Plywood offers superior strength, water resistance, and durability due to its cross-layered hardwood veneer construction, making it ideal for structural applications and exposed environments. OSB is a cost-effective alternative made from compressed wood strands, providing good shear strength and uniformity for wall sheathing and subflooring, though it is more susceptible to moisture damage than plywood.
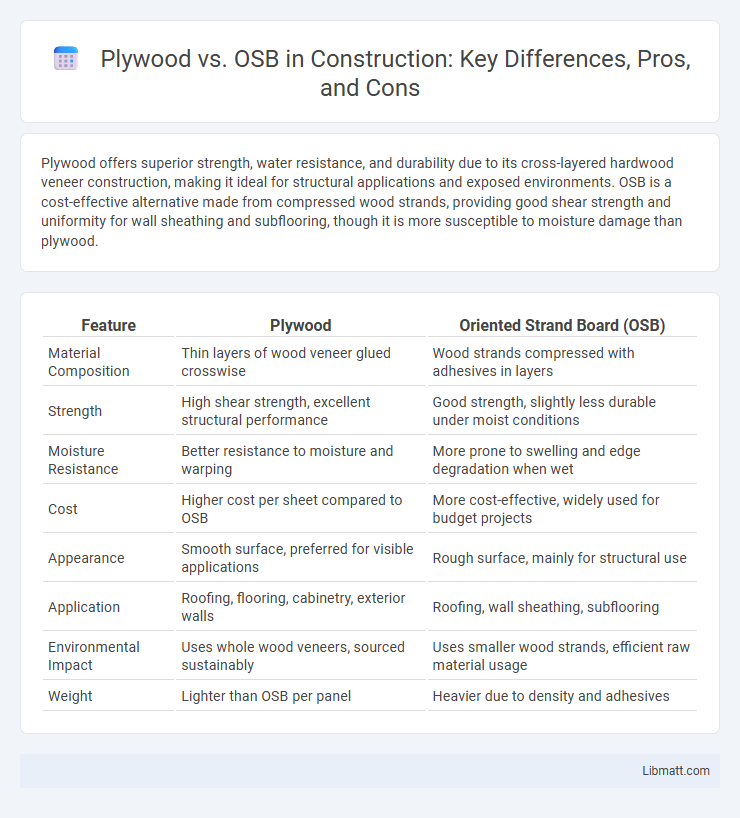
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plywood | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Thin layers of wood veneer glued crosswise | Wood strands compressed with adhesives in layers |
| Strength | High shear strength, excellent structural performance | Good strength, slightly less durable under moist conditions |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance to moisture and warping | More prone to swelling and edge degradation when wet |
| Cost | Higher cost per sheet compared to OSB | More cost-effective, widely used for budget projects |
| Appearance | Smooth surface, preferred for visible applications | Rough surface, mainly for structural use |
| Application | Roofing, flooring, cabinetry, exterior walls | Roofing, wall sheathing, subflooring |
| Environmental Impact | Uses whole wood veneers, sourced sustainably | Uses smaller wood strands, efficient raw material usage |
| Weight | Lighter than OSB per panel | Heavier due to density and adhesives |
Understanding Plywood and OSB: An Overview
Plywood consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together with grain patterns alternating for strength, while OSB (Oriented Strand Board) is made from compressed wood strands bonded with adhesives. Both materials offer durability for construction, but plywood typically provides greater moisture resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for structural applications. Your choice between plywood and OSB should consider factors such as budget, exposure to moisture, and the specific demands of your building project.
Manufacturing Process: How Plywood and OSB Are Made
Plywood is made by layering thin veneers of wood, known as plies, which are glued together with the grain of each layer running perpendicular to the last, enhancing strength and stability. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) is manufactured from compressed strands of wood arranged in specific orientations, bonded with adhesives and compressed under heat to create a dense, uniform panel. Understanding your project's structural needs helps determine whether the layered construction of plywood or the strand composition of OSB best suits your application.
Key Physical Differences Between Plywood and OSB
Plywood consists of thin layers of wood veneer glued together with grains alternating for strength, while OSB (Oriented Strand Board) is made from compressed wood strands arranged in specific orientations. Plywood typically offers greater resistance to moisture and warping due to its layered construction, whereas OSB is more uniform but can swell at edges if exposed to water. Your choice between plywood and OSB will depend on the specific strength, moisture resistance, and application requirements of your project.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plywood outperforms OSB in strength and durability due to its cross-veneered layers, providing superior resistance to bending, warping, and moisture damage. OSB, constructed from wood strands and adhesives, offers consistent strength but tends to swell and degrade faster when exposed to prolonged moisture. For applications requiring long-term structural integrity and resilience, plywood remains the preferred choice in construction and cabinetry.
Moisture Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Plywood generally performs better than OSB in moisture resistance due to its cross-laminated veneer construction, which allows water to evaporate more easily and reduces the risk of swelling and delamination. OSB tends to absorb more moisture because of its wood-strand composition and resin binders, leading to potential swelling and degradation in humid or wet conditions. For applications where moisture exposure is a concern, such as roofing or exterior sheathing, plywood is typically the preferred choice for its superior durability and dimensional stability.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Plywood offers superior workability due to its smooth surface and consistent layers, making it easier to cut, nail, and shape for various construction projects. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) is generally heavier and has a rougher texture, which can require more effort to handle and install, especially in precise applications. Your choice between plywood and OSB should consider the ease of installation needed for the project, as plywood often provides a more user-friendly experience on the job site.
Cost Comparison: Plywood vs OSB
OSB (Oriented Strand Board) typically costs 10-20% less than plywood, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale construction projects. Plywood offers better moisture resistance and structural strength but comes at a higher price point, which can impact your overall building expenses. Choosing between plywood and OSB often depends on balancing upfront material costs with long-term performance needs.
Best Applications for Plywood
Plywood is ideal for applications requiring high strength and moisture resistance, such as roofing, flooring, and wall sheathing in residential and commercial construction. Its cross-laminated veneer structure provides superior durability and flexibility, making it suitable for furniture, cabinetry, and exterior siding. Plywood's ability to hold nails and screws firmly also makes it preferred for structural panels and subflooring where structural integrity is critical.
Best Uses for OSB Panels
OSB panels excel in structural applications like wall sheathing, roof decking, and subflooring due to their strength and affordability. They provide excellent moisture resistance, making them ideal for areas prone to humidity or occasional water exposure. Your construction projects benefit from OSB's consistent density and uniformity, ensuring reliable performance in load-bearing structures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plywood is made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together, often sourced from fast-growing trees, offering better biodegradability and lower formaldehyde emissions compared to OSB, which is manufactured from wood strands and adhesives that can include resins with higher volatile organic compounds (VOCs). OSB uses smaller wood pieces and by-products, efficiently utilizing wood waste and supporting sustainability by reducing deforestation pressures, but its resin content may affect indoor air quality and environmental toxicity. Your choice between plywood and OSB should consider the balance between recycled content, adhesive emissions, and long-term environmental impacts to align with sustainable building goals.
Plywood vs OSB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com