Rigid insulation provides consistent thermal resistance with high compressive strength, ideal for exterior walls and foundations, while spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing and expands to fill gaps, enhancing your home's energy efficiency. Choosing between them depends on your project's specific needs for moisture control, ease of installation, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
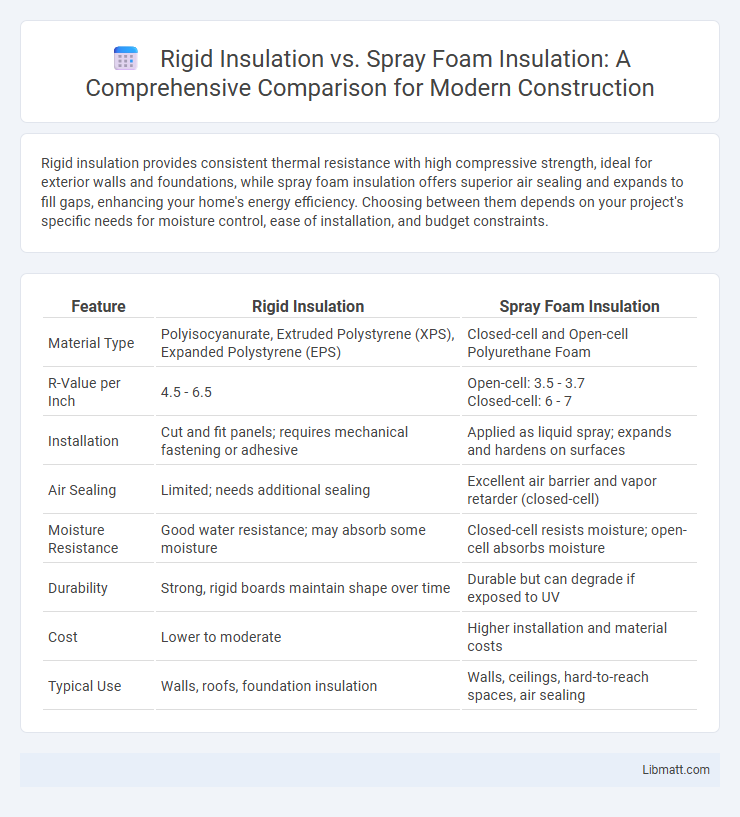
| Feature | Rigid Insulation | Spray Foam Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyisocyanurate, Extruded Polystyrene (XPS), Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Closed-cell and Open-cell Polyurethane Foam |
| R-Value per Inch | 4.5 - 6.5 | Open-cell: 3.5 - 3.7 Closed-cell: 6 - 7 |
| Installation | Cut and fit panels; requires mechanical fastening or adhesive | Applied as liquid spray; expands and hardens on surfaces |
| Air Sealing | Limited; needs additional sealing | Excellent air barrier and vapor retarder (closed-cell) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good water resistance; may absorb some moisture | Closed-cell resists moisture; open-cell absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Strong, rigid boards maintain shape over time | Durable but can degrade if exposed to UV |
| Cost | Lower to moderate | Higher installation and material costs |
| Typical Use | Walls, roofs, foundation insulation | Walls, ceilings, hard-to-reach spaces, air sealing |
Introduction to Rigid and Spray Foam Insulation
Rigid insulation panels, typically made from materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), or polyisocyanurate, offer high thermal resistance and durability, making them ideal for walls, roofs, and foundations. Spray foam insulation, available as open-cell or closed-cell varieties, provides superior air sealing and moisture resistance by expanding upon application to fill gaps and crevices, enhancing energy efficiency. Your choice between these insulation types should consider factors like installation area, R-value requirements, and budget constraints to optimize thermal performance and long-term savings.
What Is Rigid Insulation?
Rigid insulation consists of durable foam boards made from materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), or polyisocyanurate, designed to provide high thermal resistance and structural support. Unlike spray foam insulation that expands on application, rigid insulation is pre-formed and commonly used in walls, roofs, and foundations to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Your choice between rigid insulation and spray foam should consider installation ease, insulation value (R-value), and moisture resistance specific to your project needs.
What Is Spray Foam Insulation?
Spray foam insulation is a versatile material that expands upon application to fill gaps, cracks, and cavities, providing an airtight and highly effective thermal barrier. Compared to rigid insulation, spray foam adheres directly to surfaces, creating a seamless seal that reduces air leakage and improves energy efficiency. Your choice of spray foam can impact insulation R-values, moisture resistance, and overall home comfort, especially in irregular spaces where rigid panels may not fit precisely.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Rigid insulation typically offers a higher R-value per inch, providing consistent thermal resistance that effectively minimizes heat transfer in walls and roofs. Spray foam insulation, especially closed-cell foam, delivers superior air-sealing properties combined with high R-values, enhancing overall thermal performance by preventing drafts and moisture infiltration. Both materials improve energy efficiency, but spray foam excels in sealing gaps, while rigid boards provide stable insulation with less risk of settling over time.
Moisture Resistance and Air Sealing
Rigid insulation offers excellent moisture resistance due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it ideal for areas prone to dampness or water exposure. Spray foam insulation excels in air sealing by expanding to fill gaps and cracks, creating a continuous barrier that prevents air leakage and improves energy efficiency. Combining rigid insulation's moisture resistance with spray foam's superior air sealing enhances overall building envelope performance.
Installation Process Differences
Rigid insulation panels are cut to size and fitted manually between wall studs or roof rafters, requiring precise measurements for a tight fit, while spray foam insulation expands upon application, filling gaps and irregular spaces automatically. The installation of rigid insulation is labor-intensive and time-consuming, often needing additional sealing to prevent air leaks, whereas spray foam offers faster application and creates a seamless air barrier with less effort. Your choice depends on project complexity and desired insulation efficiency, with spray foam delivering superior thermal performance and air sealing in fewer steps.
Cost Analysis of Rigid vs Spray Foam
Rigid insulation typically has a lower upfront material cost ranging from $0.25 to $1.50 per square foot, while spray foam insulation costs vary between $1.00 and $3.00 per square foot depending on the type (open-cell or closed-cell). Installation expenses for spray foam tend to be higher due to the need for professional application and specialized equipment, whereas rigid boards can often be installed as a DIY project, reducing labor costs. Over time, spray foam's superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch can lead to greater energy savings, potentially offsetting its initial price difference compared to rigid insulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rigid insulation panels typically have a lower environmental impact due to their longer lifespan and the use of recycled materials like polystyrene or polyisocyanurate, which also offer high thermal resistance and energy efficiency. Spray foam insulation, while providing superior air sealing and reducing energy consumption, often relies on petrochemical-based components and blowing agents with high global warming potential, raising sustainability concerns. Choosing rigid insulation supports eco-friendlier building practices through recyclability and reduced carbon footprint, whereas spray foam requires careful consideration of chemical formulations to minimize environmental harm.
Best Applications for Each Insulation Type
Rigid insulation is best suited for exterior wall sheathing, foundation walls, and roofing applications where high compressive strength and moisture resistance are essential. Spray foam insulation excels in sealing irregular cavities, attics, and around ducts, providing superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch. Your choice depends on the specific project requirements, such as space constraints and desired thermal performance.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Rigid insulation offers high compressive strength and is ideal for exterior walls, foundations, and roofing, providing consistent thermal resistance and moisture control. Spray foam insulation delivers superior air sealing and fills gaps effectively, making it suitable for irregular spaces and enhancing energy efficiency. Selecting between rigid and spray foam insulation depends on project-specific factors such as installation area, desired R-value, budget, and moisture management requirements.
Rigid insulation vs Spray foam insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com