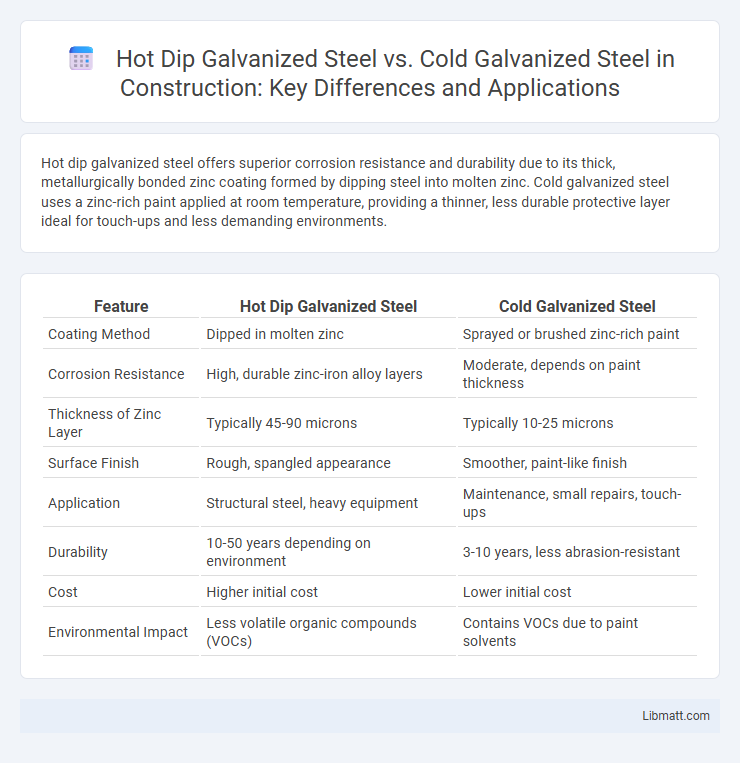
Hot dip galvanized steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability due to its thick, metallurgically bonded zinc coating formed by dipping steel into molten zinc. Cold galvanized steel uses a zinc-rich paint applied at room temperature, providing a thinner, less durable protective layer ideal for touch-ups and less demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Dip Galvanized Steel | Cold Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Dipped in molten zinc | Sprayed or brushed zinc-rich paint |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, durable zinc-iron alloy layers | Moderate, depends on paint thickness |
| Thickness of Zinc Layer | Typically 45-90 microns | Typically 10-25 microns |
| Surface Finish | Rough, spangled appearance | Smoother, paint-like finish |
| Application | Structural steel, heavy equipment | Maintenance, small repairs, touch-ups |
| Durability | 10-50 years depending on environment | 3-10 years, less abrasion-resistant |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Less volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | Contains VOCs due to paint solvents |
Overview of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is coated with a protective layer of zinc to prevent rust and corrosion, with hot dip galvanized steel featuring a thick, durable zinc coating achieved by immersing steel in molten zinc. Cold galvanized steel applies a zinc-rich paint or spray, offering a thinner coating suitable for touch-ups or less demanding environments. Your choice depends on corrosion resistance needs, with hot dip galvanizing providing superior protection for outdoor or harsh conditions.
What is Hot Dip Galvanized Steel?
Hot dip galvanized steel is steel coated by immersing it in molten zinc at approximately 450degC, forming a robust, corrosion-resistant alloy layer. This process creates a metallurgical bond between the zinc and steel, providing superior durability and protection against rust, especially in harsh environments. Hot dip galvanizing is widely used in construction, automotive, and outdoor infrastructure due to its long-lasting and maintenance-free performance.
What is Cold Galvanized Steel?
Cold galvanized steel is coated with a zinc-rich paint or spray, providing corrosion protection through a zinc dust mixture rather than a molten zinc bath used in hot dip galvanizing. This method offers a thinner, more flexible layer that can be applied on-site for touch-ups or areas where heat treatment is impractical. Your choice between cold galvanized steel and hot dip galvanized steel depends on factors like environmental exposure, application method, and desired durability.
Key Differences Between Hot Dip and Cold Galvanizing
Hot dip galvanized steel undergoes a molten zinc coating process, resulting in a thicker, more durable layer that offers superior corrosion resistance compared to cold galvanized steel, which uses zinc-rich paint or spray for surface protection. Hot dip galvanizing produces a metallurgical bond between the zinc and steel, enhancing long-term performance in harsh environments, while cold galvanizing relies on physical adhesion that may wear off faster under heavy abrasion. Your choice between these methods should consider the required durability, environmental exposure, and maintenance needs for optimal steel protection.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Hot dip galvanized steel offers superior corrosion resistance due to its thicker, uniform zinc coating formed by immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a metallurgical bond that protects against rust and environmental damage. Cold galvanized steel relies on zinc-rich paint or spray coatings, which provide moderate corrosion protection but are generally less durable and prone to wear over time. For your applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh conditions, hot dip galvanized steel ensures enhanced durability and sustained corrosion resistance.
Durability and Longevity
Hot dip galvanized steel offers superior durability and longevity due to its thick, zinc coating that provides robust protection against corrosion and harsh environmental conditions. Cold galvanized steel features a thinner zinc layer applied by spraying or brushing, which offers less corrosion resistance and may require more frequent maintenance. For your projects requiring long-term protection, hot dip galvanizing is generally the more reliable choice.
Applications of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel
Hot dip galvanized steel is widely used in construction, automotive, and infrastructure due to its superior corrosion resistance and thick zinc coating that withstand harsh environments. Your projects benefit from its durability in outdoor applications such as bridges, guardrails, and structural steel frameworks where long-term protection is crucial. This type of steel coating excels in preventing rust, making it ideal for exposed metal components subjected to weather and moisture.
Applications of Cold Galvanized Steel
Cold galvanized steel is extensively used in applications requiring fast, on-site corrosion protection such as maintenance repairs, touch-ups, and smaller steel structures. Its ease of application with spray or brush techniques makes it ideal for intricate surfaces, welded joints, and areas difficult to coat with traditional hot dip galvanizing. Common industries utilizing cold galvanized steel include automotive, construction, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Hot Dip vs Cold Galvanizing
Hot dip galvanized steel typically incurs higher initial costs due to the extensive dipping process and thicker zinc coating, offering superior corrosion resistance and longevity. Cold galvanized steel is more cost-effective upfront, applying zinc-rich paint for easier and faster repairs, but may require more frequent maintenance over time. Your choice should balance budget constraints against durability needs and long-term performance expectations in varying environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Galvanized Steel for Your Project
Hot dip galvanized steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability due to its thick zinc coating applied through immersion in molten zinc, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications. Cold galvanized steel, coated by spraying or brushing zinc-rich paint, provides adequate protection for indoor or less demanding environments with simpler maintenance requirements. Selecting the right galvanized steel depends on project exposure conditions, budget constraints, and longevity expectations, with hot dip galvanized being the preferred choice for long-term, high-exposure uses.
Hot dip galvanized steel vs cold galvanized steel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com