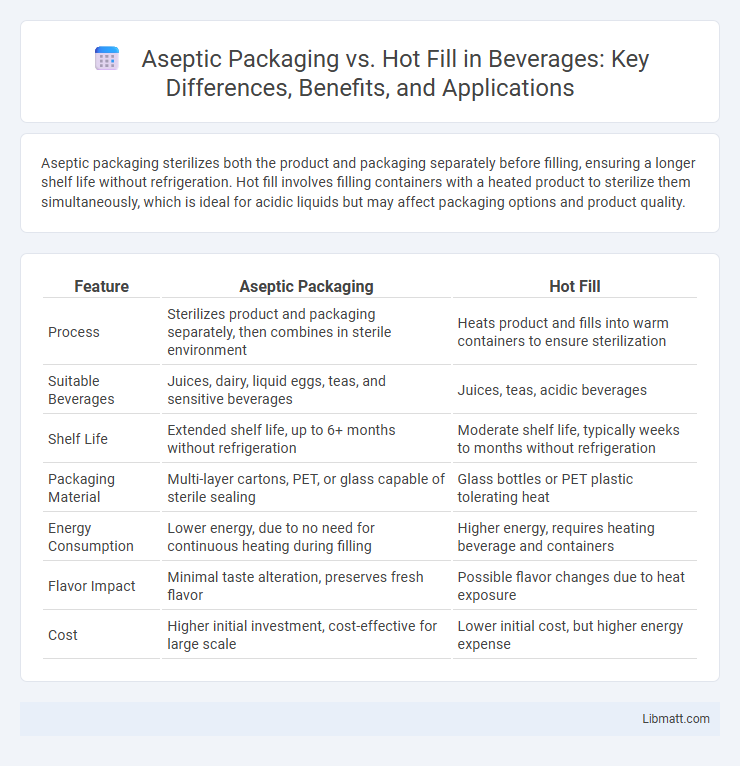
Aseptic packaging sterilizes both the product and packaging separately before filling, ensuring a longer shelf life without refrigeration. Hot fill involves filling containers with a heated product to sterilize them simultaneously, which is ideal for acidic liquids but may affect packaging options and product quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aseptic Packaging | Hot Fill |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Sterilizes product and packaging separately, then combines in sterile environment | Heats product and fills into warm containers to ensure sterilization |
| Suitable Beverages | Juices, dairy, liquid eggs, teas, and sensitive beverages | Juices, teas, acidic beverages |
| Shelf Life | Extended shelf life, up to 6+ months without refrigeration | Moderate shelf life, typically weeks to months without refrigeration |
| Packaging Material | Multi-layer cartons, PET, or glass capable of sterile sealing | Glass bottles or PET plastic tolerating heat |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy, due to no need for continuous heating during filling | Higher energy, requires heating beverage and containers |
| Flavor Impact | Minimal taste alteration, preserves fresh flavor | Possible flavor changes due to heat exposure |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, cost-effective for large scale | Lower initial cost, but higher energy expense |
Introduction to Aseptic Packaging and Hot Fill
Aseptic packaging involves sterilizing both the product and packaging separately before sealing in a sterile environment, ensuring extended shelf life without refrigeration. Hot fill requires heating the product to high temperatures and immediately filling it into pre-sterilized containers, relying on heat to sanitize the contents and packaging simultaneously. Your choice between aseptic packaging and hot fill depends on factors like product sensitivity, shelf stability, and production speed.
Definition and Process Overview
Aseptic packaging involves sterilizing the product and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, ensuring extended shelf life without refrigeration. Hot fill, on the other hand, heats the product to high temperatures before filling and sealing it in containers to kill microbes and create a vacuum seal. Your choice between aseptic packaging and hot fill depends on factors like product type, shelf life requirements, and cost considerations.
Key Differences Between Aseptic Packaging and Hot Fill
Aseptic packaging involves sterilizing both the product and the packaging separately before filling them in a sterile environment, ensuring extended shelf life without preservatives or refrigeration. Hot fill processes heat the product to a high temperature and fill it into containers while still hot, relying on heat to sterilize both product and container simultaneously but often requiring refrigeration or preservatives. Key differences include temperature control, sterilization timing, product suitability, shelf stability, and packaging material compatibility.
Advantages of Aseptic Packaging
Aseptic packaging offers extended shelf life by sterilizing both the product and the packaging separately, preserving freshness without preservatives or refrigeration. It significantly reduces microbial contamination risks, ensuring product safety and quality for weeks or months. This method also allows lightweight, space-efficient packaging, lowering transportation costs and environmental impact.
Benefits of Hot Fill Technology
Hot fill technology ensures product safety by effectively eliminating harmful microorganisms through high-temperature processing, extending shelf life without preservatives. Your products benefit from this method's ability to preserve flavor and nutrient quality while maintaining packaging integrity, especially for juices, sauces, and liquid nutraceuticals. This cost-effective solution also offers versatility with a wide range of compatible containers, promoting efficient production and enhanced consumer appeal.
Nutritional Impact on Food and Beverage Products
Aseptic packaging preserves nutritional quality by sterilizing both product and packaging separately, minimizing nutrient degradation and extending shelf life without refrigeration. Hot fill processes involve heating the product to high temperatures before filling, which can cause losses in heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Choosing aseptic methods is ideal for maintaining maximum nutrient retention in beverages and liquid foods.
Packaging Material Requirements
Aseptic packaging requires high-barrier materials such as multi-layer laminates combining plastic, aluminum foil, and paperboard to maintain sterility and prevent contamination. Hot fill packaging demands heat-resistant materials, typically PET or glass, that can withstand temperatures above 85degC during filling without deforming or leaching chemicals. Your choice between aseptic and hot fill depends on the product's thermal tolerance and shelf-life needs, with aseptic packaging providing longer shelf stability in a sterile environment.
Cost Analysis: Aseptic vs Hot Fill
Aseptic packaging often entails higher initial equipment costs due to its complex sterilization and filling processes, but it can reduce overall expenses with longer shelf life and minimal preservatives. Hot fill methods typically require less specialized machinery, leading to lower upfront investment, though they involve higher energy consumption and potential material costs from heat-resistant packaging. Your choice affects long-term cost efficiency, balancing capital expenditure against operational savings and product shelf stability.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Aseptic packaging reduces energy consumption by sterilizing products and packaging separately, enabling cold storage that lowers carbon emissions compared to the high heat requirements of hot fill processes. It typically generates less packaging waste due to its lightweight, recyclable materials like Tetra Pak cartons, which contribute to improved sustainability metrics. Hot fill methods, while effective for microbial safety, often result in higher energy use and increased greenhouse gas emissions, making aseptic packaging a more environmentally friendly option for long shelf-life beverages.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Product
Aseptic packaging extends shelf life by sterilizing both product and packaging separately before filling, making it ideal for heat-sensitive products like dairy and juices. Hot fill involves filling the container with heated product to sterilize both simultaneously, suitable for acidic beverages and sauces. Choosing the right method depends on your product's heat stability, desired shelf life, and packaging compatibility to ensure safety and quality.
Aseptic packaging vs hot fill Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com