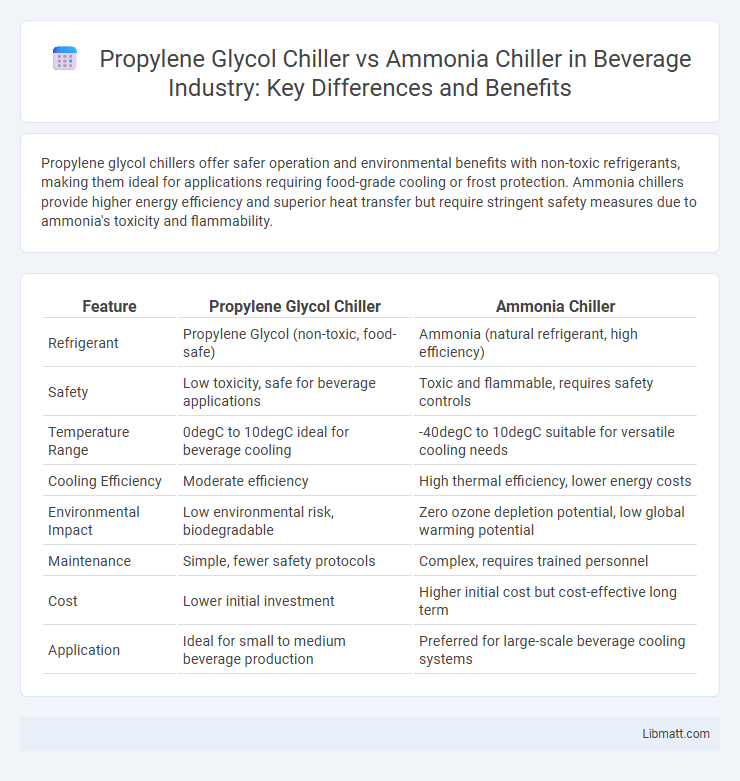
Propylene glycol chillers offer safer operation and environmental benefits with non-toxic refrigerants, making them ideal for applications requiring food-grade cooling or frost protection. Ammonia chillers provide higher energy efficiency and superior heat transfer but require stringent safety measures due to ammonia's toxicity and flammability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Propylene Glycol Chiller | Ammonia Chiller |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerant | Propylene Glycol (non-toxic, food-safe) | Ammonia (natural refrigerant, high efficiency) |
| Safety | Low toxicity, safe for beverage applications | Toxic and flammable, requires safety controls |
| Temperature Range | 0degC to 10degC ideal for beverage cooling | -40degC to 10degC suitable for versatile cooling needs |
| Cooling Efficiency | Moderate efficiency | High thermal efficiency, lower energy costs |
| Environmental Impact | Low environmental risk, biodegradable | Zero ozone depletion potential, low global warming potential |
| Maintenance | Simple, fewer safety protocols | Complex, requires trained personnel |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial cost but cost-effective long term |
| Application | Ideal for small to medium beverage production | Preferred for large-scale beverage cooling systems |
Overview of Propylene Glycol and Ammonia Chillers
Propylene glycol chillers use a non-toxic, food-grade antifreeze solution, ideal for applications requiring safety and corrosion resistance, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals. Ammonia chillers operate with ammonia as a refrigerant, known for its high energy efficiency and strong heat transfer properties, commonly employed in large industrial refrigeration systems. Both systems offer distinct advantages depending on environmental regulations, operating temperatures, and application-specific safety requirements.
How Propylene Glycol Chillers Work
Propylene glycol chillers use a mixture of propylene glycol and water as a coolant, circulating it through a closed-loop system to absorb and transfer heat efficiently. The glycol solution lowers the freezing point, preventing the coolant from freezing in low-temperature applications, making it ideal for sensitive environments. Your system benefits from safe, non-toxic, and corrosion-resistant cooling with precise temperature control compared to ammonia chillers.
How Ammonia Chillers Operate
Ammonia chillers operate by utilizing ammonia as a refrigerant in a vapor-compression cycle, where ammonia evaporates at low pressure to absorb heat and condenses at high pressure to release heat. The system relies on ammonia's high latent heat of vaporization, providing efficient thermal transfer and energy savings compared to alternatives like propylene glycol chillers. Ammonia chillers require specialized equipment resistant to ammonia's corrosive nature and strict safety protocols due to its toxicity and flammability.
Key Differences Between Propylene Glycol and Ammonia Systems
Propylene glycol chillers use a non-toxic, antifreeze solution ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications, offering safer handling and corrosion resistance. Ammonia chillers provide higher energy efficiency and superior heat transfer capabilities but require stringent safety measures due to ammonia's toxicity and flammability. The choice between these systems depends on application-specific safety requirements, environmental regulations, and energy efficiency priorities.
Efficiency Comparison: Propylene Glycol vs Ammonia
Ammonia chillers generally offer higher thermal efficiency due to ammonia's superior thermodynamic properties, resulting in lower energy consumption compared to propylene glycol chillers. Propylene glycol chillers, while less energy-efficient, provide greater safety by being non-toxic and non-flammable, making them suitable for environments with strict safety regulations. The choice between the two relies on balancing efficiency needs with safety and environmental considerations.
Safety Considerations for Each Chiller Type
Propylene glycol chillers offer enhanced safety due to their non-toxic and non-flammable properties, making them ideal for environments with strict health and safety regulations. Ammonia chillers, while highly efficient, pose greater risks because ammonia is toxic and flammable, requiring robust leak detection and ventilation systems to protect personnel. Your decision should weigh the safety protocols needed for ammonia against the lower hazard profile of propylene glycol chillers.
Environmental Impact: Propylene Glycol vs Ammonia
Propylene glycol chillers have a lower environmental risk due to their non-toxic and biodegradable nature, reducing potential hazards in case of leaks or spills. Ammonia chillers offer high energy efficiency but pose significant environmental and safety concerns, including toxicity and potential for harmful emissions. Your choice should balance ecological safety with operational efficiency, considering the specific environmental regulations and risk management strategies in place.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Propylene glycol chillers typically require less frequent maintenance due to their corrosion-resistant fluid and simpler system components, resulting in lower upkeep costs compared to ammonia chillers. Ammonia chillers demand rigorous safety inspections and specialized handling to address toxicity and potential leaks, which increase maintenance complexity and expenses. Your choice between these chillers should consider the balance between glycol's easier maintenance and ammonia's higher operational and safety management costs.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Propylene glycol chillers are widely preferred in food processing, pharmaceutical, and HVAC industries due to their non-toxic, corrosion-resistant properties and environmental safety. Ammonia chillers dominate large-scale industrial refrigeration applications such as cold storage and chemical manufacturing, favored for high energy efficiency and superior cooling performance. Industry preferences lean towards propylene glycol systems when safety and chemical compatibility are critical, while ammonia systems are chosen for their cost-effectiveness and thermal conductivity in heavy-duty refrigeration.
Choosing the Right Chiller for Your Facility
Choosing the right chiller for your facility depends on factors like temperature requirements, energy efficiency, and safety. Propylene glycol chillers are ideal for applications needing freeze protection and non-toxic refrigerants, making them suitable for food processing and pharmaceutical industries. Ammonia chillers offer superior energy efficiency and cooling capacity but require careful handling due to toxicity, often preferred in large industrial settings with stringent environmental controls.
Propylene glycol chiller vs ammonia chiller Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com