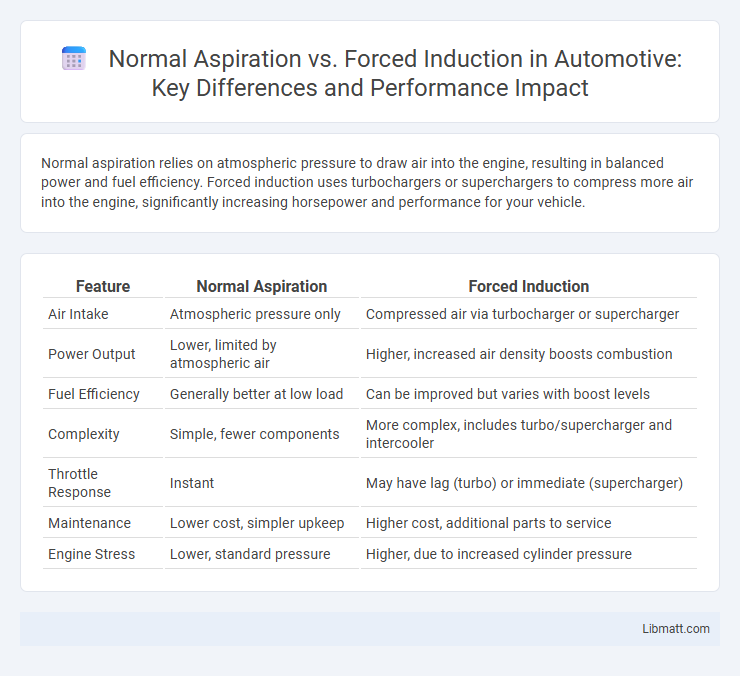
Normal aspiration relies on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the engine, resulting in balanced power and fuel efficiency. Forced induction uses turbochargers or superchargers to compress more air into the engine, significantly increasing horsepower and performance for your vehicle.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Normal Aspiration | Forced Induction |
|---|---|---|
| Air Intake | Atmospheric pressure only | Compressed air via turbocharger or supercharger |
| Power Output | Lower, limited by atmospheric air | Higher, increased air density boosts combustion |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally better at low load | Can be improved but varies with boost levels |
| Complexity | Simple, fewer components | More complex, includes turbo/supercharger and intercooler |
| Throttle Response | Instant | May have lag (turbo) or immediate (supercharger) |
| Maintenance | Lower cost, simpler upkeep | Higher cost, additional parts to service |
| Engine Stress | Lower, standard pressure | Higher, due to increased cylinder pressure |
Introduction to Engine Aspiration Methods
Engine aspiration methods define how air enters an internal combustion engine, significantly impacting performance and efficiency. Normal aspiration, or naturally aspirated engines, rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber without external assistance. Forced induction, including turbocharging and supercharging, uses compressors to increase air density, allowing more oxygen for combustion and resulting in higher power output and improved engine responsiveness.
What is Naturally Aspirated (NA) Engine?
A Naturally Aspirated (NA) engine relies solely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber without the aid of turbochargers or superchargers. This type of engine typically provides more linear throttle response and predictable power delivery compared to forced induction systems. NA engines often exhibit simpler design and maintenance requirements, though they generally produce less horsepower per liter than forced induction counterparts.
Forced Induction Explained: Turbocharging and Supercharging
Forced induction enhances engine performance by increasing air intake pressure through turbocharging or supercharging, allowing more oxygen for combustion and significantly boosting power output. Turbochargers use exhaust gases to spin a turbine that compresses the air entering the engine, improving efficiency and power without direct engine power loss. Superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, providing immediate boost at lower RPMs but with a slight reduction in overall efficiency due to the engine power required to operate the compressor.
Performance Comparison: NA vs Forced Induction
Normal aspiration delivers power through natural air intake, resulting in linear throttle response and predictable performance. Forced induction, such as turbocharging or supercharging, significantly increases engine output by compressing more air into the combustion chamber, boosting horsepower and torque. Your choice impacts acceleration and efficiency, with forced induction offering superior performance gains, especially at higher RPMs.
Fuel Efficiency and Economy Analysis
Normal aspiration engines typically offer better fuel efficiency due to their simpler design and lower internal friction, leading to reduced fuel consumption in everyday driving. Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged variants, increase air intake and power output but may consume more fuel under heavy load or aggressive acceleration because of the higher demand for fuel. Your choice between the two should consider driving habits and fuel economy goals, as forced induction can provide performance benefits with a trade-off in average fuel economy.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Normal aspiration engines generally require less maintenance due to their simpler design, with fewer components that can fail compared to forced induction systems. Forced induction, such as turbocharging or supercharging, increases engine stress and heat, demanding more frequent inspections and higher-quality lubricants to maintain reliability. Your vehicle's maintenance schedule will vary significantly based on forced induction, so staying proactive ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Long-Term
Normal aspiration engines have lower upfront costs due to simpler design and fewer components, making them more affordable for initial purchase and maintenance. Forced induction, including turbocharging and supercharging, involves higher initial expenses because of added complexity, specialized parts, and potential engine reinforcement. Long-term costs for forced induction can increase due to higher maintenance demands, potential reliability concerns, and more expensive repairs if boosted components fail.
Driving Experience: Throttle Response and Power Delivery
Normal aspiration offers a more linear throttle response, providing smooth and predictable power delivery that enhances everyday driving comfort. Forced induction, such as turbocharging or supercharging, delivers rapid throttle response with a significant boost in power, resulting in a more aggressive and dynamic driving experience. Your choice between these systems will directly impact acceleration feel and overall engine responsiveness during different driving conditions.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Regulations
Normal aspiration engines produce fewer emissions due to simpler combustion processes, often meeting environmental regulations more easily. Forced induction increases power by compressing air, but can lead to higher nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and stricter regulatory scrutiny. You should consider the environmental impact and compliance requirements when choosing between these engine types for cleaner operation.
Choosing the Right Engine Aspiration for Your Needs
Choosing the right engine aspiration depends on your performance goals and driving preferences. Normal aspiration engines offer reliable power delivery and fuel efficiency, making them suitable for everyday driving and long-term durability. Forced induction engines, using turbochargers or superchargers, provide increased horsepower and torque, ideal for high-performance driving but may require more maintenance and fuel.
normal aspiration vs forced induction Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com