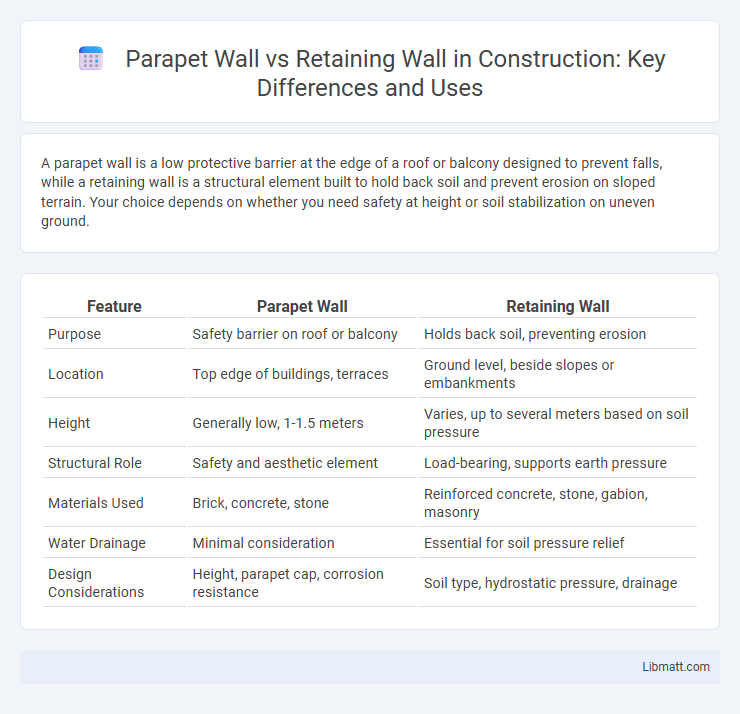
A parapet wall is a low protective barrier at the edge of a roof or balcony designed to prevent falls, while a retaining wall is a structural element built to hold back soil and prevent erosion on sloped terrain. Your choice depends on whether you need safety at height or soil stabilization on uneven ground.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parapet Wall | Retaining Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Safety barrier on roof or balcony | Holds back soil, preventing erosion |
| Location | Top edge of buildings, terraces | Ground level, beside slopes or embankments |
| Height | Generally low, 1-1.5 meters | Varies, up to several meters based on soil pressure |
| Structural Role | Safety and aesthetic element | Load-bearing, supports earth pressure |
| Materials Used | Brick, concrete, stone | Reinforced concrete, stone, gabion, masonry |
| Water Drainage | Minimal consideration | Essential for soil pressure relief |
| Design Considerations | Height, parapet cap, corrosion resistance | Soil type, hydrostatic pressure, drainage |
Understanding Parapet Walls: Definition and Purpose
A parapet wall is a low protective barrier extending above the edge of a roof, balcony, or terrace, primarily designed for safety and aesthetic enhancement. Unlike retaining walls that hold back soil or earth, parapet walls serve to prevent falls, conceal rooftop equipment, and provide a decorative architectural feature. Your building's safety and appearance can be significantly improved with a well-designed parapet wall that meets structural and local building code requirements.
What Is a Retaining Wall? Functions and Features
A retaining wall is a structure designed to hold back soil or rock from a building, preventing erosion and providing support on sloped terrains. Its primary function is to stabilize landscapes by resisting lateral pressure from soil, ensuring your property remains secure and level. Retaining walls often feature drainage systems to prevent water buildup and are constructed from durable materials like concrete, stone, or timber for long-lasting strength.
Key Differences Between Parapet Walls and Retaining Walls
Parapet walls are low protective barriers built along the edge of roofs, balconies, or terraces to prevent falls and provide safety, while retaining walls are structural elements designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion or landslides. Parapet walls primarily serve safety and aesthetic purposes with minimal load-bearing requirements, whereas retaining walls must withstand lateral earth pressure and provide soil stabilization. Materials like brick, concrete, or stone can be used for both, but retaining walls require stronger construction techniques such as reinforced concrete or terracing for effective support.
Structural Roles in Construction: Parapet vs Retaining Walls
Parapet walls primarily serve as safety barriers on rooftops, balconies, or terraces, preventing falls while also providing some protection against weather elements. Retaining walls are engineered to hold back soil and prevent erosion or landslides, supporting significant lateral earth pressure in landscaping and foundation projects. Understanding your construction needs is crucial, as parapet walls focus on safety and aesthetics, whereas retaining walls provide essential structural support for terrain stability.
Materials Used for Parapet and Retaining Walls
Parapet walls are commonly constructed using materials such as reinforced concrete, brick, stone, or precast panels, designed to provide safety and aesthetic appeal on rooftops and balconies. Retaining walls require robust materials like reinforced concrete, gabion, timber, stone masonry, or segmental concrete blocks to effectively resist lateral soil pressure and prevent erosion. The choice of materials depends on structural demands, environmental exposure, and load-bearing requirements of the specific wall type.
Design Considerations for Parapet and Retaining Walls
Design considerations for parapet walls focus on height, load resistance, and safety regulations to prevent falls, often requiring lightweight materials and proper reinforcement to withstand wind and seismic forces. Retaining walls demand structural stability against earth pressure, drainage solutions to avoid hydrostatic buildup, and foundation strength to prevent sliding or overturning under soil loads. Your choice between parapet and retaining walls hinges on specific site conditions, load requirements, and intended function to ensure durability and safety.
Installation Process: Parapet Wall vs Retaining Wall
The installation process of a parapet wall involves constructing a low protective barrier along the edge of a roof or balcony, typically poured with reinforced concrete or masonry units atop the main structure for safety and aesthetic purposes. In contrast, a retaining wall requires excavation and foundation preparation to resist lateral soil pressure, often utilizing gravity, cantilever, or anchored designs with materials like concrete, stone, or treated timber. Proper drainage systems and geotechnical assessments are critical during retaining wall installation to ensure stability, whereas parapet walls focus on structural attachment to the building frame.
Cost Comparison: Parapet Wall vs Retaining Wall
Parapet walls generally incur lower construction costs compared to retaining walls due to their simpler design and reduced material requirements, primarily used as safety barriers on rooftops or terraces. Retaining walls involve higher expenses driven by soil pressure management, extensive excavation, drainage systems, and reinforced structural elements to prevent earth movement. Your budget considerations should factor in the intended structural function and site conditions, as retaining walls demand greater investment for long-term stability and safety.
Durability and Maintenance: Which Wall Type Lasts Longer?
Parapet walls, typically constructed as low protective barriers on rooftops or balconies, offer moderate durability but require regular maintenance to prevent water infiltration and material degradation. Retaining walls, designed to hold back soil, are often built with robust materials like reinforced concrete or stone, providing greater longevity and structural strength under varying soil pressures. Your choice depends on the specific application, but retaining walls generally last longer with less frequent maintenance compared to parapet walls.
Choosing the Right Wall: When to Use Parapet or Retaining Walls
Parapet walls are designed primarily for safety and aesthetic purposes, often placed on the edge of roofs or balconies to prevent falls. Retaining walls serve a structural function by holding back soil or earth in landscaping and construction projects, preventing erosion and providing stability. Selecting between a parapet wall and a retaining wall depends on the need for safety barriers versus soil retention and load-bearing capacity.
Parapet wall vs retaining wall Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com