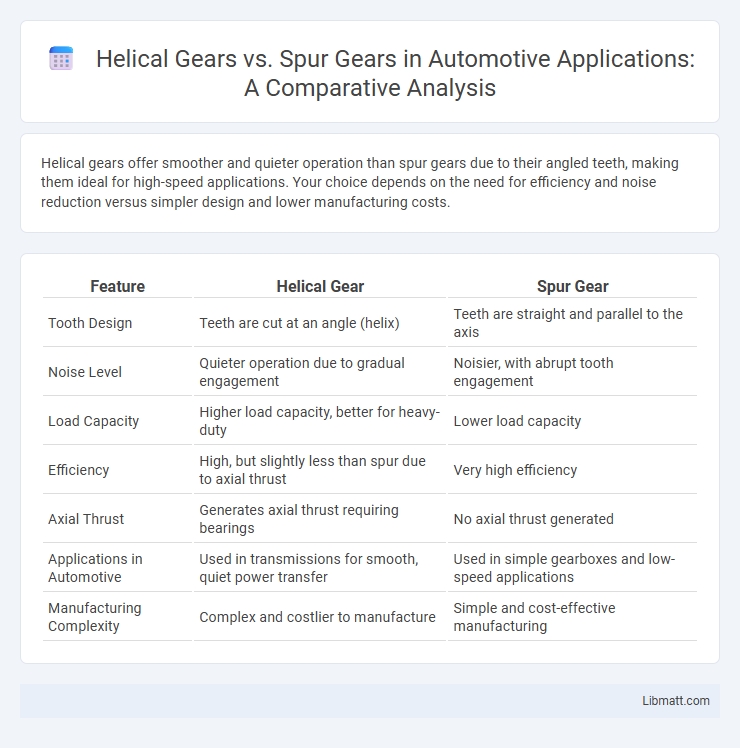
Helical gears offer smoother and quieter operation than spur gears due to their angled teeth, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Your choice depends on the need for efficiency and noise reduction versus simpler design and lower manufacturing costs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Helical Gear | Spur Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Design | Teeth are cut at an angle (helix) | Teeth are straight and parallel to the axis |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation due to gradual engagement | Noisier, with abrupt tooth engagement |
| Load Capacity | Higher load capacity, better for heavy-duty | Lower load capacity |
| Efficiency | High, but slightly less than spur due to axial thrust | Very high efficiency |
| Axial Thrust | Generates axial thrust requiring bearings | No axial thrust generated |
| Applications in Automotive | Used in transmissions for smooth, quiet power transfer | Used in simple gearboxes and low-speed applications |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Complex and costlier to manufacture | Simple and cost-effective manufacturing |
Introduction to Helical and Spur Gears
Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which have straight teeth and transfer power abruptly. Spur gears are typically used for simple, low-speed applications due to their efficiency and ease of manufacturing, while helical gears excel in high-speed, high-load environments. Your choice between these gears will depend on the balance needed between noise reduction, load capacity, and complexity in mechanical design.
Basic Structure and Design Differences
Helical gears feature angled teeth that create a diagonal pattern, allowing for smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which have straight teeth parallel to the gear's axis. The angled teeth of helical gears engage gradually, distributing load more evenly and reducing noise and vibration, while spur gears transmit power with simple and direct tooth contact. Your choice between the two depends on the application's need for noise reduction and load capacity versus simplicity and cost-effectiveness in gear design.
How Helical Gears Work
Helical gears operate by engaging teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear axis, creating a gradual and smooth transfer of power through more contact points compared to spur gears. This angled tooth design enables helical gears to handle higher loads and run quieter due to the continuous tooth engagement. The angled teeth also generate axial thrust which requires bearings to absorb these forces, making their application suitable for high-speed and high-torque scenarios.
How Spur Gears Work
Spur gears operate by transmitting motion and power through straight teeth mounted parallel to the gear's axis, allowing them to efficiently engage and mesh with other spur gears. Their design ensures direct, straightforward force transfer, making them ideal for applications requiring constant speed and torque. You benefit from their simplicity and effectiveness in driving parallel shafts with minimal friction and noise.
Efficiency Comparison
Helical gears generally offer higher efficiency compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which allow for smoother and quieter operation with less vibration. Spur gears tend to have higher losses from impact and noise caused by their straight teeth, resulting in slightly lower mechanical efficiency, especially at high speeds. Your choice between the two should consider that helical gears typically maintain better efficiency in applications requiring continuous, high-speed operation.
Noise and Vibration Levels
Helical gears generate less noise and vibration compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which engage gradually and provide smoother transmission of power. Spur gears produce higher noise levels because their teeth engage abruptly along the entire face width, causing impact and vibration. This difference makes helical gears preferable in applications requiring quieter operation and reduced mechanical stress.
Load Capacity and Strength
Helical gears possess higher load capacity and strength compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which distribute forces more evenly and provide smoother engagement. You benefit from reduced noise and increased durability when using helical gears in high-load applications, while spur gears, with their straight teeth, are better suited for lower load scenarios with simpler design requirements. The enhanced strength of helical gears makes them ideal for heavy machinery and automotive transmissions where reliability under stress is critical.
Applications in Industry
Helical gears are widely used in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery due to their smooth, quiet operation and ability to handle high loads. Spur gears, favored in simple mechanical devices like conveyor systems and gear pumps, offer efficient power transmission with straightforward design and manufacturing. Industries choose helical gears for precision and noise-sensitive environments, while spur gears excel in cost-effective, high-speed applications.
Maintenance and Durability
Helical gears offer superior durability due to their angled teeth, which provide smoother and quieter operation, reducing wear and extending maintenance intervals compared to spur gears. Spur gears, with straight teeth, are prone to higher noise levels and greater stress concentration, leading to more frequent maintenance and shorter lifespan under heavy load conditions. Proper lubrication and alignment are critical for both gear types to maximize performance and prevent premature failure.
Pros and Cons Summary
Helical gears offer smoother and quieter operation due to angled teeth, enhancing load capacity and efficiency, but they generate axial thrust requiring additional support and are more complex to manufacture. Spur gears provide simpler design, lower cost, and ease of maintenance with parallel teeth, yet they tend to produce more noise and vibration under high-speed or heavy-load conditions. The choice between helical and spur gears depends on the application's noise tolerance, load requirements, and budget constraints.
Helical gear vs Spur gear Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com