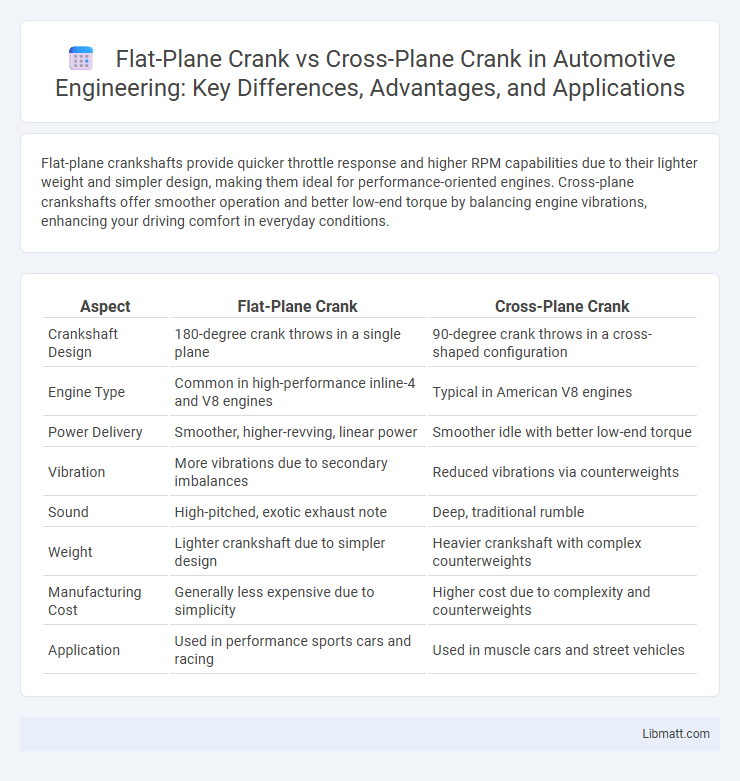
Flat-plane crankshafts provide quicker throttle response and higher RPM capabilities due to their lighter weight and simpler design, making them ideal for performance-oriented engines. Cross-plane crankshafts offer smoother operation and better low-end torque by balancing engine vibrations, enhancing your driving comfort in everyday conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flat-Plane Crank | Cross-Plane Crank |
|---|---|---|
| Crankshaft Design | 180-degree crank throws in a single plane | 90-degree crank throws in a cross-shaped configuration |
| Engine Type | Common in high-performance inline-4 and V8 engines | Typical in American V8 engines |
| Power Delivery | Smoother, higher-revving, linear power | Smoother idle with better low-end torque |
| Vibration | More vibrations due to secondary imbalances | Reduced vibrations via counterweights |
| Sound | High-pitched, exotic exhaust note | Deep, traditional rumble |
| Weight | Lighter crankshaft due to simpler design | Heavier crankshaft with complex counterweights |
| Manufacturing Cost | Generally less expensive due to simplicity | Higher cost due to complexity and counterweights |
| Application | Used in performance sports cars and racing | Used in muscle cars and street vehicles |
Introduction to Crankshaft Designs
Flat-plane crankshafts feature a 180-degree firing interval that delivers rapid throttle response and higher revving capability, often favored in performance and racing engines. Cross-plane crankshafts use a 90-degree crankpin angle, providing smoother power delivery and reduced vibrations, making them common in V8 muscle and luxury vehicles. Your choice between these crankshaft designs impacts engine sound, performance characteristics, and overall driving experience.
What is a Flat-Plane Crank?
A flat-plane crank is a type of crankshaft design commonly found in high-performance inline-four engines, characterized by its 180-degree crankpin arrangement that resembles a flat line when viewed from the side. This design reduces rotational mass and allows for quicker engine response and higher revving capabilities, making it ideal for sports cars. Your engine benefits from increased power output and a distinctive, sharp exhaust note due to the evenly spaced firing intervals created by the flat-plane crank.
What is a Cross-Plane Crank?
A cross-plane crankshaft features crankpins spaced at 90-degree angles, creating an uneven firing order that enhances torque delivery and smoothness in inline and V8 engines. Its unique design reduces engine vibrations and provides a distinctive exhaust note favored in performance motorcycles and high-performance cars. Understanding the cross-plane crank helps you appreciate how engine balance and power output are optimized for better drivability and sound.
Structural Differences
Flat-plane crankshafts feature crankpins arranged at 180-degree intervals, resulting in evenly spaced firing intervals and reduced rotational inertia, which enhances high-rev performance. Cross-plane crankshafts have crankpins positioned at 90-degree angles, creating uneven firing pulses that improve torque delivery and engine balance. The structural design of flat-plane cranks offers lighter weight and simpler construction, while cross-plane cranks provide smoother operation due to better primary and secondary vibration cancellation.
Performance Characteristics
Flat-plane crankshafts deliver quicker throttle response and higher RPM potential due to their lighter weight and reduced rotational inertia, enhancing acceleration and top-end power in sports cars. Cross-plane crankshafts generate smoother engine operation and better low-end torque by balancing inertial forces, improving drivability and reducing vibrations in muscle and luxury vehicles. These distinct performance characteristics influence engine sound, torque delivery, and overall vehicle dynamics according to application requirements.
Sound and Vibration Comparison
Flat-plane crank engines produce a higher-pitched, more aggressive sound with a distinctive exhaust note often favored in sports cars due to their even firing order and reduced rotational inertia, resulting in sharper throttle response and increased vibration. Cross-plane crank engines generate a deeper, rumbling exhaust tone commonly associated with V8s, featuring an uneven firing order that smooths vibrations for a more refined driving experience. Your choice between these crankshaft designs influences both engine sound character and vibration levels, balancing emotional appeal versus mechanical smoothness.
Application in Automotive Engines
Flat-plane crankshafts are commonly used in high-performance sports cars and racing engines due to their ability to reduce rotational inertia and increase engine responsiveness. Cross-plane crankshafts dominate in V8 automotive engines, particularly in muscle cars and luxury vehicles, because they offer smoother operation and better vibration absorption. The choice between flat-plane and cross-plane cranks significantly impacts engine characteristics such as power delivery, exhaust sound, and overall driving dynamics.
Pros and Cons of Flat-Plane Cranks
Flat-plane cranks offer a lighter rotational mass that enables quicker engine revs and improved throttle response, making them ideal for high-performance sports cars. However, they tend to produce more vibration due to less inherent balance, which can affect ride comfort and engine durability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize sharper engine feedback and power delivery or smoother operation and refinement.
Pros and Cons of Cross-Plane Cranks
Cross-plane cranks offer smoother engine operation and reduced vibration by spacing crankpins at 90-degree intervals, resulting in a distinct exhaust note favored in V8 engines. Their design enhances low-end torque and improves traction in high-performance road vehicles, but they are typically heavier and more complex to manufacture than flat-plane cranks. The increased rotational inertia limits the engine's ability to achieve very high RPMs, making cross-plane cranks less suitable for lightweight racing applications.
Which Crankshaft is Best for You?
Choosing between a flat-plane crank and a cross-plane crank depends on your performance goals and riding style. Flat-plane cranks offer higher revving capabilities and a more aggressive exhaust note, ideal for sportbike enthusiasts seeking sharp throttle response and lighter engine weight. Cross-plane cranks provide smoother power delivery and better torque at lower RPMs, making them suitable for riders prioritizing comfort and everyday usability.
Flat-plane crank vs Cross-plane crank Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com