Sequential injection delivers fuel to each cylinder independently in a precise order, improving fuel efficiency and emissions control, while batch injection sprays fuel into multiple cylinders simultaneously without synchronization to the intake stroke. Your engine's performance and responsiveness depend on the injection method, with sequential injection generally providing smoother operation and better fuel economy.
Table of Comparison
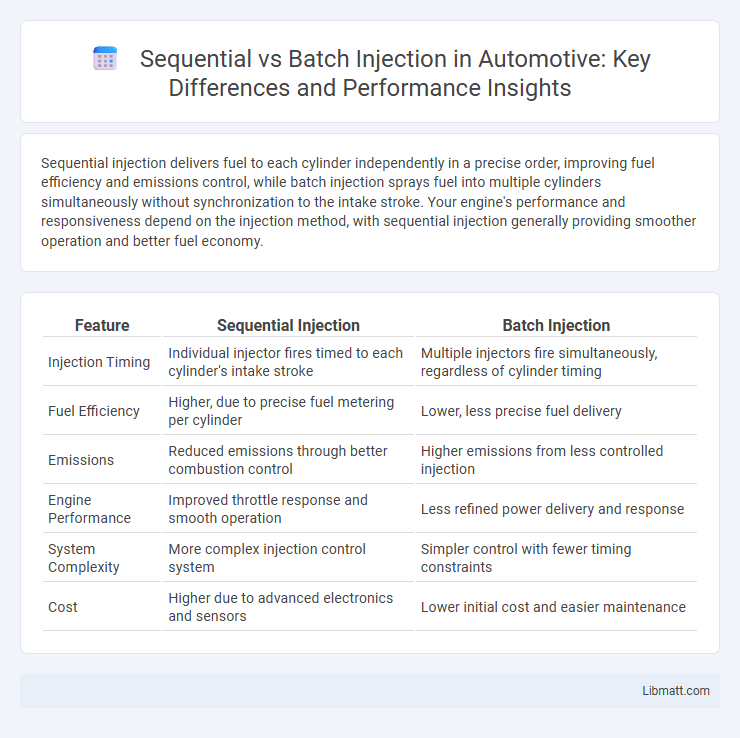
| Feature | Sequential Injection | Batch Injection |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Timing | Individual injector fires timed to each cylinder's intake stroke | Multiple injectors fire simultaneously, regardless of cylinder timing |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher, due to precise fuel metering per cylinder | Lower, less precise fuel delivery |
| Emissions | Reduced emissions through better combustion control | Higher emissions from less controlled injection |
| Engine Performance | Improved throttle response and smooth operation | Less refined power delivery and response |
| System Complexity | More complex injection control system | Simpler control with fewer timing constraints |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced electronics and sensors | Lower initial cost and easier maintenance |
Introduction to Sequential and Batch Injection
Sequential injection delivers fuel to each cylinder individually in a precise, timed sequence, improving combustion efficiency and reducing emissions. Batch injection supplies fuel simultaneously to multiple cylinders, often leading to less precise fuel delivery and potentially higher fuel consumption. Choosing between sequential and batch injection impacts engine performance, fuel economy, and emission levels.
Definition and Key Concepts
Sequential injection refers to introducing samples or reagents one at a time in a specific order, ensuring precise control and minimal cross-contamination during analysis. Batch injection involves processing multiple samples simultaneously or in groups, which increases throughput but may require more complex data handling and risk of sample interaction. Understanding these approaches helps you optimize workflow efficiency and accuracy in laboratory or industrial processes.
How Sequential Injection Works
Sequential injection involves delivering fuel into each cylinder individually and precisely timed to its intake stroke, optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions. This method uses sensors to monitor engine parameters and adjusts injection timing and quantity for each cylinder, enhancing fuel economy and performance. Compared to batch injection, sequential injection provides more accurate fuel delivery by synchronizing with the engine's firing order and speed.
How Batch Injection Works
Batch injection works by sending multiple malicious payloads in a single HTTP request, exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications that process bulk data inputs simultaneously. This method increases the attack surface by allowing injection of multiple commands or queries that execute together, often overwhelming security filters and making detection harder. Your systems must implement robust input validation and parameterized queries to mitigate risks associated with batch injection attacks.
Advantages of Sequential Injection
Sequential injection offers precise control over reagent introduction, minimizing reagent consumption and reducing waste. Your analytical results benefit from improved accuracy and reproducibility due to the controlled and consistent timing of sample and reagent mixing. This technique also enhances flexibility in method development, allowing customized reaction conditions for complex assays.
Advantages of Batch Injection
Batch injection enables higher throughput by allowing multiple data records to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing the number of individual database transactions. This method improves system efficiency and minimizes network latency, leading to faster data ingestion in large-scale applications. Additionally, batch injection reduces resource consumption on both the client and server sides, optimizing performance and lowering operational costs.
Comparative Analysis: Sequential vs Batch Injection
Sequential injection delivers reagents one at a time, allowing precise control over reaction intervals and minimizing cross-contamination, which enhances analytical accuracy. Batch injection processes multiple samples simultaneously, increasing throughput but potentially compromising individual sample integrity due to overlapping reactions. The choice between sequential and batch injection depends on the balance needed between accuracy and efficiency in analytical workflows.
Applications and Use Cases
Sequential injection excels in applications requiring precise, real-time control of fuel delivery, such as performance tuning and variable engine loads in modern gasoline engines. Batch injection is commonly used in simpler engine designs or retrofit applications where cost efficiency and ease of implementation take priority without sacrificing basic emission standards. Your choice depends on whether your system demands dynamic fuel management or a straightforward, cost-effective solution.
Factors Influencing Method Selection
Factors influencing the choice between sequential and batch injection methods include sample throughput requirements, analyte stability, and instrument sensitivity. Sequential injection suits high-throughput scenarios with rapid, automated processing, while batch injection benefits precise, controlled environments handling complex matrices. The chemical compatibility of reagents and the desired analytical accuracy also play critical roles in method selection.
Future Trends in Injection Techniques
Future trends in injection techniques emphasize the integration of sequential and batch injection methods to optimize fuel efficiency and emissions control. Advanced electronic control units increasingly enable precise timing and quantity adjustments in sequential injection, enhancing combustion stability and reducing pollutant output. Your vehicle's performance and environmental footprint can benefit significantly from these innovations as manufacturers adopt smarter, adaptive injection systems driven by real-time data analytics.
sequential vs batch injection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com