Hydronic radiant floor heating uses warm water circulated through pipes beneath the floor, offering energy efficiency and consistent heat for larger spaces, while electric radiant floor heating relies on electrically charged cables or mats for quicker installation and more precise temperature control, ideal for smaller areas. Choosing hydronic systems reduces utility costs and suits your home's long-term heating needs, whereas electric systems provide flexibility and lower upfront expenses.
Table of Comparison
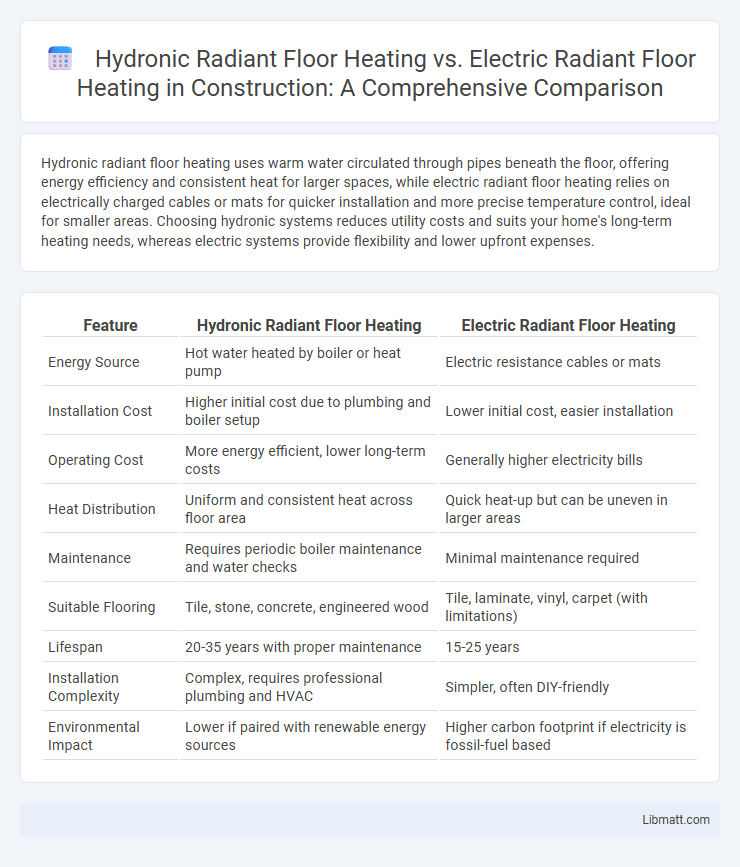
| Feature | Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating | Electric Radiant Floor Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Hot water heated by boiler or heat pump | Electric resistance cables or mats |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost due to plumbing and boiler setup | Lower initial cost, easier installation |
| Operating Cost | More energy efficient, lower long-term costs | Generally higher electricity bills |
| Heat Distribution | Uniform and consistent heat across floor area | Quick heat-up but can be uneven in larger areas |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic boiler maintenance and water checks | Minimal maintenance required |
| Suitable Flooring | Tile, stone, concrete, engineered wood | Tile, laminate, vinyl, carpet (with limitations) |
| Lifespan | 20-35 years with proper maintenance | 15-25 years |
| Installation Complexity | Complex, requires professional plumbing and HVAC | Simpler, often DIY-friendly |
| Environmental Impact | Lower if paired with renewable energy sources | Higher carbon footprint if electricity is fossil-fuel based |
Introduction to Radiant Floor Heating Systems
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems circulate warm water through tubing embedded in the floor, offering high energy efficiency and consistent heat distribution ideal for larger spaces or whole-home solutions. Electric radiant floor heating uses electric cables or mats installed beneath the flooring surface, providing rapid heat response and simpler installation suited for smaller areas or renovations. Both systems deliver comfortable, even warmth by directly heating the floor, reducing energy loss compared to traditional forced-air heating.
How Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating Works
Hydronic radiant floor heating circulates heated water through a network of pipes embedded beneath the floor, efficiently transferring warmth to the surface and surrounding air. This system uses a boiler or water heater to warm the water, which is then pumped continuously to maintain consistent heat distribution across large areas. Hydronic systems are energy-efficient, suitable for both residential and commercial buildings, and compatible with various heat sources, including solar and geothermal energy.
How Electric Radiant Floor Heating Works
Electric radiant floor heating operates by using electric heating cables or mats embedded beneath the floor surface to generate heat through electrical resistance. The system converts electrical energy directly into heat, which is transferred evenly across the floor, providing consistent warmth throughout the room. This method offers rapid heating response times and precise temperature control compared to hydronic systems that use heated water circulating through pipes.
Installation Process: Hydronic vs Electric
Hydronic radiant floor heating installation involves running a network of flexible PEX tubing beneath the floor, connected to a boiler or water heater, requiring professional expertise and more extensive labor due to plumbing integration. Electric radiant floor heating installation consists of laying electric mats or cables directly under the floor surface, offering a simpler, quicker, and less invasive process often suitable for retrofit projects. Hydronic systems typically require additional components like pumps and manifolds, while electric systems need precise electrical wiring and connection to a dedicated circuit breaker for efficient and safe operation.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems typically offer superior energy efficiency as they use heated water circulated through pipes, allowing for lower water temperatures and more consistent heat distribution. Electric radiant floor heating systems convert electricity directly into heat through resistive cables or mats, which can result in higher operating costs depending on electricity rates. Choosing hydronic heating can reduce your energy consumption and utility bills, especially in larger spaces or whole-home installations.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Expenses
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems typically have higher initial installation costs due to the complexity of plumbing and boiler setup, ranging from $6 to $20 per square foot, but offer lower long-term operating expenses because they use water heated by efficient boilers or solar systems. Electric radiant floor heating generally involves lower upfront costs, averaging $8 to $12 per square foot, but incurs higher monthly energy bills since electricity is more expensive than natural gas or propane used in hydronic systems. Over time, hydronic systems provide better cost efficiency for large areas and continuous heating, while electric systems suit smaller spaces or supplemental heating where upfront budget constraints are critical.
Maintenance Requirements
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems require periodic inspection of boilers, pumps, and piping to prevent leaks and ensure efficient water circulation. Electric radiant floor heating demands minimal maintenance, primarily involving routine checks of electrical connections and thermostat functionality. Both systems benefit from professional evaluations every few years to maintain optimal performance and safety.
Best Applications for Each System
Hydronic radiant floor heating is best suited for large areas and new construction projects due to its high efficiency and ability to warm multiple rooms with a single boiler system. Electric radiant floor heating excels in smaller spaces, bathrooms, or retrofit installations where quick heating and easy installation are priorities. Your choice depends on factors such as floor size, budget, and long-term energy efficiency goals.
Comfort and Heating Performance
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems provide superior comfort by delivering consistent, evenly distributed warmth through heated water circulating in pipes beneath the floor, maintaining stable temperatures and reducing cold spots. Electric radiant floor heating offers quicker heat-up times and precise zoning control but may result in less even heat distribution compared to hydronic systems. The hydronic system's ability to sustain higher heat output and efficiency makes it ideal for large spaces, while electric systems excel in smaller areas or supplemental heating applications.
Choosing the Right System for Your Home
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems use heated water circulated through pipes, offering greater energy efficiency and lower operating costs compared to electric radiant floor heating, which relies on electrical resistance cables or mats embedded in the floor. Homes with larger spaces or colder climates benefit from hydronic systems due to their ability to provide consistent warmth and handle extensive floor areas effectively. Electric systems are easier to install and ideal for smaller areas or renovations, making the choice dependent on factors like home size, budget, installation complexity, and energy source availability.
Hydronic radiant floor heating vs electric radiant floor heating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com