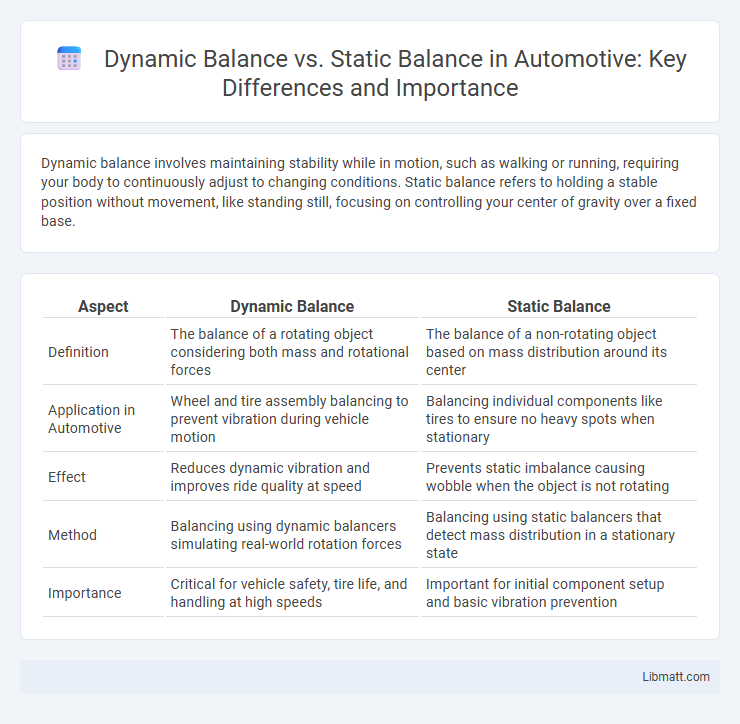
Dynamic balance involves maintaining stability while in motion, such as walking or running, requiring your body to continuously adjust to changing conditions. Static balance refers to holding a stable position without movement, like standing still, focusing on controlling your center of gravity over a fixed base.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dynamic Balance | Static Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The balance of a rotating object considering both mass and rotational forces | The balance of a non-rotating object based on mass distribution around its center |
| Application in Automotive | Wheel and tire assembly balancing to prevent vibration during vehicle motion | Balancing individual components like tires to ensure no heavy spots when stationary |
| Effect | Reduces dynamic vibration and improves ride quality at speed | Prevents static imbalance causing wobble when the object is not rotating |
| Method | Balancing using dynamic balancers simulating real-world rotation forces | Balancing using static balancers that detect mass distribution in a stationary state |
| Importance | Critical for vehicle safety, tire life, and handling at high speeds | Important for initial component setup and basic vibration prevention |
Introduction to Balance: Dynamic vs Static
Dynamic balance involves maintaining stability while in motion or transitioning between movements, requiring continuous adjustments to body positioning. Static balance, on the other hand, is the ability to hold a steady posture without movement, such as standing still on one leg. Understanding the differences between these types of balance helps you improve overall coordination and prevent falls during various activities.
Defining Dynamic Balance
Dynamic balance refers to the ability to maintain stability and control of the body while in motion or transitioning between movements, crucial for activities like walking, running, and sports performance. It involves continuous adjustments of the musculoskeletal system and nervous system to respond to changing external forces and maintain equilibrium. Your dynamic balance is essential for preventing falls and enhancing coordination during complex movements.
Defining Static Balance
Static balance refers to the ability to maintain the body's center of gravity within its base of support while remaining still or stationary. It is crucial for activities such as standing upright or holding a posture without movement, relying heavily on proprioceptive feedback from muscles, joints, and the vestibular system. Unlike dynamic balance, which involves maintaining stability during motion, static balance emphasizes control during periods of stillness and stability.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Static Balance
Dynamic balance involves maintaining stability while in motion or transitioning between movements, requiring continuous adjustments and muscle coordination. Static balance is the ability to hold a stable position without movement, relying heavily on proprioceptive feedback and core muscle engagement. Key differences include the influence of external forces and movement speed, where dynamic balance demands adaptability to changing environments, whereas static balance emphasizes steadiness and minimal sway.
Importance of Dynamic Balance in Daily Life
Dynamic balance enables smooth and coordinated movement during activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs, which are essential for maintaining independence and preventing falls. Unlike static balance, which involves maintaining posture while stationary, dynamic balance adapts to constant changes in your environment and body position. Developing strong dynamic balance improves overall stability, reduces injury risk, and enhances performance in everyday tasks and physical activities.
Importance of Static Balance in Daily Activities
Static balance is crucial for maintaining stability during stationary activities such as standing, sitting, or holding a posture, which are essential for everyday tasks like cooking, working at a desk, or grooming. This ability minimizes the risk of falls and injuries by providing a solid foundation for controlled movement and proper body alignment. Improving your static balance enhances overall functional independence and safety in daily life.
Factors Affecting Both Types of Balance
Muscle strength, proprioception, and visual input significantly influence both dynamic and static balance, with vestibular function playing a crucial role in maintaining equilibrium during movement and stillness. Surface stability and environmental conditions affect static balance more profoundly, whereas dynamic balance is highly dependent on coordination, reaction time, and neuromuscular control. Age-related decline, neurological disorders, and fatigue impair both types of balance by reducing sensory integration and motor responses, crucial for preventing falls and maintaining postural control.
Assessment Methods for Dynamic and Static Balance
Assessment methods for dynamic balance often include the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, functional reach test, and gait analysis, which evaluate an individual's ability to maintain stability during movement. Static balance assessment typically involves tests such as the Romberg test, single-leg stance, and force plate measurement, focusing on posture control while maintaining a stationary position. Both dynamic and static balance assessments provide crucial data for diagnosing balance impairments and tailoring rehabilitation programs effectively.
Training Techniques to Improve Dynamic and Static Balance
Training techniques to improve dynamic balance include exercises like single-leg hops, balance board drills, and agility ladder runs, which enhance coordination, proprioception, and strength during movement. Static balance training focuses on holds such as single-leg stands, yoga poses like Tree Pose, and using stability balls to develop core stability and postural control while maintaining stillness. Incorporating proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) and resistance training can further optimize improvements in both dynamic and static balance capabilities.
Choosing the Right Balance Exercises for Your Goals
Choosing the right balance exercises depends on your specific fitness goals, whether improving dynamic balance for movement and coordination or enhancing static balance for stability and posture control. Dynamic balance exercises like walking lunges and single-leg hops help with agility and functional mobility, vital for sports and everyday activities. Static balance training, such as standing on one leg or using a balance board, strengthens core muscles and enhances control during stationary positions, ideal for fall prevention and injury recovery.
Dynamic balance vs Static balance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com