Kombucha and water kefir are both fermented beverages rich in probiotics that support gut health, but kombucha is made from sweetened tea and has a tangy, slightly acidic flavor while water kefir is brewed from sugar water or fruit juice, resulting in a milder, sweeter taste. You can choose kombucha for its robust antioxidants and unique flavor complexity, whereas water kefir offers a gentler probiotic profile ideal for those preferring a less tart drink.
Table of Comparison
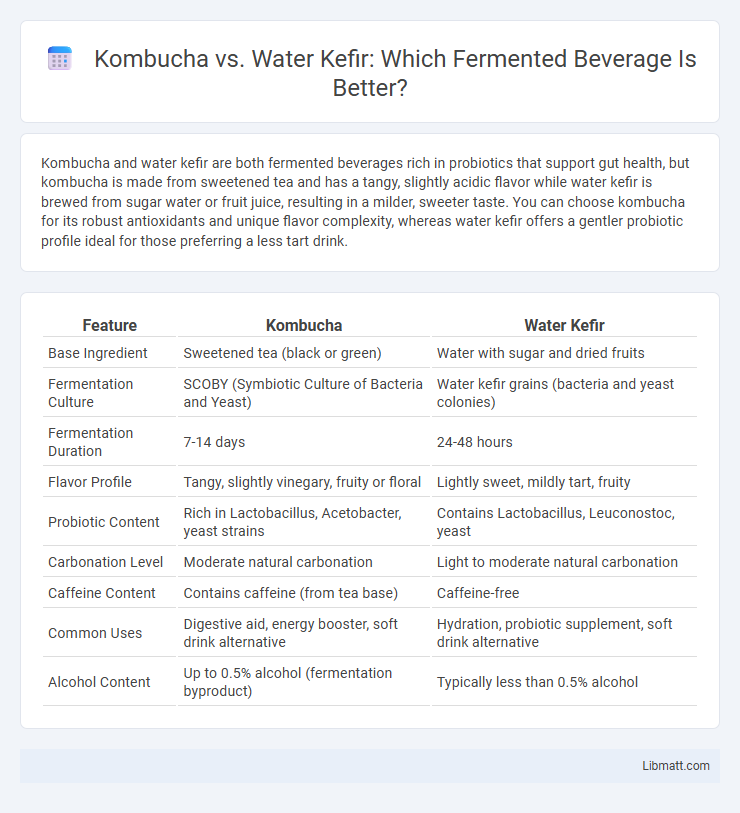
| Feature | Kombucha | Water Kefir |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Sweetened tea (black or green) | Water with sugar and dried fruits |
| Fermentation Culture | SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) | Water kefir grains (bacteria and yeast colonies) |
| Fermentation Duration | 7-14 days | 24-48 hours |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, slightly vinegary, fruity or floral | Lightly sweet, mildly tart, fruity |
| Probiotic Content | Rich in Lactobacillus, Acetobacter, yeast strains | Contains Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, yeast |
| Carbonation Level | Moderate natural carbonation | Light to moderate natural carbonation |
| Caffeine Content | Contains caffeine (from tea base) | Caffeine-free |
| Common Uses | Digestive aid, energy booster, soft drink alternative | Hydration, probiotic supplement, soft drink alternative |
| Alcohol Content | Up to 0.5% alcohol (fermentation byproduct) | Typically less than 0.5% alcohol |
Introduction to Kombucha and Water Kefir
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage produced by fermenting sweetened black or green tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY), known for its tangy flavor and probiotic benefits. Water kefir is a naturally effervescent fermented drink made by fermenting sugar water or fruit juice with water kefir grains containing a diverse mix of bacteria and yeast strains, offering a milder taste and rich probiotic content. Both beverages support gut health through their probiotics, but they differ in base ingredients, fermentation cultures, and flavor profiles.
Origins and History of Each Beverage
Kombucha originated over 2,000 years ago in Northeast China, known as the "Tea of Immortality," and gained popularity across Russia and Eastern Europe before spreading worldwide. Water kefir traces back to Mexican and Eastern European cultures, where natural sugar-water fermentation was an ancient tradition involving kefir grains composed of bacteria and yeast. Both beverages showcase centuries-old fermentation techniques that reflect regional preferences for probiotic-rich, fermented drinks.
Key Differences in Fermentation Process
Kombucha ferments using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) that primarily converts sweetened tea into a tangy, effervescent beverage rich in organic acids, vitamins, and probiotics. Water kefir relies on water kefir grains composed of different bacteria and yeasts that metabolize sugars in a sugary water solution, producing a lighter, milder probiotic drink with a distinct mineral and fruity flavor. Understanding these key differences in fermentation can help you choose the best probiotic drink tailored to your taste preference and digestive health goals.
Nutritional Profiles Compared
Kombucha typically contains probiotics, organic acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants derived from fermented tea, offering potential digestive and immune system benefits. Water kefir, made from fermenting sugar water with kefir grains, provides a diverse range of probiotic strains, essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, and lower acidity than kombucha. Both beverages contain live cultures promoting gut health, but water kefir generally has fewer calories and a milder taste due to its lower sugar content and different fermentation process.
Probiotic Content and Health Benefits
Kombucha and water kefir both offer potent probiotic content, with kombucha containing a diverse range of beneficial bacteria and yeast strains such as Gluconacetobacter and Saccharomyces, enhancing gut health and digestion. Water kefir also provides probiotics like Lactobacillus and Streptococcus species, supporting immune function and promoting a healthy microbiome. Regular consumption of either fermented drink may improve digestion, boost immunity, and contribute to detoxification through the presence of organic acids and antioxidants.
Taste, Texture, and Flavor Variations
Kombucha offers a tangy, slightly vinegary taste with a fizzy texture, often accompanied by fruity or floral flavor variations depending on the tea and fermentation time. Water kefir has a mildly sweet, less acidic flavor with a lighter carbonation and a smoother, more effervescent mouthfeel. Your preference may vary based on whether you enjoy bold, complex flavors in kombucha or the gentle, crisp refreshment provided by water kefir.
Brewing Methods and Home Preparation
Kombucha is brewed by fermenting sweetened black or green tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) for 7 to 14 days at room temperature, producing a tangy, effervescent drink. Water kefir, on the other hand, uses water kefir grains to ferment sugar water, fruit juice, or coconut water, typically fermenting for 24 to 48 hours for a milder, lightly carbonated beverage. Your choice of brewing method influences the flavor profile, fermentation time, and starter culture maintenance required for successful home preparation.
Safety Considerations and Potential Risks
Kombucha and water kefir are both fermented beverages with distinct safety considerations due to their fermentation processes. Kombucha, brewed from sweetened tea and SCOBY, carries a higher risk of contamination and over-fermentation, potentially leading to excessive acidity or harmful bacteria if not prepared in sterile conditions. Water kefir, fermented with kefir grains, typically has a lower alcohol content and milder acidity, making it generally safer, but both require careful hygiene practices to prevent mold or yeast contamination, ensuring your homemade brews remain safe for consumption.
Suitability for Different Dietary Needs
Kombucha is a fermented tea rich in probiotics and antioxidants, making it suitable for those seeking digestive health benefits and antioxidants in their diet. Water kefir, being dairy-free and lower in acidity, is ideal for individuals with lactose intolerance or sensitive stomachs who want a gentle probiotic boost. Your choice between kombucha and water kefir depends on your specific dietary needs, such as tolerance to acidity and preference for tea-based or fruit-based fermentation.
Which Should You Choose? Final Comparison
Kombucha and water kefir both offer probiotic benefits but differ in flavor profile and fermentation process, with kombucha having a tangy, slightly vinegary taste and water kefir being milder and sweeter. Kombucha contains higher caffeine and antioxidants due to tea fermentation, while water kefir is caffeine-free, making it suitable for sensitive individuals and children. Choose kombucha for digestive health and energy boosts, and water kefir for a gentler probiotic drink with less acidity and a naturally fruity taste.
Kombucha vs water kefir Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com