The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases into the combustion chamber, while the PCV valve manages crankcase ventilation by redirecting blow-by gases back into the intake manifold for combustion. Your vehicle relies on both valves to maintain efficient engine performance and lower harmful pollutants.
Table of Comparison
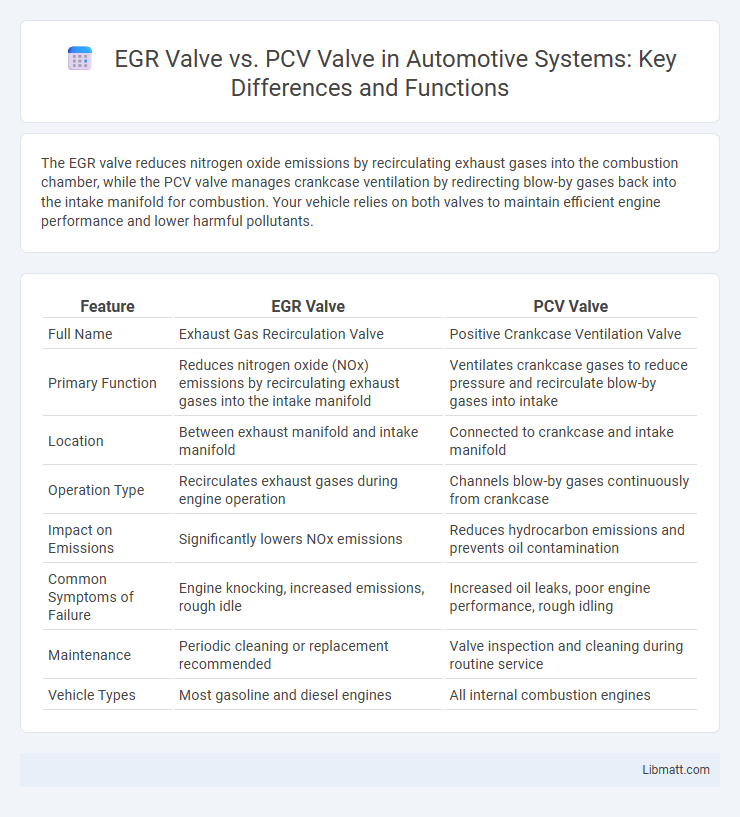
| Feature | EGR Valve | PCV Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve | Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve |
| Primary Function | Reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating exhaust gases into the intake manifold | Ventilates crankcase gases to reduce pressure and recirculate blow-by gases into intake |
| Location | Between exhaust manifold and intake manifold | Connected to crankcase and intake manifold |
| Operation Type | Recirculates exhaust gases during engine operation | Channels blow-by gases continuously from crankcase |
| Impact on Emissions | Significantly lowers NOx emissions | Reduces hydrocarbon emissions and prevents oil contamination |
| Common Symptoms of Failure | Engine knocking, increased emissions, rough idle | Increased oil leaks, poor engine performance, rough idling |
| Maintenance | Periodic cleaning or replacement recommended | Valve inspection and cleaning during routine service |
| Vehicle Types | Most gasoline and diesel engines | All internal combustion engines |
Overview: EGR Valve vs PCV Valve
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, improving engine efficiency and lowering pollution. The PCV valve regulates crankcase gases by redirecting them into the intake manifold for combustion, preventing engine oil contamination and reducing hydrocarbon emissions. Understanding the differences between your EGR valve and PCV valve helps maintain optimal engine performance and emission control.
Purpose and Function of EGR Valve
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, lowering combustion temperatures and improving environmental compliance. Unlike the PCV valve, which manages crankcase pressure and controls blow-by gases, the EGR valve primarily targets emission control and engine efficiency. Understanding the purpose and function of your EGR valve helps maintain optimal engine performance and meets emission standards.
Role and Operation of PCV Valve
The PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) valve regulates the flow of gases from the engine crankcase to the intake manifold, playing a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and maintaining engine efficiency. It operates by allowing controlled venting of blow-by gases, preventing pressure buildup and ensuring these gases are re-burned during combustion. Unlike the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve that recirculates exhaust gases to lower combustion temperatures, the PCV valve primarily manages crankcase ventilation to promote cleaner engine operation and reduce oil contamination.
Key Differences Between EGR and PCV Valves
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the engine's combustion chamber, while the PCV valve controls the release of crankcase vapors to prevent pollution and oil contamination. Your vehicle relies on the EGR valve primarily for emission control and engine efficiency, whereas the PCV valve maintains proper ventilation within the engine crankcase. Both valves play crucial roles in vehicle performance but target different pollutants and engine functions.
Common Symptoms of EGR Valve Failure
Common symptoms of EGR valve failure include rough engine idle, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions due to improper recirculation of exhaust gases. Your vehicle may also experience a noticeable loss of power and engine knocking as a result of carbon buildup or valve sticking. Unlike PCV valve issues, EGR valve problems often trigger the check engine light with specific diagnostic trouble codes related to the emission control system.
Signs of PCV Valve Malfunction
A malfunctioning PCV valve often causes rough idling, increased oil consumption, and excessive engine sludge buildup. You may notice a check engine light, poor fuel economy, or a hissing noise from the valve area. Unlike the EGR valve, which primarily controls exhaust gas recirculation, the PCV valve regulates crankcase ventilation and its failure directly affects engine performance and emissions.
Impact on Engine Performance
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases into the intake manifold, which can improve fuel efficiency but may cause rough idling or reduced engine power if clogged. The PCV valve controls crankcase gases by redirecting them into the combustion chamber, maintaining proper engine pressure and preventing oil contamination, thus ensuring smoother engine operation and longevity. Malfunction in either valve can lead to decreased engine performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
Maintenance Tips for EGR and PCV Valves
Maintaining your EGR and PCV valves involves regular inspection and cleaning to prevent carbon buildup and ensure optimal engine performance. Use high-quality cleaners designed for EGR valves and replace PCV valves at recommended intervals to avoid vacuum leaks and engine misfires. Proper maintenance of these components enhances fuel efficiency and reduces harmful emissions.
Cost Comparison: EGR Valve vs. PCV Valve Replacement
EGR valve replacement typically costs between $150 and $400 due to its complex design and location within the engine, while PCV valve replacement is more affordable, generally ranging from $20 to $80. Labor costs for EGR valves are higher because of the extensive removal process required, whereas PCV valves are easier to access, resulting in lower installation expenses. The overall maintenance cost for the PCV valve remains minimal compared to the more frequent and costly repairs associated with EGR valve malfunctions.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right valve for your vehicle depends on its specific emission control system and engine type, with the EGR valve managing exhaust gas recirculation to reduce NOx emissions in gasoline and diesel engines, while the PCV valve controls crankcase ventilation to prevent oil contamination and reduce harmful pollutants. Understanding the function of each valve is essential, as the EGR valve regulates exhaust gases to improve combustion efficiency, whereas the PCV valve maintains engine pressure and removes blow-by gases. Proper diagnosis and replacement with OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts ensure optimal engine performance and compliance with emission standards.
EGR valve vs PCV valve Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com