Hydronic heating systems use heated water circulated through pipes to warm your space efficiently and provide consistent, even heat, making them ideal for larger areas and longer usage periods. Electric radiant heating relies on electric cables or mats embedded in floors or walls, offering quick installation and precise zone control but may result in higher operating costs compared to hydronic systems.
Table of Comparison
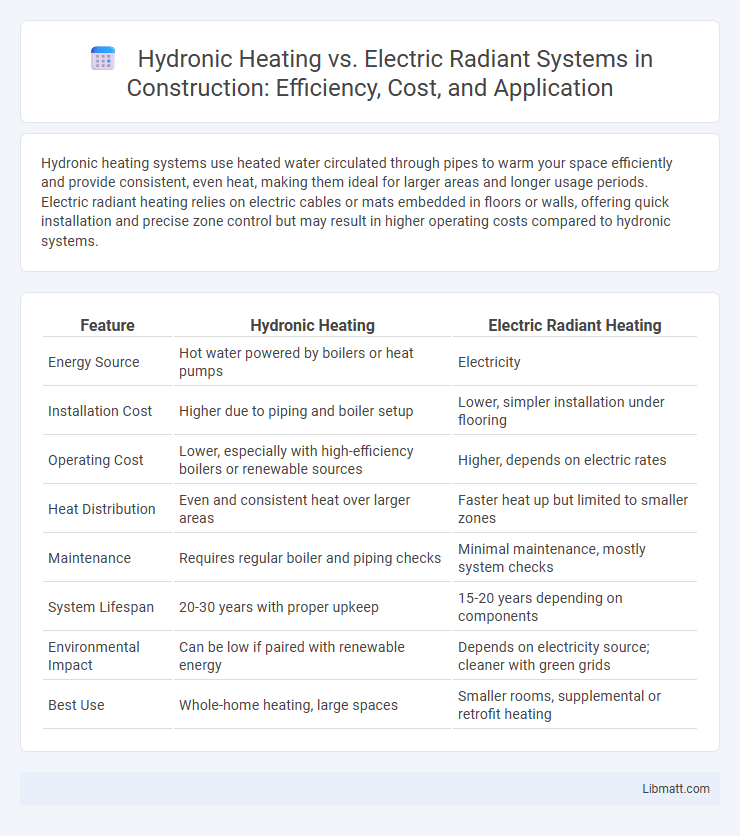
| Feature | Hydronic Heating | Electric Radiant Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Hot water powered by boilers or heat pumps | Electricity |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to piping and boiler setup | Lower, simpler installation under flooring |
| Operating Cost | Lower, especially with high-efficiency boilers or renewable sources | Higher, depends on electric rates |
| Heat Distribution | Even and consistent heat over larger areas | Faster heat up but limited to smaller zones |
| Maintenance | Requires regular boiler and piping checks | Minimal maintenance, mostly system checks |
| System Lifespan | 20-30 years with proper upkeep | 15-20 years depending on components |
| Environmental Impact | Can be low if paired with renewable energy | Depends on electricity source; cleaner with green grids |
| Best Use | Whole-home heating, large spaces | Smaller rooms, supplemental or retrofit heating |
Introduction to Hydronic Heating and Electric Radiant Systems
Hydronic heating systems use heated water circulated through pipes to warm floors or radiators, offering energy-efficient and consistent temperature control. Electric radiant systems rely on electric cables or mats installed beneath flooring, providing quick and direct heat ideal for smaller spaces or supplemental warmth. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best solution for your home's comfort and energy needs.
How Hydronic Heating Works
Hydronic heating works by circulating hot water through a network of pipes installed beneath floors, radiating consistent warmth throughout the space. This system relies on a boiler or water heater to heat the water, which is then pumped through tubes embedded in floors or walls, providing efficient, even heat distribution. Your home benefits from quieter operation and energy efficiency compared to electric radiant systems, making hydronic heating ideal for larger areas.
How Electric Radiant Heating Operates
Electric radiant heating operates by using electric resistance wires or mats embedded in the floor to generate heat, which then radiates evenly upward to warm the space. This system provides rapid response times and precise temperature control because each heating element can be independently regulated. Unlike hydronic heating that relies on circulating warm water, electric radiant heating eliminates the need for boilers, pumps, or extensive piping, making installation simpler and maintenance lower.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Hydronic heating systems typically offer higher energy efficiency due to their ability to use water as a heat transfer medium, which retains and distributes heat more evenly with less energy loss compared to electric radiant systems. These systems can integrate with renewable energy sources like solar thermal or high-efficiency boilers, further reducing overall energy consumption. Electric radiant heating tends to have higher operating costs and energy use because it directly converts electricity to heat, often leading to increased energy demand during peak hours.
Installation Process and Costs
Hydronic heating systems involve installing a network of water-filled tubes beneath floors or within walls, requiring professional plumbing expertise and typically higher upfront costs due to complex pipework and boiler setup. Electric radiant heating uses electric mats or cables embedded under flooring, offering easier and faster installation with lower initial expenses but potentially higher operating costs. Your choice between these systems should weigh the installation complexity and budget constraints against long-term energy savings.
Operating Costs and Maintenance
Hydronic heating typically offers lower operating costs compared to electric radiant systems due to its use of water heated by more efficient boilers or heat pumps, especially when paired with natural gas or solar energy sources. Maintenance for hydronic systems involves regular checks on boilers, pumps, and pipes to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance, which may require professional servicing. Electric radiant systems have higher energy costs but involve minimal maintenance since they have no moving parts, wires are embedded in floors or panels, and there is no risk of leaks, making them more hassle-free for your long-term use.
Comfort Levels and Heat Distribution
Hydronic heating systems provide consistent, even heat distribution by circulating warm water through pipes, creating a stable and comfortable indoor environment with minimal temperature fluctuations. Electric radiant systems heat surfaces directly, offering quick warmth but sometimes resulting in uneven heat distribution and potential cold spots. Hydronic systems excel in sustained comfort and energy efficiency, especially in larger spaces, while electric radiant tends to suit smaller areas with faster heating needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydronic heating systems use water heated by a boiler, often powered by natural gas, propane, or renewable energy sources, making them more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly compared to electric radiant heating that relies on electricity, which can come from fossil fuels. The sustainability of hydronic systems improves significantly when paired with solar thermal panels or heat pumps, reducing carbon emissions and lowering your overall environmental footprint. Electric radiant heating may have a smaller initial carbon footprint in regions with clean electricity grids, but its sustainability depends heavily on the electricity source, making hydronic heating a more versatile option for eco-conscious homeowners.
Best Applications for Each System
Hydronic heating excels in large spaces and homes with existing plumbing due to its efficiency in distributing heat through water pipes, making it ideal for cold climates or areas requiring consistent warmth. Electric radiant systems perform best in smaller rooms, retrofit projects, or spaces where quick installation and precise temperature control are priorities, such as bathrooms or under tile floors. Understanding your home layout and heating needs will help determine which system delivers optimal comfort and energy savings.
Choosing the Right Heating Solution for Your Home
Hydronic heating systems use heated water circulated through pipes to provide consistent, energy-efficient warmth, making them ideal for larger homes or spaces where long-term comfort is a priority. Electric radiant heating offers quick installation and precise temperature control, suited for smaller areas or rooms requiring supplemental heat. Assess your home's size, insulation, and energy costs to determine whether hydronic or electric radiant heating best meets your comfort needs and budget.
Hydronic heating vs Electric radiant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com