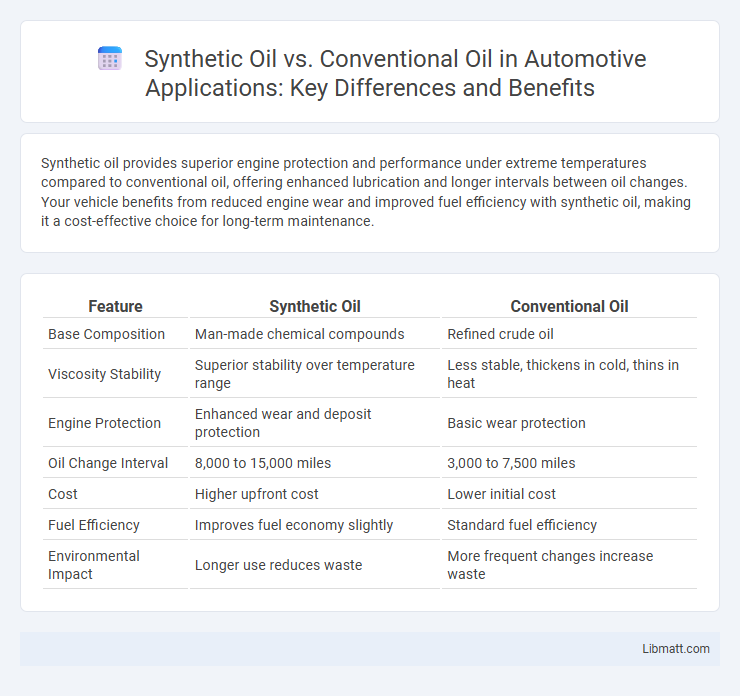
Synthetic oil provides superior engine protection and performance under extreme temperatures compared to conventional oil, offering enhanced lubrication and longer intervals between oil changes. Your vehicle benefits from reduced engine wear and improved fuel efficiency with synthetic oil, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Oil | Conventional Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Base Composition | Man-made chemical compounds | Refined crude oil |
| Viscosity Stability | Superior stability over temperature range | Less stable, thickens in cold, thins in heat |
| Engine Protection | Enhanced wear and deposit protection | Basic wear protection |
| Oil Change Interval | 8,000 to 15,000 miles | 3,000 to 7,500 miles |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves fuel economy slightly | Standard fuel efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | Longer use reduces waste | More frequent changes increase waste |
Introduction to Motor Oils
Motor oils are essential lubricants designed to reduce friction, wear, and heat in internal combustion engines. Synthetic oils are chemically engineered to provide superior performance, enhanced thermal stability, and longer oil change intervals compared to conventional oils derived from refined crude. Understanding the differences between synthetic and conventional motor oils helps optimize engine protection and fuel efficiency.
What is Synthetic Oil?
Synthetic oil is a man-made lubricant engineered through chemical synthesis to provide superior performance and protection compared to conventional oil derived from crude oil. It offers enhanced viscosity stability, improved resistance to thermal breakdown, and better lubrication at extreme temperatures, extending engine life and efficiency. This engineered formulation reduces engine wear, minimizes deposits, and delivers consistent performance under harsh driving conditions.
What is Conventional Oil?
Conventional oil, also known as mineral oil, is derived directly from crude oil through refining processes and contains natural impurities and hydrocarbons of varying molecular sizes. It offers basic lubrication properties suitable for many older or low-demand engines but breaks down faster under extreme temperatures and stress compared to synthetic alternatives. Regular oil changes are necessary to maintain engine performance when using conventional oil.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Conventional Oil
Synthetic oil offers superior engine protection due to its uniform molecular structure and enhanced additives, resulting in better performance under extreme temperatures and longer oil change intervals. Conventional oil, derived from crude oil, contains more impurities and degrades faster, making it suitable for older vehicles with less demanding engine requirements. Your choice between synthetic and conventional oil impacts engine longevity, fuel efficiency, and maintenance costs, making synthetic oil a preferred option for modern engines.
Performance Benefits of Synthetic Oil
Synthetic oil offers superior performance benefits over conventional oil, including enhanced engine protection through better thermal stability and reduced oxidation under high temperatures. Its advanced formulation ensures improved lubrication, which reduces engine wear, enhances fuel efficiency, and supports longer oil change intervals. You can expect smoother engine operation and increased reliability, especially in extreme driving conditions or high-performance vehicles.
Cost Comparison: Synthetic vs Conventional Oil
Synthetic oil typically costs between $40 to $70 per oil change, while conventional oil ranges from $20 to $45, making synthetic oil more expensive upfront. Despite the higher cost, synthetic oil offers longer-lasting protection and extended oil change intervals of up to 10,000 to 15,000 miles compared to 3,000 to 5,000 miles for conventional oil. Over time, the extended service intervals and superior engine performance can offset the initial price difference, providing better value for vehicle maintenance.
Engine Protection and Longevity
Synthetic oil offers superior engine protection and longevity by providing enhanced resistance to thermal breakdown and oxidation compared to conventional oil. Its uniform molecular structure ensures better lubrication, reducing engine wear and extending the lifespan of crucial engine components. Regular use of synthetic oil can result in improved engine performance and fewer maintenance issues over time.
Environmental Impact
Synthetic oil offers enhanced environmental benefits compared to conventional oil due to its superior engine efficiency and longer drain intervals, which reduce oil waste and lower overall consumption. Its advanced formulation produces fewer harmful emissions and improves fuel economy, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Reduced frequency of oil changes also diminishes the environmental hazards associated with oil disposal and contamination.
Suitable Applications for Each Oil Type
Synthetic oil is ideal for high-performance engines, turbocharged vehicles, and extreme temperature conditions due to its superior thermal stability and enhanced lubrication properties. Conventional oil suits older car models, light-duty vehicles, and engines with simple designs, providing adequate protection for everyday driving at a lower cost. Understanding your engine's requirements helps you choose the appropriate oil, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Choosing the Right Oil for Your Vehicle
Synthetic oil offers superior engine protection and improved performance by resisting high temperatures and reducing engine wear compared to conventional oil. Conventional oil, derived from crude oil, is generally more affordable but requires more frequent changes to maintain optimal engine health. Choosing the right oil for your vehicle depends on your driving habits, manufacturer recommendations, and long-term maintenance goals to ensure engine longevity.
Synthetic oil vs Conventional oil Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com