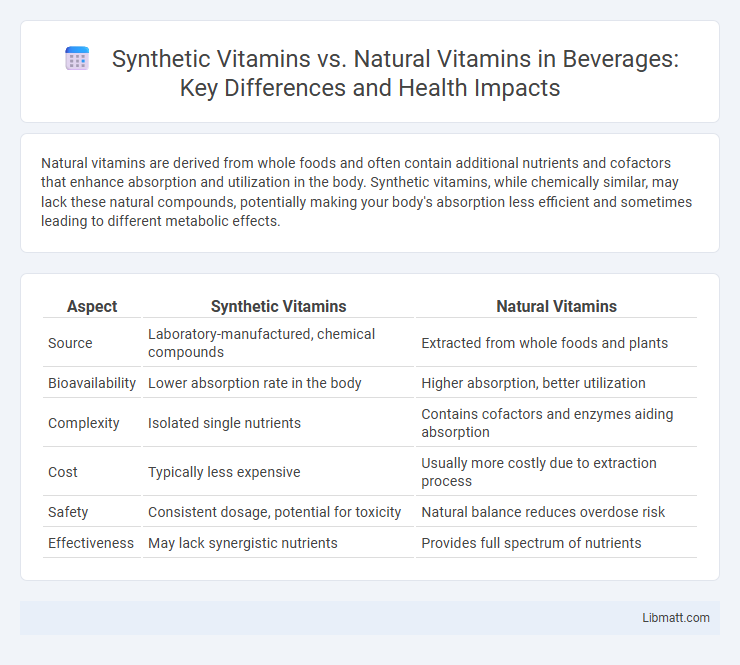
Natural vitamins are derived from whole foods and often contain additional nutrients and cofactors that enhance absorption and utilization in the body. Synthetic vitamins, while chemically similar, may lack these natural compounds, potentially making your body's absorption less efficient and sometimes leading to different metabolic effects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synthetic Vitamins | Natural Vitamins |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Laboratory-manufactured, chemical compounds | Extracted from whole foods and plants |
| Bioavailability | Lower absorption rate in the body | Higher absorption, better utilization |
| Complexity | Isolated single nutrients | Contains cofactors and enzymes aiding absorption |
| Cost | Typically less expensive | Usually more costly due to extraction process |
| Safety | Consistent dosage, potential for toxicity | Natural balance reduces overdose risk |
| Effectiveness | May lack synergistic nutrients | Provides full spectrum of nutrients |
Introduction to Vitamins: Natural vs Synthetic
Natural vitamins are derived directly from plant or animal sources and contain complex compounds that enhance bioavailability and synergistic effects. Synthetic vitamins are chemically produced in laboratories, often replicating the active ingredient but lacking the additional cofactors found in natural forms. Studies show that natural vitamins may offer better absorption and efficacy, though synthetic versions remain essential in addressing nutrient deficiencies cost-effectively.
Defining Synthetic and Natural Vitamins
Synthetic vitamins are artificially manufactured compounds designed to mimic the chemical structure of vitamins found in natural food sources. Natural vitamins are derived directly from whole foods, containing a complex mix of nutrients and cofactors essential for optimal absorption and effectiveness. Understanding the differences in bioavailability and source can help you make informed choices about supplementation and overall nutrition.
Sources of Natural Vitamins
Natural vitamins are primarily obtained from whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and animal products, offering a complex matrix of nutrients that enhance bioavailability. For example, vitamin C is abundant in citrus fruits and berries, while fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K are found in leafy greens, fish liver oils, and dairy. These natural sources provide not only vitamins but also cofactors, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that work synergistically to support optimal absorption and efficacy.
How Synthetic Vitamins Are Made
Synthetic vitamins are produced through chemical synthesis or fermentation processes that replicate the molecular structure of natural vitamins. These vitamins are often manufactured in controlled laboratory environments using petroleum-based or plant-based raw materials. Advanced techniques such as enzymatic reactions and crystallization ensure the purity and potency of synthetic vitamins, making them suitable for supplementation and fortification.
Bioavailability: Absorption Differences
Natural vitamins often exhibit higher bioavailability due to their complex matrices that enhance absorption in the digestive tract. Synthetic vitamins, while chemically similar, may lack co-factors and enzyme binding partners, resulting in less efficient uptake. Your body may absorb natural vitamins more effectively, supporting optimal nutritional benefits.
Efficacy and Health Benefits Compared
Natural vitamins are often more bioavailable, meaning Your body can absorb and utilize them more effectively than synthetic counterparts. Studies show synthetic vitamins may lack certain cofactors found in natural sources, potentially reducing their overall efficacy and health benefits. Choosing natural vitamins from whole foods or high-quality supplements supports better nutrient synergy and long-term wellness outcomes.
Safety Concerns and Side Effects
Synthetic vitamins often raise safety concerns due to their isolated chemical forms, which may not be as easily absorbed or utilized by the body compared to natural vitamins derived from whole foods. Side effects from synthetic vitamins can include nausea, headaches, or more serious risks like toxicity when taken in excessive amounts, while natural vitamins generally have a lower risk of overdose. Your choice between synthetic and natural vitamins should consider these factors, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking multiple supplements.
Labeling and Identifying Vitamin Types
Labeling of synthetic vitamins often includes terms like "ascorbic acid" or "dl-" prefix, indicating chemically manufactured compounds, whereas natural vitamins use terms such as "whole food vitamin C" or "d-alpha-tocopherol" to denote their plant-based or animal-based origins. Identifying vitamin types on labels requires scrutinizing ingredient lists and source descriptions, as synthetic vitamins may lack the full spectrum of cofactors found in natural counterparts. Regulatory agencies mandate clear labeling to help consumers distinguish between isolated synthetic nutrients and complex natural vitamin blends.
Consumer Considerations and Preferences
Consumers often weigh the bioavailability and ingredient sources when choosing between synthetic vitamins and natural vitamins, with natural vitamins typically preferred for their plant-based origins and perceived purity. Your preference may also depend on cost, as synthetic vitamins are generally more affordable and widely available, while natural vitamins might align better with holistic health values. Understanding the form and origin of the vitamin supplements can help optimize nutrient absorption and overall effectiveness for individual health goals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Vitamins
Selecting between synthetic and natural vitamins depends on personal health goals and absorption efficiency. Natural vitamins often provide a complex mix of nutrients and cofactors that enhance bioavailability, while synthetic vitamins can offer precise dosages and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating individual dietary needs, medical conditions, and product quality ensures optimal vitamin supplementation for overall wellness.
Synthetic vitamins vs natural vitamins Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com