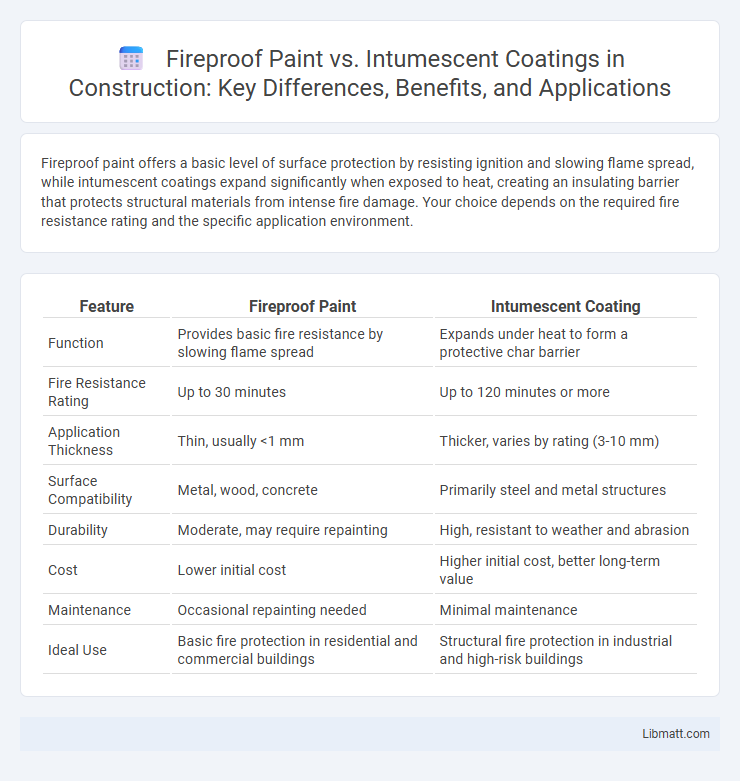
Fireproof paint offers a basic level of surface protection by resisting ignition and slowing flame spread, while intumescent coatings expand significantly when exposed to heat, creating an insulating barrier that protects structural materials from intense fire damage. Your choice depends on the required fire resistance rating and the specific application environment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fireproof Paint | Intumescent Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides basic fire resistance by slowing flame spread | Expands under heat to form a protective char barrier |
| Fire Resistance Rating | Up to 30 minutes | Up to 120 minutes or more |
| Application Thickness | Thin, usually <1 mm | Thicker, varies by rating (3-10 mm) |
| Surface Compatibility | Metal, wood, concrete | Primarily steel and metal structures |
| Durability | Moderate, may require repainting | High, resistant to weather and abrasion |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, better long-term value |
| Maintenance | Occasional repainting needed | Minimal maintenance |
| Ideal Use | Basic fire protection in residential and commercial buildings | Structural fire protection in industrial and high-risk buildings |
Introduction to Fireproof Paint and Intumescent Coating
Fireproof paint and intumescent coating are specialized materials designed to enhance the fire resistance of structural elements by forming protective barriers during exposure to high temperatures. Fireproof paint typically offers a heat-resistant coating that slows heat transfer, while intumescent coatings expand significantly when heated, creating an insulating char that protects underlying surfaces. These solutions are essential in fire safety engineering, with applications in building construction, steel structures, and industrial environments to meet fire protection regulations and improve structural integrity under fire conditions.
Understanding Fire Protection Mechanisms
Fireproof paint forms a protective layer that resists fire penetration by creating a barrier to heat and flames, primarily through heat-resistant pigments and binders. Intumescent coatings expand when exposed to high temperatures, producing an insulating char layer that significantly slows heat transfer to underlying structures. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for selecting the appropriate fire protection method based on application requirements, such as structural steel fireproofing or surface finish aesthetics.
Key Differences Between Fireproof Paint and Intumescent Coating
Fireproof paint provides a protective layer that resists flames and heat but generally has lower insulation properties than intumescent coating. Intumescent coating expands when exposed to high temperatures, forming an insulating char that significantly delays structural steel's temperature rise, enhancing fire resistance. The key difference lies in intumescent coating's ability to swell and insulate, whereas fireproof paint primarily acts as a surface barrier against heat and flames.
How Fireproof Paint Works
Fireproof paint works by creating a protective thermal barrier that slows heat transfer, helping to prevent structural damage during a fire. Intumescent coatings expand when exposed to high temperatures, forming an insulating char layer that significantly increases fire resistance. Your choice depends on the required fire rating and application surface, as intumescent coatings typically offer higher performance for steel structures.
How Intumescent Coating Works
Intumescent coating works by swelling when exposed to high temperatures, forming a thick, insulating char layer that slows heat transfer and protects structural materials from fire damage. This thermal barrier helps maintain the integrity of steel beams and other substrates under intense heat, extending the time before failure occurs. Your choice of fire protection can benefit from intumescent coatings when a thinner, more aesthetically pleasing finish is required compared to traditional fireproof paint.
Application Areas: Where Each Is Used
Fireproof paint is commonly applied on residential buildings, wooden structures, and industrial equipment to provide basic flame resistance and delay ignition. Intumescent coatings are primarily used in commercial buildings, steel frameworks, and structural steel components to enhance fire protection by expanding and insulating surfaces during high heat exposure. Both materials serve specific safety requirements, with fireproof paint suited for general fire resistance and intumescent coatings designed for critical structural fireproofing.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Fireproof paint typically offers moderate durability and requires periodic reapplication to maintain its protective properties, especially in high-exposure environments. Intumescent coatings provide superior durability with longer-lasting fire resistance and generally need less frequent maintenance due to their thicker, more resilient layers. Your choice between these fire protection solutions should consider the balance between initial application effort and long-term upkeep demands.
Installation Process and Best Practices
Fireproof paint offers a straightforward installation process, typically applied with brushes or rollers on clean, dry surfaces and requiring multiple coats for optimal fire resistance. Intumescent coatings demand more precise surface preparation, including priming, and are best applied by trained professionals using spray equipment to ensure uniform thickness and effective charring during a fire. Best practices for both materials emphasize adherence to manufacturer specifications, thorough surface cleaning, and adequate curing times to maximize protective performance.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Fireproof paint generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to intumescent coating, making it a budget-friendly option for basic fire resistance needs. Intumescent coating tends to be more expensive due to its advanced fire-protective properties and longer lifespan, but it provides superior performance for critical structural elements. When planning your project budget, consider not only initial expenses but also long-term durability and maintenance costs associated with each fire protection solution.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Fireproof paint offers a cost-effective, thin-layer solution ideal for environments requiring moderate flame resistance and aesthetic appeal, typically protecting steel structures up to 30 minutes. Intumescent coatings provide superior fire protection by expanding significantly when exposed to heat, forming an insulating char layer that safeguards structural integrity for up to several hours. Selecting the right solution depends on factors such as required fire resistance duration, budget constraints, surface type, and compliance with local fire safety regulations.
Fireproof paint vs intumescent coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com