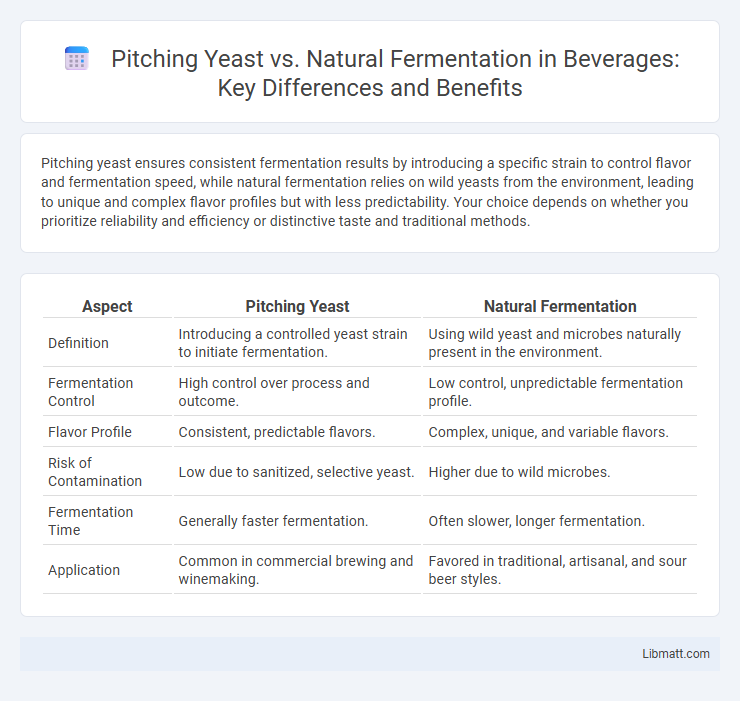
Pitching yeast ensures consistent fermentation results by introducing a specific strain to control flavor and fermentation speed, while natural fermentation relies on wild yeasts from the environment, leading to unique and complex flavor profiles but with less predictability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize reliability and efficiency or distinctive taste and traditional methods.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pitching Yeast | Natural Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introducing a controlled yeast strain to initiate fermentation. | Using wild yeast and microbes naturally present in the environment. |
| Fermentation Control | High control over process and outcome. | Low control, unpredictable fermentation profile. |
| Flavor Profile | Consistent, predictable flavors. | Complex, unique, and variable flavors. |
| Risk of Contamination | Low due to sanitized, selective yeast. | Higher due to wild microbes. |
| Fermentation Time | Generally faster fermentation. | Often slower, longer fermentation. |
| Application | Common in commercial brewing and winemaking. | Favored in traditional, artisanal, and sour beer styles. |
Introduction to Yeast Pitching and Natural Fermentation
Yeast pitching involves adding a specific strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to wort or must, ensuring controlled fermentation and consistent flavor profiles in beer and wine production. Natural fermentation relies on wild yeast and bacteria present in the environment, promoting unique and variable aromas and tastes but with less predictability. Choosing between pitching yeast and natural fermentation impacts the microbial diversity, fermentation time, and end-product characteristics significantly.
Understanding Yeast Pitching in Brewing
Yeast pitching in brewing involves adding a controlled amount of cultured yeast to wort to ensure consistent fermentation, precise flavor profiles, and predictable alcohol content. Natural fermentation relies on wild yeasts and bacteria present in the environment, which can introduce unique but variable flavors and may result in slower or less predictable fermentation. Understanding your yeast pitching method is crucial for achieving your desired beer quality and fermentation efficiency.
What Is Natural Fermentation?
Natural fermentation is a process where wild yeast and bacteria naturally present in the environment initiate and drive the fermentation without added cultured yeast strains. This method relies on microorganisms found on grain surfaces, in the air, or within the brewing environment to convert sugars into alcohol and other flavor compounds. It results in complex, unique profiles influenced by local microbial terroir, often yielding sour or funky characteristics in beverages like sour beers and spontaneously fermented ciders.
Key Differences Between Yeast Pitching and Natural Fermentation
Pitching yeast involves adding a controlled, selected strain of yeast to your wort, ensuring predictable fermentation rates and consistent flavor profiles. Natural fermentation relies on wild yeasts and bacteria present in the environment, leading to complex, unique flavors but with less control over fermentation speed and outcomes. Your brewing process will differ significantly in timing, risk of contamination, and flavor consistency between these two methods.
Advantages of Pitching Yeast
Pitching yeast offers consistent and controlled fermentation, ensuring predictable flavor profiles and efficient sugar conversion in brewing and baking. This method reduces the risk of contamination and off-flavors commonly associated with natural fermentation. By using a specific yeast strain, you can achieve faster fermentation times and reproducible results tailored to your product's desired characteristics.
Benefits of Natural Fermentation
Natural fermentation enhances beer complexity by encouraging diverse wild yeast and bacteria strains, resulting in unique and robust flavor profiles. It promotes probiotic qualities, improving gut health and digestion through the presence of beneficial microorganisms. Additionally, natural fermentation reduces reliance on commercial yeast, lowering production costs and supporting traditional brewing methods.
Flavor Profiles: Yeast Pitching vs. Natural Fermentation
Yeast pitching provides consistent flavor profiles with predictable esters and phenols, ideal for crafting specific beer styles. Natural fermentation introduces wild yeast and bacteria, creating complex, unpredictable flavors characterized by sourness, funk, and unique earthy notes. Your choice impacts the final taste, with pitching yeast delivering reliability and natural fermentation offering depth and originality.
Control and Consistency in Fermentation Methods
Pitching yeast provides precise control over fermentation by introducing a specific strain, ensuring consistent flavor profiles and predictable fermentation times. Natural fermentation relies on wild yeast and bacteria from the environment, which can lead to variable results and unique, complex flavors but less predictability. Your choice between these methods impacts the consistency and reproducibility of your final product, with pitching yeast offering reliability and natural fermentation embracing variability.
Considerations for Home Brewers and Professionals
Pitching yeast ensures consistent fermentation rates and predictable flavor profiles, making it ideal for professionals seeking precision in brewing. Natural fermentation introduces wild yeast and bacteria, offering complex flavors but requiring careful environmental control to avoid spoilage, which can challenge home brewers. Your choice depends on balancing desired flavor complexity with fermentation reliability and sanitation practices.
Choosing the Right Fermentation Method for Your Brew
Selecting between pitching yeast and natural fermentation impacts the flavor, fermentation time, and yeast control in your brew. Pitching a cultivated yeast strain offers consistency, predictable alcohol levels, and quicker fermentation, ideal for precise brewing outcomes. Natural fermentation leverages native wild yeasts, creating complex, unique flavor profiles but requires more time and risk management during production.
Pitching yeast vs natural fermentation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com