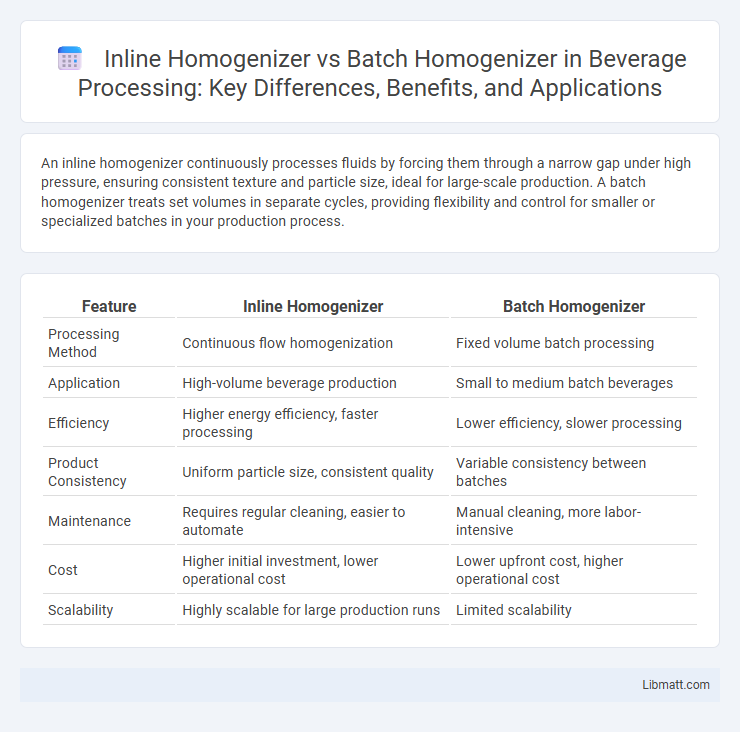
An inline homogenizer continuously processes fluids by forcing them through a narrow gap under high pressure, ensuring consistent texture and particle size, ideal for large-scale production. A batch homogenizer treats set volumes in separate cycles, providing flexibility and control for smaller or specialized batches in your production process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inline Homogenizer | Batch Homogenizer |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Continuous flow homogenization | Fixed volume batch processing |
| Application | High-volume beverage production | Small to medium batch beverages |
| Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency, faster processing | Lower efficiency, slower processing |
| Product Consistency | Uniform particle size, consistent quality | Variable consistency between batches |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning, easier to automate | Manual cleaning, more labor-intensive |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operational cost | Lower upfront cost, higher operational cost |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large production runs | Limited scalability |
Overview of Homogenization Technology
Inline homogenizers utilize continuous flow processes to achieve particle size reduction and uniform mixing through high-pressure mechanisms, offering efficient processing for large volumes. Batch homogenizers operate on a closed system where materials are homogenized in discrete quantities, allowing precise control over consistency and formulation but often requiring longer processing times. Both technologies leverage mechanical shear and pressure differentials to produce stable emulsions, dispersions, or suspensions critical in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.
What Is an Inline Homogenizer?
An inline homogenizer is a high-efficiency device designed to continuously mix, emulsify, and reduce particle size within a liquid stream, optimizing product consistency and stability. Unlike batch homogenizers, which process materials in separate containers, inline homogenizers operate directly in the flow path, enabling faster processing and improved scalability. Your production line benefits from reduced processing times and enhanced product quality with the precise shear and pressure control offered by inline homogenizers.
What Is a Batch Homogenizer?
A batch homogenizer processes materials in discrete volumes, mixing and reducing particle sizes within a sealed vessel to ensure uniform texture and consistency. Commonly used in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries, batch homogenizers allow precise control over processing time and shear forces for small to medium production scales. This equipment is ideal for specialized formulations requiring thorough blending without continuous flow processing.
Key Differences: Inline vs Batch Homogenizers
Inline homogenizers operate continuously, processing liquids as they flow through the system, ensuring consistent product uniformity and high throughput. Batch homogenizers treat a fixed volume of product at a time, offering greater control over small-scale or varied formulations but with longer processing times. Your choice between inline vs batch homogenizers depends on production scale, process efficiency, and desired product consistency.
Advantages of Inline Homogenizers
Inline homogenizers offer continuous processing, enabling consistent product quality and reduced processing time compared to batch homogenizers. They provide superior scalability for large production volumes while minimizing contamination risks through closed-system operation. Enhanced energy efficiency and ease of integration with existing production lines further distinguish inline homogenizers as the preferred choice for high-demand homogenization applications.
Advantages of Batch Homogenizers
Batch homogenizers offer precise control over processing parameters, making them ideal for small to medium-scale production with consistent product quality. Their flexibility allows for easy adjustment of formulation and processing time, accommodating diverse sample types and research needs. These homogenizers are also simpler to clean and maintain, reducing cross-contamination risks in pharmaceutical and food industries.
Typical Applications for Inline Homogenizers
Inline homogenizers are typically used in applications requiring continuous processing and high throughput, such as beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics manufacturing. They excel in emulsifying, dispersing, and particle size reduction, ensuring consistent product quality and stability. Your choice of an inline homogenizer supports efficient large-scale production with precise control over flow rates and homogenization parameters.
Typical Applications for Batch Homogenizers
Batch homogenizers are typically used in industries requiring precise control over small to medium volumes, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing, where product consistency and quality are critical. These homogenizers excel in applications involving viscous liquids, emulsions, and suspensions, ensuring uniform particle size reduction and stable formulations. Your production process benefits from their flexibility and easy cleaning, making them ideal for research, pilot-scale, and specialty product manufacturing.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Homogenizer
When choosing between an inline homogenizer and a batch homogenizer, consider factors such as processing volume, desired consistency, and production speed. Inline homogenizers provide continuous processing ideal for large-scale operations, while batch homogenizers offer flexibility for small to medium volumes and varied product formulations. Your choice should align with production goals, available space, and maintenance capabilities to ensure optimal homogenization efficiency.
Inline vs Batch Homogenizer: Which Is Best for Your Process?
Inline homogenizers provide continuous processing with consistent particle size reduction and high throughput, making them ideal for large-scale production. Batch homogenizers offer greater flexibility for small to medium volumes, enabling precise control over processing parameters for varied formulations. Selecting between inline and batch homogenizers depends on production scale, process consistency requirements, and product specificity to optimize efficiency and quality.
Inline homogenizer vs batch homogenizer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com