Open channel radiators expose the heating element directly to the air inside the room, allowing for faster heat dissipation but potentially less efficiency in maintaining consistent warmth. Closed channel radiators encase the heating element within sealed panels, improving energy efficiency and reducing heat loss while providing a safer and cleaner heating solution for Your space.
Table of Comparison
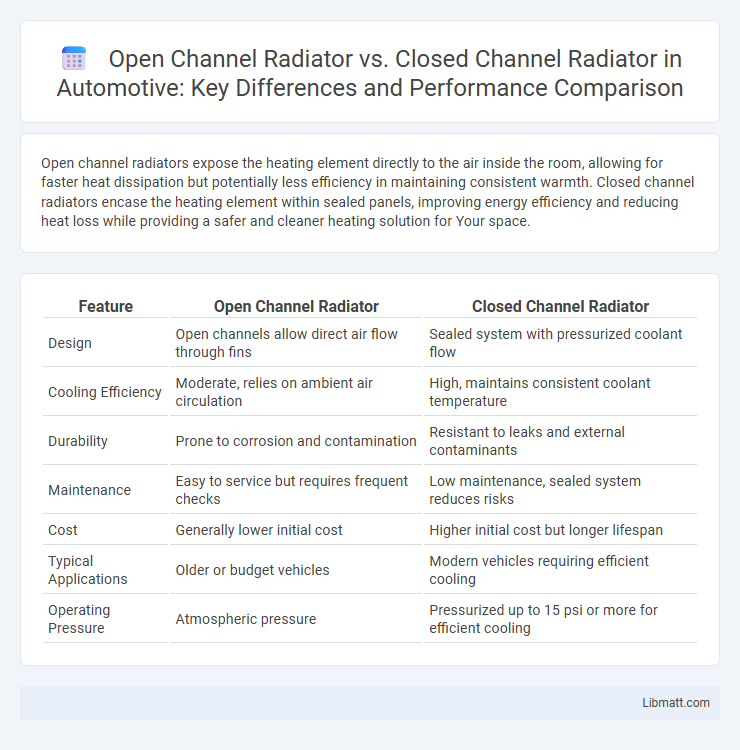
| Feature | Open Channel Radiator | Closed Channel Radiator |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Open channels allow direct air flow through fins | Sealed system with pressurized coolant flow |
| Cooling Efficiency | Moderate, relies on ambient air circulation | High, maintains consistent coolant temperature |
| Durability | Prone to corrosion and contamination | Resistant to leaks and external contaminants |
| Maintenance | Easy to service but requires frequent checks | Low maintenance, sealed system reduces risks |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Typical Applications | Older or budget vehicles | Modern vehicles requiring efficient cooling |
| Operating Pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Pressurized up to 15 psi or more for efficient cooling |
Introduction to Open Channel vs Closed Channel Radiators
Open Channel Radiators feature exposed cooling fins and open flow paths, enabling efficient heat dissipation through direct air contact. Closed Channel Radiators incorporate sealed channels that contain coolant fluid, promoting better pressure control and preventing contamination. The fundamental distinction lies in the airflow and fluid containment methods, impacting performance in various thermal management applications.
Understanding Radiator Channel Designs
Open channel radiators feature exposed cooling channels that allow direct air flow, enhancing heat dissipation efficiency in low-pressure environments. Closed channel radiators have sealed channels that contain coolant within, offering superior control over fluid dynamics and reducing leaks, making them ideal for high-pressure systems. The choice between open and closed designs depends on application requirements for cooling efficiency, maintenance, and system pressure tolerance.
How Open Channel Radiators Work
Open channel radiators function by allowing coolant to flow directly through an open path exposed to air, enabling efficient heat dissipation as the liquid transfers heat to the surrounding atmosphere. This type of radiator relies on atmospheric pressure to maintain coolant circulation without the use of seals, reducing complexity but increasing vulnerability to contamination and evaporation. The design prioritizes direct evaporation cooling and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for applications where simplicity outweighs the risk of exposure.
Mechanisms of Closed Channel Radiators
Closed channel radiators operate by confining sound waves within narrow channels, enhancing acoustic output through constructive interference and minimizing energy loss. Their mechanism relies on the precise control of airflow and resonance within sealed pathways, which improves sound projection efficiency compared to open channel systems. This design reduces external noise leakage and optimizes directional sound dispersion for clearer audio performance in various applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Open channel radiators offer enhanced thermal performance due to their increased surface area and direct exposure to ambient air, facilitating efficient heat dissipation. Closed channel radiators feature sealed designs that improve durability but may have slightly reduced heat transfer rates compared to open configurations. The choice between open and closed systems depends on balancing thermal efficiency with protective enclosure requirements.
Efficiency and Cooling Capabilities
Open Channel Radiators offer higher cooling efficiency due to their increased airflow and direct heat dissipation capabilities, making them ideal for systems with strong ventilation requirements. Closed Channel Radiators provide superior protection against contaminants and fluid leakage, maintaining consistent cooling performance in sealed environments but often at slightly reduced heat transfer rates. Efficiency comparisons reveal Open Channel designs excel in maximizing thermal conductivity, while Closed Channel systems prioritize durability and reliability under varying pressure conditions.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Open channel radiators require frequent maintenance due to exposure to airborne contaminants, leading to potential clogging and corrosion, which shortens their lifespan. Closed channel radiators offer enhanced durability by sealing coolant within a corrosion-resistant metal housing, minimizing contamination risks and reducing the need for regular upkeep. The sealed design of closed channel radiators also improves thermal efficiency and prolongs operational life, making them more reliable in harsh environments.
Cost Analysis: Open vs Closed Channel Radiators
Open channel radiators generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to closed channel radiators due to simpler manufacturing processes and materials. Closed channel radiators, though more expensive initially, provide better heat retention and energy efficiency, potentially reducing long-term operational costs for Your heating system. Evaluating both installation expenses and ongoing energy savings is crucial in determining the most cost-effective solution for your specific space.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Open Channel Radiators excel in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation in environments with minimal contamination risk, such as electronics cooling and HVAC systems. Closed Channel Radiators are better suited for use cases demanding sealed systems to prevent fluid leakage and contamination, including automotive cooling and industrial machinery. You should choose Open Channel Radiators for accessible maintenance scenarios, while Closed Channel Radiators are ideal for harsh or sealed environments where reliability is critical.
Choosing the Right Radiator Channel Type
Selecting the appropriate radiator channel type hinges on application requirements such as heat dissipation efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance needs. Open channel radiators offer superior airflow and easier cleaning, making them ideal for high-performance cooling in environments where contamination is minimal. Closed channel radiators provide enhanced protection against dust and moisture, increasing durability and reliability in harsh or dirty conditions, essential for industrial or outdoor systems.
Open Channel Radiator vs Closed Channel Radiator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com