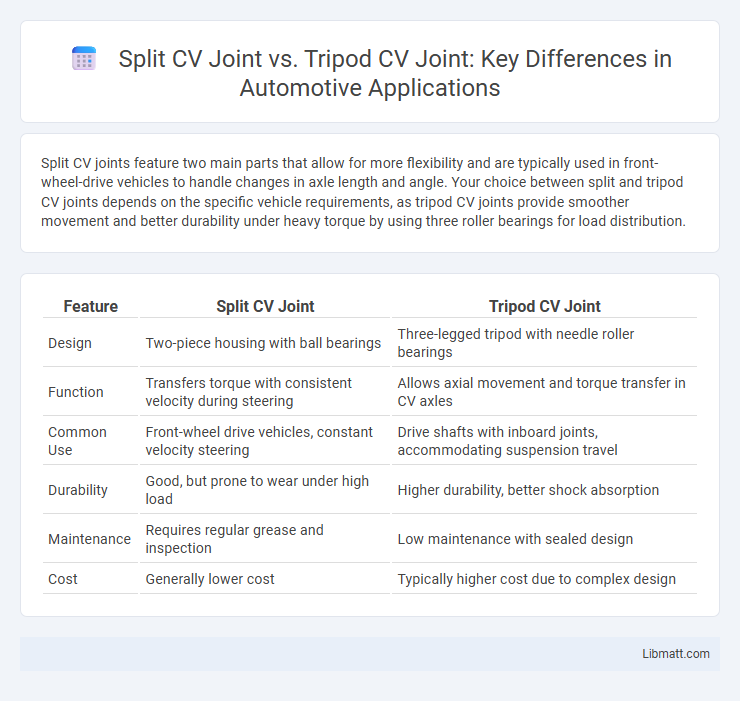
Split CV joints feature two main parts that allow for more flexibility and are typically used in front-wheel-drive vehicles to handle changes in axle length and angle. Your choice between split and tripod CV joints depends on the specific vehicle requirements, as tripod CV joints provide smoother movement and better durability under heavy torque by using three roller bearings for load distribution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Split CV Joint | Tripod CV Joint |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Two-piece housing with ball bearings | Three-legged tripod with needle roller bearings |
| Function | Transfers torque with consistent velocity during steering | Allows axial movement and torque transfer in CV axles |
| Common Use | Front-wheel drive vehicles, constant velocity steering | Drive shafts with inboard joints, accommodating suspension travel |
| Durability | Good, but prone to wear under high load | Higher durability, better shock absorption |
| Maintenance | Requires regular grease and inspection | Low maintenance with sealed design |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to complex design |
Introduction to CV Joints
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are essential components in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, allowing the transmission of torque at a constant speed while accommodating steering and suspension movement. Split CV joints feature separate parts that facilitate flexible motion and ease of maintenance, whereas Tripod CV joints use a three-pronged design to provide smooth power transfer with reduced friction and noise. Understanding the structural differences between Split and Tripod CV joints helps in selecting the appropriate joint type for specific vehicle applications and performance requirements.
What is a Split CV Joint?
A Split CV Joint is a type of constant velocity joint designed with separable components that allow for easier maintenance and replacement, typically found in front-wheel-drive vehicles. It features a segmented outer race and matching inner parts that work together to transmit torque while accommodating the up-and-down motion of the suspension. This design contrasts with the Tripod CV Joint, which uses a three-lobed roller and tripod mechanism for smooth power transfer and flexibility in steering angles.
What is a Tripod CV Joint?
A Tripod CV Joint is a type of constant velocity joint commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles to transmit torque smoothly while allowing for suspension movement and steering angles. It features a three-pronged inner hub that fits into a tripod-shaped bearing on the driveshaft, providing flexibility and reducing friction during rotation. Compared to Split CV Joints, Tripod CV Joints offer enhanced axial movement and durability, making them ideal for high-flexion applications.
Design Differences: Split vs Tripod CV Joints
Split CV joints feature a two-piece design consisting of an outer and inner joint that allows for greater flexibility and smoother power transfer in tight turns, while tripod CV joints use a three-legged inner race with needle bearings that provide superior axial displacement and reduced friction. You can expect Split joints to perform better under higher angles due to their ball bearing system, whereas Tripod joints excel in absorbing axle movement during suspension travel. Understanding these design differences helps you choose the right CV joint tailored to your vehicle's specific drivetrain and suspension needs.
Performance Comparison: Split and Tripod CV Joints
Split CV joints provide enhanced flexibility and smooth power transfer by allowing independent movement of the joint's components, resulting in improved durability under varying angles. Tripod CV joints excel in handling axial movement and absorbing torque fluctuations, making them ideal for vehicles requiring high vibration resistance and efficient torque transmission. Understanding the performance differences helps you select the right CV joint to optimize your vehicle's driveline efficiency and longevity.
Durability and Lifespan
Split CV joints offer enhanced durability due to their robust design that evenly distributes load across the joint, resulting in a longer lifespan under heavy use. Tripod CV joints, while effective in managing axial movement, typically experience faster wear on their needle bearings, which can reduce their overall durability and lifespan. You should consider Split CV joints for applications requiring extended service life and consistent performance in demanding conditions.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Split CV joints require more frequent inspection and lubrication due to their exposed boot design, making maintenance crucial to prevent dirt infiltration and premature wear. Tripod CV joints, with their enclosed design, offer better protection against contaminants, reducing the frequency of repairs and extending component life. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about servicing schedules and repair needs for optimal vehicle performance.
Applications in Modern Vehicles
Split CV joints are primarily used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, offering high torque capacity and durability in high-performance applications. Tripod CV joints excel in accommodating axial movement and are commonly found in independent suspension systems, providing smooth power transfer with reduced vibration. Both joints contribute to improved vehicle handling and longevity, adapting to the dynamic demands of modern drivetrains.
Cost Analysis: Split vs Tripod CV Joints
Split CV joints generally offer a lower initial cost due to simpler manufacturing and fewer components compared to tripod CV joints, which involve a more complex design and higher production expenses. However, tripod CV joints provide enhanced durability and smoother torque transfer, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Your choice between split and tripod CV joints should consider upfront expenses alongside longevity and performance needs for optimal value.
Choosing the Right CV Joint for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right CV joint depends on your vehicle's driving conditions and suspension design, with split CV joints offering enhanced durability and maintenance ease in high-torque applications, while tripod CV joints provide smoother movement and better flexibility suited for lighter vehicles with complex suspension systems. Understanding the specific load requirements and articulation angles helps optimize performance and longevity, as split joints excel in heavy-duty scenarios and tripod joints minimize vibration for urban driving. Prioritize compatibility with your vehicle's axle assembly and consider manufacturer recommendations to ensure reliable power transfer and minimize drivetrain wear.
Split CV Joint vs Tripod CV Joint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com