Zero sugar soda contains no sugar and typically has fewer or no calories, making it a popular choice for those looking to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing flavor. Your choice between diet soda and zero sugar soda should consider ingredient differences, as some zero sugar sodas may use alternative sweeteners or flavorings that impact taste and health preferences.
Table of Comparison
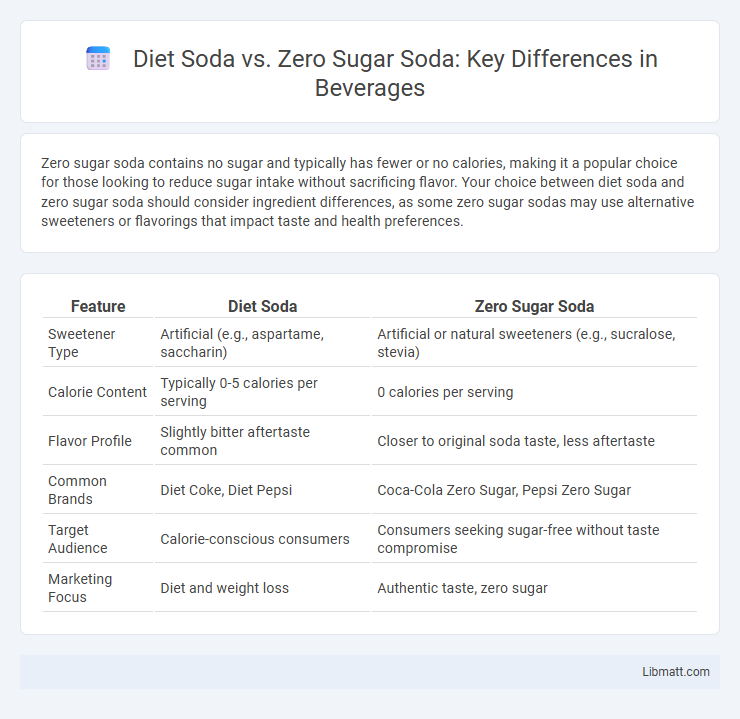
| Feature | Diet Soda | Zero Sugar Soda |
|---|---|---|
| Sweetener Type | Artificial (e.g., aspartame, saccharin) | Artificial or natural sweeteners (e.g., sucralose, stevia) |
| Calorie Content | Typically 0-5 calories per serving | 0 calories per serving |
| Flavor Profile | Slightly bitter aftertaste common | Closer to original soda taste, less aftertaste |
| Common Brands | Diet Coke, Diet Pepsi | Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, Pepsi Zero Sugar |
| Target Audience | Calorie-conscious consumers | Consumers seeking sugar-free without taste compromise |
| Marketing Focus | Diet and weight loss | Authentic taste, zero sugar |
Introduction to Diet Soda and Zero Sugar Soda
Diet soda and zero sugar soda are both popular low-calorie alternatives to regular sugary beverages, designed to appeal to health-conscious consumers. Diet soda typically uses artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, saccharin, or sucralose, offering a sweet taste without added calories. Zero sugar soda often emphasizes the absence of any sugar content while maintaining similar taste profiles, frequently using the same sweeteners but sometimes marketed with different branding and flavor formulations.
Understanding the Key Differences
Diet soda typically contains artificial sweeteners like aspartame and aims to provide a low-calorie alternative to regular soda, while zero sugar soda often uses a blend of sweeteners such as sucralose or acesulfame potassium for a similar purpose. Both beverages are designed to reduce sugar intake but may differ in taste profiles, ingredient formulations, and brand marketing strategies. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed choices based on flavor preferences and potential health considerations.
Ingredients Comparison
Diet soda typically contains artificial sweeteners such as aspartame or saccharin combined with caramel color, phosphoric acid, and natural flavors, while zero sugar soda mainly uses sucralose or acesulfame potassium as sweeteners with similar additives like citric acid and preservatives. Both beverages avoid sugar, but zero sugar options often emphasize cleaner labels with fewer artificial or controversial ingredients, catering to health-conscious consumers. Ingredient transparency and differences in sweetener blends influence consumer preference and potential health implications in diet versus zero sugar sodas.
Sweeteners Used in Each
Diet soda typically uses aspartame or saccharin as its primary sweeteners, offering a low-calorie alternative to regular soda. Zero sugar soda often incorporates a blend of sweeteners such as sucralose, acesulfame potassium, or erythritol to enhance flavor without added sugar. Both options provide sweetness with minimal calories but differ in the specific artificial or natural sweeteners used to achieve their taste profiles.
Calorie and Nutritional Profiles
Diet soda and zero sugar soda both contain minimal to zero calories, making them popular choices for calorie-conscious consumers. Nutritionally, diet sodas typically use artificial sweeteners such as aspartame or sucralose, providing sweetness without carbohydrates or sugar, while zero sugar sodas also rely on similar sweeteners but may vary in additives or electrolyte content depending on the brand. Both beverages offer negligible amounts of vitamins, minerals, or macronutrients, emphasizing their role as calorie-free alternatives to regular sugary drinks.
Taste and Flavor Variations
Diet soda and zero sugar soda differ primarily in their sweetener blends, resulting in distinct taste and flavor profiles. Diet sodas often use aspartame or saccharin, lending a slightly sharper and sometimes metallic aftertaste, while zero sugar sodas frequently incorporate a combination of sucralose, stevia, or acesulfame potassium for a smoother, more balanced sweetness. Consumer preferences vary widely, with some favoring the crisp, classic diet soda flavor and others preferring the cleaner, less synthetic taste of zero sugar alternatives.
Health Impacts and Considerations
Diet soda and zero sugar soda both aim to reduce calorie intake by replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners such as aspartame or sucralose, but their health impacts can vary based on individual sensitivity to these additives. Studies highlight potential issues like altered gut microbiota, increased cravings for sweet foods, or metabolic effects that may influence weight management and insulin response. Your choice between the two should consider your personal health goals, any pre-existing conditions like diabetes, and tolerance for artificial sweeteners to minimize possible adverse effects.
Consumer Preferences and Popular Brands
Consumer preferences for diet soda versus zero sugar soda increasingly favor beverages with natural sweeteners and clean-label ingredients, reflecting a shift toward health-conscious choices. Popular brands like Diet Coke and Pepsi Zero Sugar dominate the market, with Diet Coke appealing to traditional diet soda consumers and Pepsi Zero Sugar attracting those seeking a closer taste to regular soda without sugar. Marketing strategies emphasize zero-calorie content and distinctive flavor profiles, influencing brand loyalty and purchase decisions among millennials and Gen Z demographics.
Misconceptions and Marketing Strategies
Diet soda and zero sugar soda are often misunderstood as identical, but marketing strategies highlight subtle differences targeting health-conscious consumers. Misconceptions include assumptions about ingredient safety and taste, with zero sugar sodas frequently promoted as a cleaner, more natural option despite similar artificial sweeteners. Your choice should be informed by understanding that both products use marketing to emphasize benefits while downplaying potential drawbacks related to artificial additives.
Choosing the Right Soda for Your Lifestyle
Choosing the right soda for your lifestyle depends on your health goals and taste preferences, with diet soda offering a classic sweet flavor often preferred by long-time soda drinkers. Zero sugar soda caters to those seeking a refreshing option without calories or artificial sweeteners, sometimes using natural sweeteners like stevia. Understanding the differences in ingredients and potential health impacts can help you make a choice that supports your daily nutrition and hydration needs.
Diet soda vs zero sugar soda Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com