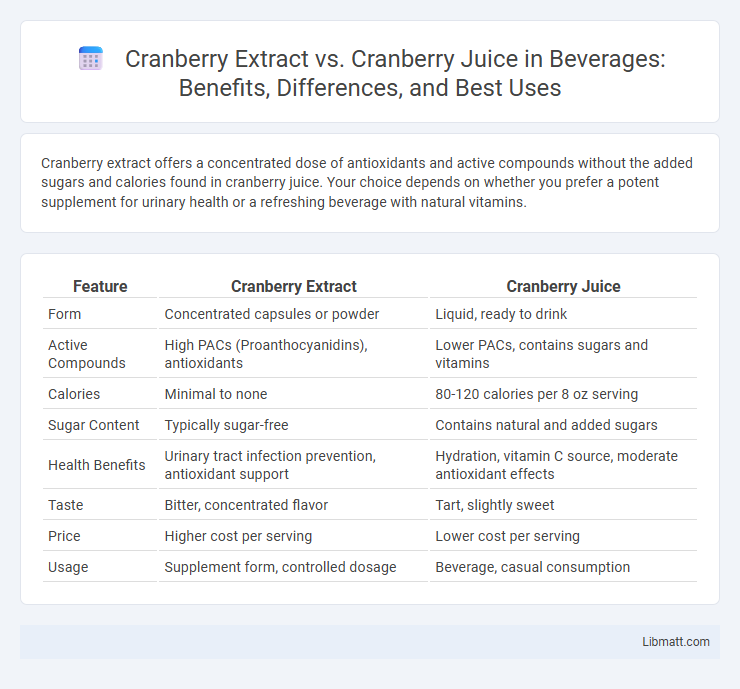
Cranberry extract offers a concentrated dose of antioxidants and active compounds without the added sugars and calories found in cranberry juice. Your choice depends on whether you prefer a potent supplement for urinary health or a refreshing beverage with natural vitamins.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cranberry Extract | Cranberry Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Concentrated capsules or powder | Liquid, ready to drink |
| Active Compounds | High PACs (Proanthocyanidins), antioxidants | Lower PACs, contains sugars and vitamins |
| Calories | Minimal to none | 80-120 calories per 8 oz serving |
| Sugar Content | Typically sugar-free | Contains natural and added sugars |
| Health Benefits | Urinary tract infection prevention, antioxidant support | Hydration, vitamin C source, moderate antioxidant effects |
| Taste | Bitter, concentrated flavor | Tart, slightly sweet |
| Price | Higher cost per serving | Lower cost per serving |
| Usage | Supplement form, controlled dosage | Beverage, casual consumption |
Introduction to Cranberry Extract and Cranberry Juice
Cranberry extract contains concentrated antioxidants and active compounds like proanthocyanidins, offering potent support for urinary tract health. Cranberry juice, while hydrating and rich in vitamin C, typically has lower concentrations of these key phytochemicals and may contain added sugars. Choosing cranberry extract can deliver more targeted benefits, especially if you want to maximize the protective properties of cranberries in your diet.
Nutritional Differences Between Extract and Juice
Cranberry extract contains higher concentrations of active compounds like proanthocyanidins and antioxidants compared to cranberry juice, which is often diluted and sweetened, reducing its nutrient density. Extracts typically provide more potent anti-inflammatory and urinary tract health benefits, while juice offers hydration and some vitamin C content. Cranberry juice may contain added sugars, increasing calorie content, whereas extracts are usually low in calories and sugar-free.
Key Bioactive Compounds in Cranberry Products
Cranberry extract contains higher concentrations of proanthocyanidins and flavonoids compared to cranberry juice, providing more potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. While cranberry juice is rich in vitamin C and natural sugars, the extract delivers targeted bioactive compounds that support urinary tract health more effectively. Your choice between the two should consider the desired bioactive intake and health goals.
Health Benefits: Cranberry Extract vs Cranberry Juice
Cranberry extract contains a concentrated dose of antioxidants and proanthocyanidins, which can more effectively support urinary tract health and reduce the risk of infections compared to cranberry juice. Cranberry juice often contains added sugars and lower levels of active compounds, which may diminish its overall health benefits. Choosing cranberry extract can provide your body with a higher potency of beneficial nutrients for improved immune support.
Effectiveness for Urinary Tract Health
Cranberry extract contains higher concentrations of active compounds like proanthocyanidins, which are more effective in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs) compared to cranberry juice. The extract's potency offers better anti-adhesion properties that help inhibit bacteria from sticking to the urinary tract walls. Your choice between the two should consider dosage precision and sugar content, with cranberry extract typically providing a more targeted approach for urinary tract health.
Sugar Content and Calorie Comparison
Cranberry extract contains significantly lower sugar and calorie content compared to cranberry juice, making it a healthier option for those monitoring their sugar intake. While an 8-ounce serving of cranberry juice typically has about 30-40 grams of sugar and 100-120 calories, cranberry extract supplements often provide concentrated benefits with minimal or no added sugars and fewer calories. Choosing cranberry extract over juice helps reduce daily sugar consumption without sacrificing the antioxidant and health benefits of cranberries.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Cranberry extract may cause stomach upset or allergic reactions in some individuals, while cranberry juice, often high in sugar, can contribute to increased calorie intake and affect blood sugar levels. Both forms can interact with blood-thinning medications like warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding complications. You should consult your healthcare provider before adding cranberry supplements or juice to your regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking prescription drugs.
Best Uses and Applications for Each Form
Cranberry extract offers a concentrated dose of antioxidants and proanthocyanidins, making it ideal for targeting urinary tract health and boosting immune support through supplements and capsules. Cranberry juice provides hydration with natural vitamins and a milder concentration of active compounds, suitable for daily consumption and flavoring beverages or smoothies. Your choice depends on whether you seek potent therapeutic effects from extract or a refreshing, nutrient-rich drink from juice.
Choosing the Right Cranberry Product for You
Cranberry extract offers a concentrated dose of antioxidants and proanthocyanidins, making it ideal for targeted urinary tract health, while cranberry juice provides hydration and a more enjoyable way to consume cranberry benefits with added sugars. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize potency and convenience or taste and hydration in your daily routine. Consider factors like sugar content, dosage, and intended health outcomes to select the cranberry product that best supports your wellness goals.
Conclusion: Which is Better, Cranberry Extract or Juice?
Cranberry extract offers a more concentrated dose of active compounds like proanthocyanidins, providing stronger antioxidant and urinary tract health benefits compared to cranberry juice, which contains more sugars and fewer bioactive nutrients. Your choice depends on individual health goals--cranberry extract suits those seeking potent effects without added calories, while juice can be a refreshing, lower-potency option. Research consistently supports extract as the superior form for targeted health benefits.
Cranberry extract vs cranberry juice Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com