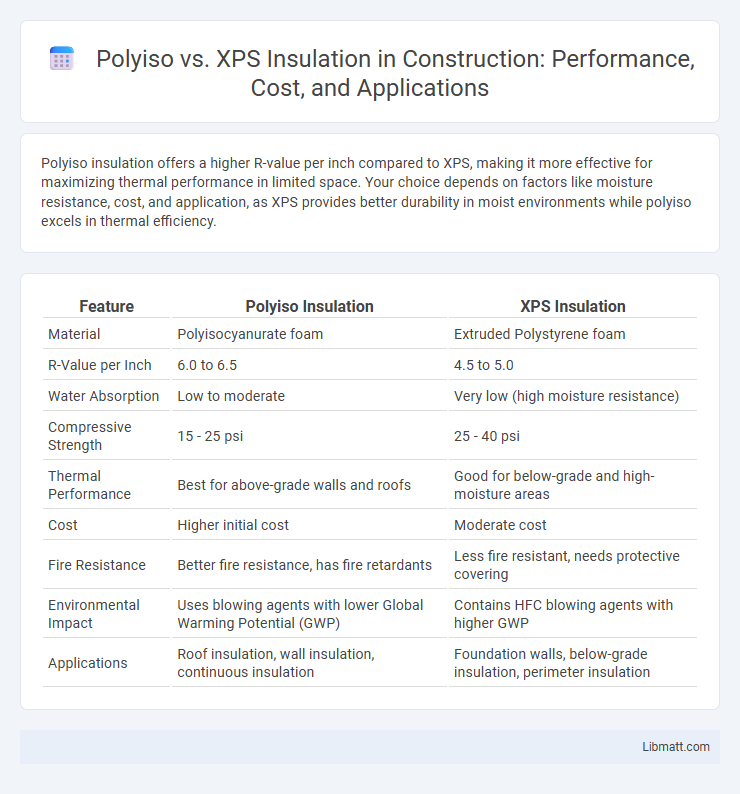
Polyiso insulation offers a higher R-value per inch compared to XPS, making it more effective for maximizing thermal performance in limited space. Your choice depends on factors like moisture resistance, cost, and application, as XPS provides better durability in moist environments while polyiso excels in thermal efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyiso Insulation | XPS Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyisocyanurate foam | Extruded Polystyrene foam |
| R-Value per Inch | 6.0 to 6.5 | 4.5 to 5.0 |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | Very low (high moisture resistance) |
| Compressive Strength | 15 - 25 psi | 25 - 40 psi |
| Thermal Performance | Best for above-grade walls and roofs | Good for below-grade and high-moisture areas |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate cost |
| Fire Resistance | Better fire resistance, has fire retardants | Less fire resistant, needs protective covering |
| Environmental Impact | Uses blowing agents with lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) | Contains HFC blowing agents with higher GWP |
| Applications | Roof insulation, wall insulation, continuous insulation | Foundation walls, below-grade insulation, perimeter insulation |
Introduction to Polyiso and XPS Insulation
Polyiso and XPS insulation are two prevalent options for enhancing thermal efficiency in buildings. Polyiso, or polyisocyanurate, boasts a high R-value per inch, making it ideal for space-constrained applications, while XPS (extruded polystyrene) provides robust moisture resistance and consistent thermal performance. Your choice between these materials depends on factors like climate, installation area, and budget constraints.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso) insulation is composed of rigid foam boards made from a closed-cell polyisocyanurate foam core sandwiched between facers like foil or fiberglass, produced through a chemical reaction between isocyanates and polyols using blowing agents in a controlled process. Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) insulation consists of closed-cell polystyrene foam created by melting polystyrene crystals and adding blowing agents such as HFCs or pentanes, which are then extruded into rigid boards with a consistent density and smooth surface. The manufacturing process of Polyiso typically results in a higher thermal resistance due to its chemical structure and blowing agents, while XPS offers durability and moisture resistance through its extrusion and cell structure.
Thermal Performance: R-Value Comparison
Polyiso insulation typically offers a higher R-value per inch, ranging between 6 to 6.5, compared to XPS which averages around 5.0 per inch, making Polyiso more efficient in thermal performance for the same thickness. Your choice of insulation impacts energy savings and comfort, as greater R-value means better resistance to heat flow. However, Polyiso's R-value can decrease at lower temperatures, while XPS remains more stable in colder climates.
Moisture Resistance and Absorption
Polyiso insulation offers moderate moisture resistance but can absorb water over time, potentially reducing its thermal performance. XPS insulation demonstrates superior moisture resistance with low water absorption rates, maintaining consistent R-values even in damp conditions. Choosing XPS for your project enhances durability in environments prone to moisture exposure, preserving insulation efficiency longer.
Fire Safety and Chemical Properties
Polyiso insulation offers superior fire resistance due to its higher ignition temperature and ability to form a protective char layer when exposed to flames, reducing fire spread risks. XPS insulation has a lower melting point and can release toxic gases when burned, posing greater chemical hazards in fire situations. Choosing Polyiso can enhance your building's fire safety performance because of its better fire retardant properties and more stable chemical composition under high heat.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyiso insulation typically has a lower environmental impact due to its higher R-value per inch, which requires less material for the same insulation performance, reducing resource consumption and waste. XPS insulation often involves blowing agents with higher global warming potential, leading to greater greenhouse gas emissions during production, whereas advancements in Polyiso formulations aim to use more environmentally friendly blowing agents. Choosing Polyiso can enhance your building's sustainability by optimizing energy efficiency and minimizing carbon footprint over the insulation's lifecycle.
Installation: Ease and Best Practices
Polyiso insulation features rigid foam boards that are lightweight and easy to cut, allowing for quick installation on walls and roofs with minimal tools, while XPS insulation offers moisture resistance and structural strength, making it suitable for below-grade or damp environments but requiring careful sealing to prevent air leaks. Best practices for Polyiso include using compatible adhesives and taping joints to enhance thermal performance, whereas XPS boards should be tightly fitted and sealed at seams to maintain insulation integrity. You can streamline installation by selecting the appropriate insulation type based on the specific application area, ensuring optimal efficiency and longevity.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Polyiso insulation generally offers a higher initial cost compared to XPS but provides superior R-value per inch, enhancing long-term energy savings and overall value. XPS tends to have lower upfront expenses, making it a budget-friendly choice for short-term projects, though it may require more thickness to achieve similar performance. Your investment in Polyiso can lead to lower heating and cooling costs over time, balancing out the higher initial price with improved energy efficiency.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Polyiso insulation is widely used in commercial roofing systems due to its high R-value per inch and excellent thermal resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. XPS insulation is preferred for below-grade applications such as foundation walls and slabs because of its superior moisture resistance and compressive strength. Both materials are commonly employed in wall assemblies, but polyiso excels in environments requiring vapor permeability while XPS suits wet or damp conditions.
Polyiso vs XPS: Which is Right for Your Project?
Polyiso insulation offers a higher R-value per inch, typically around R-6 to R-6.5, making it ideal for projects requiring superior thermal performance in thinner layers. XPS insulation provides consistent moisture resistance and compressive strength, often favored in below-grade or high-moisture environments. Choosing between Polyiso and XPS depends on your project's thermal requirements, exposure conditions, and budget considerations.
Polyiso vs XPS insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com