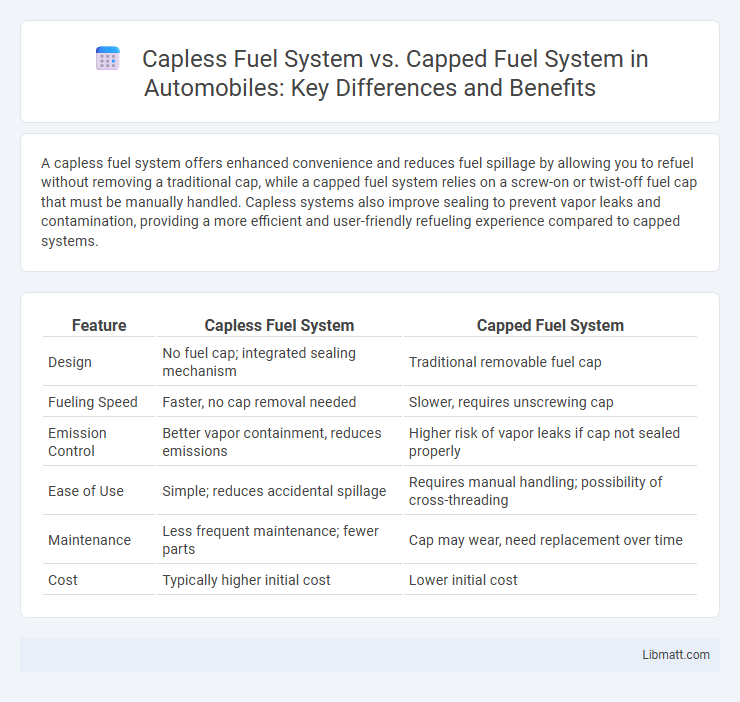
A capless fuel system offers enhanced convenience and reduces fuel spillage by allowing you to refuel without removing a traditional cap, while a capped fuel system relies on a screw-on or twist-off fuel cap that must be manually handled. Capless systems also improve sealing to prevent vapor leaks and contamination, providing a more efficient and user-friendly refueling experience compared to capped systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Capless Fuel System | Capped Fuel System |
|---|---|---|
| Design | No fuel cap; integrated sealing mechanism | Traditional removable fuel cap |
| Fueling Speed | Faster, no cap removal needed | Slower, requires unscrewing cap |
| Emission Control | Better vapor containment, reduces emissions | Higher risk of vapor leaks if cap not sealed properly |
| Ease of Use | Simple; reduces accidental spillage | Requires manual handling; possibility of cross-threading |
| Maintenance | Less frequent maintenance; fewer parts | Cap may wear, need replacement over time |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Fuel Systems
Fuel systems play a critical role in modern vehicles by storing and delivering fuel efficiently to the engine. Capless fuel systems eliminate the traditional fuel cap, using a sealed mechanism that prevents fuel evaporation and reduces emissions, while capped fuel systems rely on a removable fuel cap to secure the fuel tank. Understanding the differences between these systems helps you maintain fuel efficiency and environmental compliance.
What is a Capless Fuel System?
A capless fuel system eliminates the traditional screw-on fuel cap by using a spring-loaded flap or seal that provides a secure closure, preventing fuel evaporation and reducing emissions. This design allows for easier and faster refueling, as you simply insert the nozzle without having to remove or hold a cap. Your vehicle benefits from improved convenience and less risk of fuel contamination or spillage with a capless fuel system compared to a capped fuel system.
Understanding Capped Fuel Systems
Capped fuel systems use traditional screw-on caps that create a physical barrier to seal the fuel tank, preventing fuel evaporation and contamination. These caps rely on rubber gaskets to maintain a tight seal, which may wear out over time and require replacement to ensure proper function. Understanding capped fuel systems helps you maintain your vehicle's fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by regularly inspecting and securing the fuel cap.
Key Differences Between Capless and Capped Fuel Systems
Capless fuel systems eliminate the traditional screw-on cap by incorporating a sealed, spring-loaded flap that opens automatically when refueling, reducing evaporation and the risk of fuel spillage. Capped fuel systems rely on a manual screw or flip cap, requiring users to tighten or untighten the cap to secure the fuel tank, which can lead to potential fuel vapor leaks if not properly sealed. The capless design enhances convenience and environmental protection by maintaining a tighter seal and minimizing volatile organic compound emissions compared to capped systems.
Advantages of Capless Fuel Systems
Capless fuel systems offer significant advantages such as faster and easier refueling, reducing spills and fumes for a cleaner, safer experience. These systems improve fuel vapor containment, enhancing fuel efficiency and lowering emissions, which supports environmental goals. You benefit from increased convenience paired with minimized maintenance, as capless designs prevent dirt and debris from entering the fuel tank.
Benefits of Capped Fuel Systems
Capped fuel systems provide reliable sealing that prevents fuel evaporation and contamination, enhancing engine performance and fuel efficiency. They offer ease of maintenance and compatibility with traditional fueling stations, ensuring safe and secure fuel storage. Your vehicle benefits from added protection against environmental elements and reduced risk of fuel leaks with a capped fuel system.
Common Problems with Capless Fuel Systems
Capless fuel systems often face issues such as debris buildup and malfunctioning seals, which can lead to fuel contamination and difficulty in refueling. Unlike capped systems, capless designs may allow dirt or water to enter the filler neck if the internal flap isn't properly maintained. Understanding these common problems helps you ensure proper maintenance and avoid potential fuel system damage.
Maintenance Tips for Both Fuel Systems
Maintaining a capless fuel system involves regularly inspecting the sealing valve to prevent dirt and debris buildup, ensuring smooth nozzle insertion during refueling without fuel spillage. For capped fuel systems, routinely check and replace the fuel cap gasket to avoid vapor leaks and contamination, and securely tighten the cap after each refuel to maintain fuel system integrity. Your proactive maintenance helps optimize fuel efficiency and prevents potential engine issues regardless of the fuel system type.
Fuel Efficiency and Safety Comparison
Capless fuel systems enhance fuel efficiency by reducing evaporation loss, ensuring more fuel remains in the tank compared to traditional capped fuel systems prone to vapor leakage. Safety improves as capless designs minimize fuel spills and exposure to harmful vapors, lowering fire risks during refueling. Your vehicle benefits from these advancements with cleaner emissions and a more secure fueling process.
Choosing the Right Fuel System for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right fuel system for your vehicle depends on convenience, maintenance, and environmental factors. Capless fuel systems offer quick refueling with a sealed design to reduce evaporation and fuel contamination, while capped systems require manual securing but are widely compatible and easier to repair. Evaluate your vehicle's usage, ease of access, and local emissions regulations to determine which fuel system best suits your needs.
Capless Fuel System vs Capped Fuel System Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com