DC fast charging delivers high power directly to your electric vehicle's battery, enabling rapid charging in a short time, ideal for long trips and quick top-ups. AC charging supplies alternating current through your onboard charger at a slower rate, making it suitable for overnight or home charging where speed is less critical.
Table of Comparison
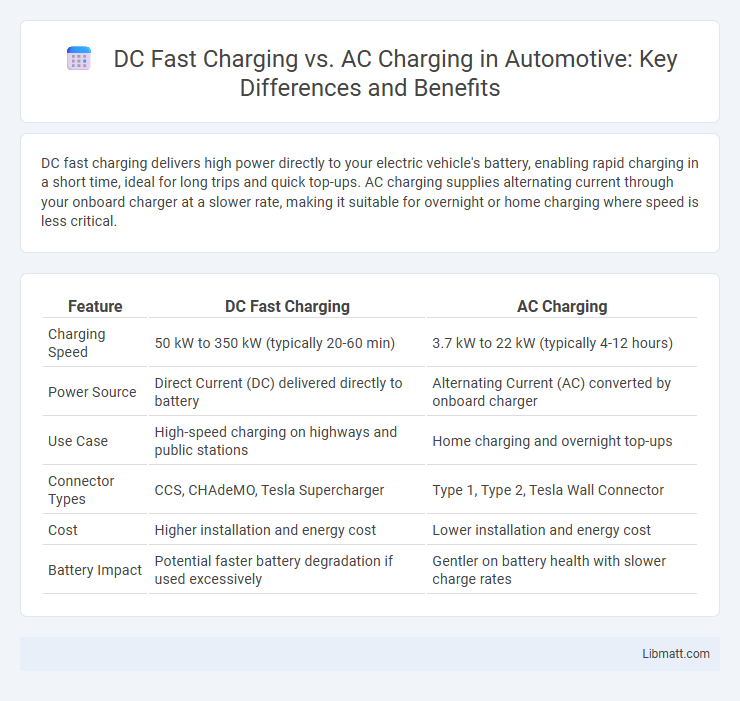
| Feature | DC Fast Charging | AC Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | 50 kW to 350 kW (typically 20-60 min) | 3.7 kW to 22 kW (typically 4-12 hours) |
| Power Source | Direct Current (DC) delivered directly to battery | Alternating Current (AC) converted by onboard charger |
| Use Case | High-speed charging on highways and public stations | Home charging and overnight top-ups |
| Connector Types | CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger | Type 1, Type 2, Tesla Wall Connector |
| Cost | Higher installation and energy cost | Lower installation and energy cost |
| Battery Impact | Potential faster battery degradation if used excessively | Gentler on battery health with slower charge rates |
Introduction to Electric Vehicle Charging
DC fast charging delivers high power directly to your electric vehicle's battery, significantly reducing charging time compared to AC charging, which supplies power through an onboard charger at a slower rate. AC charging is typically used for overnight or workplace charging with lower power levels, whereas DC fast chargers provide rapid energy replenishment for long-distance travel. Understanding these differences helps optimize your charging strategy for convenience and efficiency.
What is DC Fast Charging?
DC fast charging delivers direct current (DC) electricity directly to an electric vehicle's battery, enabling significantly faster recharge times compared to alternating current (AC) charging, which requires onboard conversion. By bypassing the vehicle's internal charger, DC fast chargers provide high power output--typically ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW--allowing electric vehicles to regain 80% battery capacity in roughly 20-30 minutes. This rapid charging technology is essential for long-distance travel and reducing downtime, especially in public charging networks.
What is AC Charging?
AC charging delivers alternating current from the power grid to an electric vehicle (EV), requiring the car's onboard charger to convert it into direct current (DC) for battery storage. Typically operating at lower power levels (up to 22 kW for home or public stations), AC charging is slower compared to DC fast charging but more commonly available at residences and workplaces. This method suits overnight or extended charging periods, supporting gradual energy replenishment without stressing the EV battery.
Key Differences Between DC Fast Charging and AC Charging
DC fast charging delivers direct current directly to your electric vehicle's battery, enabling rapid energy transfer and significantly shorter charging times compared to AC charging, which requires your vehicle's onboard charger to convert alternating current. AC charging, commonly available at homes and workplaces, typically provides slower charging speeds due to the limited capacity of onboard chargers and lower power output levels. The key differences lie in power delivery method, charging speed, infrastructure requirements, and compatibility with vehicle charging systems.
Charging Speed Comparison
DC fast charging delivers significantly higher power levels, typically ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW, enabling electric vehicles (EVs) to charge from 20% to 80% in approximately 20 to 40 minutes. In contrast, AC charging operates at lower power levels, usually between 3.7 kW and 22 kW, which can require several hours for a full charge depending on the EV's battery capacity. The substantial difference in charging speed makes DC fast charging ideal for long trips and rapid top-ups, whereas AC charging is more suited for overnight home or workplace charging.
Infrastructure and Availability
DC fast charging infrastructure delivers high-power direct current directly to electric vehicle batteries, enabling rapid recharge times at dedicated stations typically found along highways and urban centers. AC charging relies on alternating current supplied through residential or workplace chargers, with broader availability but significantly slower charging speeds due to onboard vehicle converters. The widespread adoption of DC fast chargers is growing but remains limited by higher installation costs and grid demands, whereas AC chargers offer more extensive coverage for everyday use and overnight charging at home.
Vehicle Compatibility and Limitations
DC fast charging delivers high voltage power directly to your vehicle's battery, enabling rapid charging but requiring specific compatibility with your electric car's onboard systems, typically found in newer EV models. AC charging relies on the vehicle's onboard charger to convert alternating current to direct current, limiting charging speed but ensuring broader compatibility across most EVs. Understanding these compatibility and system limitations helps you choose the ideal charging method based on your vehicle's specifications and charging needs.
Cost Implications
DC fast charging systems typically involve higher installation and equipment costs compared to AC charging due to the need for specialized power electronics and infrastructure upgrades. Operating expenses for DC fast chargers might be elevated because of increased energy demand and maintenance requirements, while AC chargers generally incur lower ongoing costs. Your investment decision should weigh the faster charging benefits against the greater upfront and operational expenses of DC fast charging solutions.
Impact on Battery Health
DC fast charging delivers high voltage directly to the battery, enabling rapid energy transfer but generating increased heat, which can accelerate battery degradation over time. AC charging provides a slower, controlled current through the onboard charger, resulting in lower thermal stress and better preservation of battery lifespan. Frequent use of DC fast charging should be balanced with regular AC charging to optimize overall battery health and performance.
Which Charging Option is Right for You?
DC fast charging delivers high power directly to the battery, making it ideal for quick top-ups during long trips or when time is limited, with charging speeds reaching up to 350 kW. AC charging, typically ranging from 3.7 kW to 22 kW, is well-suited for overnight or extended home charging, providing a slower but more convenient and widely accessible option. Choosing the right charging method depends on your driving habits, daily range needs, and access to charging infrastructure.
DC fast charging vs AC charging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com