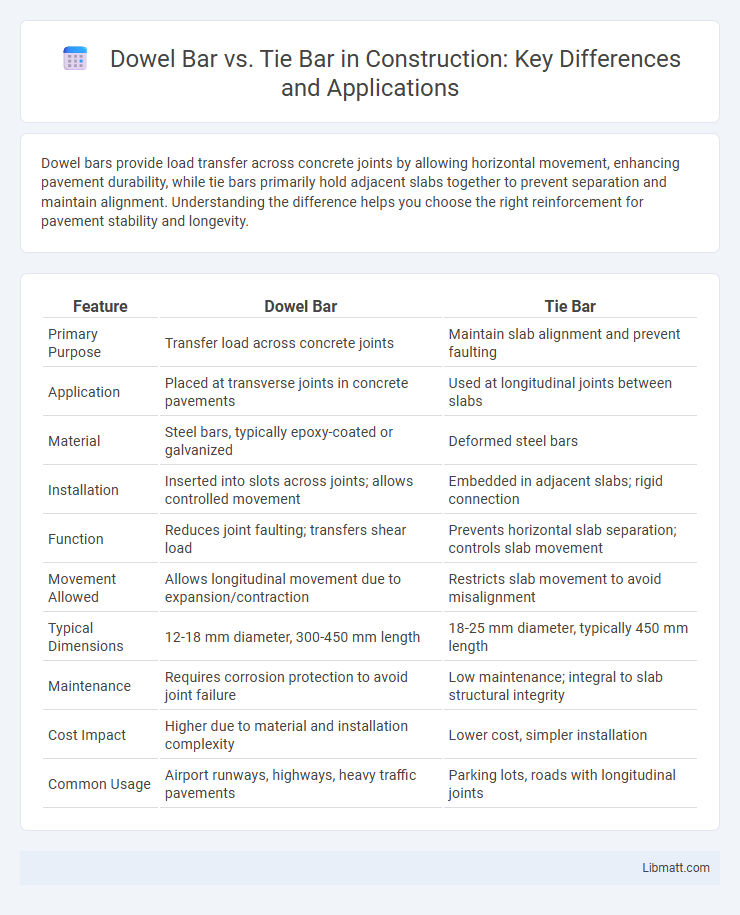
Dowel bars provide load transfer across concrete joints by allowing horizontal movement, enhancing pavement durability, while tie bars primarily hold adjacent slabs together to prevent separation and maintain alignment. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right reinforcement for pavement stability and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dowel Bar | Tie Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Transfer load across concrete joints | Maintain slab alignment and prevent faulting |
| Application | Placed at transverse joints in concrete pavements | Used at longitudinal joints between slabs |
| Material | Steel bars, typically epoxy-coated or galvanized | Deformed steel bars |
| Installation | Inserted into slots across joints; allows controlled movement | Embedded in adjacent slabs; rigid connection |
| Function | Reduces joint faulting; transfers shear load | Prevents horizontal slab separation; controls slab movement |
| Movement Allowed | Allows longitudinal movement due to expansion/contraction | Restricts slab movement to avoid misalignment |
| Typical Dimensions | 12-18 mm diameter, 300-450 mm length | 18-25 mm diameter, typically 450 mm length |
| Maintenance | Requires corrosion protection to avoid joint failure | Low maintenance; integral to slab structural integrity |
| Cost Impact | Higher due to material and installation complexity | Lower cost, simpler installation |
| Common Usage | Airport runways, highways, heavy traffic pavements | Parking lots, roads with longitudinal joints |
Introduction to Dowel Bars and Tie Bars
Dowel bars are smooth, cylindrical steel rods used to transfer load across concrete joints in pavements, preventing faulting and ensuring even load distribution. Tie bars are deformed steel bars embedded in concrete slabs to hold adjacent slabs together and control horizontal movement, enhancing slab stability. Both play critical roles in maintaining structural integrity and extending the lifespan of concrete pavements by managing stress and preventing cracks.
Purpose and Function of Dowel Bars
Dowel bars serve to transfer loads across concrete pavement joints, reducing stress and preventing faulting while allowing for horizontal movement caused by temperature changes. Unlike tie bars, which hold adjacent slabs together to control longitudinal cracking, dowel bars primarily ensure smooth load distribution and maintain pavement alignment. Your pavement's durability largely depends on the correct installation and function of these dowel bars in managing joint performance.
Purpose and Function of Tie Bars
Tie bars serve the purpose of holding adjacent concrete slabs together to prevent them from moving apart under load, ensuring structural integrity and avoiding joint faulting in pavements. Unlike dowel bars that facilitate load transfer across expansion joints by allowing horizontal movement, tie bars restrict lateral movement, maintaining alignment and load continuity across contraction joints. Proper installation of tie bars improves pavement durability by distributing stresses and reducing the risk of slab displacement.
Key Differences Between Dowel Bars and Tie Bars
Dowel bars are cylindrical steel rods placed across concrete joints to transfer load and facilitate joint movement, enhancing pavement durability and reducing cracking. Tie bars are deformed steel bars used to hold adjacent slabs together, preventing separation and maintaining alignment without load transfer capabilities. The primary difference lies in dowel bars enabling load transfer while tie bars provide structural stability by restraining slab movement.
Material and Design Specifications
Dowel bars are typically made from high-strength steel with a smooth surface and specific dimensions, such as a diameter of 1.25 inches and length ranging from 12 to 18 inches, designed for load transfer across concrete joints. Tie bars are also made of deformed steel with ribbed surfaces to improve bonding and are usually shorter in length, commonly about 18 to 24 inches, functioning primarily to hold adjacent slabs together and control joint movement. Both components conform to ASTM standards like ASTM A615 for reinforcing steel but differ in their geometric design tailored to distinct structural roles in pavement construction.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Dowel bar installation requires precise alignment and proper embedment within concrete joints to facilitate load transfer and minimize slab movement. Tie bar installation involves securing bars across slab cracks or joints to maintain slab integrity and prevent separation, typically anchored firmly within the concrete mix. Best practices include using appropriate spacing, ensuring corrosion-resistant materials, and verifying bar placement depth to optimize joint performance and durability.
Performance and Load Distribution
Dowel bars provide superior load transfer across concrete pavement joints by allowing horizontal movement while maintaining alignment, reducing faulting and enhancing durability under heavy traffic loads. Tie bars function primarily to hold adjacent slabs together without load transfer capacity, controlling slab separation and reducing joint widening but not distributing loads effectively. Effective load distribution with dowel bars minimizes pavement distress and extends service life, while tie bars mainly enhance slab stability without improving load performance.
Applications in Pavement Construction
Dowel bars and tie bars are essential components in pavement construction for load transfer and joint stability. Dowel bars are primarily used in concrete slab joints to transfer loads across adjacent slabs, reducing stress and preventing faulting in highways and airport runways. Tie bars connect slabs within the same pavement section to maintain alignment and control slab movement, especially in continuously reinforced concrete pavements and bridge decks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Dowel bars provide superior load transfer between concrete slabs, reducing joint faulting and extending pavement life, but they require precise installation and can be costly. Tie bars help maintain slab alignment and prevent lateral movement, offering a simpler and more economical solution, though they are less effective at load transfer and may lead to joint deterioration over time. Your choice depends on balancing long-term durability with installation complexity and budget constraints.
Choosing Between Dowel Bars and Tie Bars
Choosing between dowel bars and tie bars depends on the specific structural requirements of a concrete pavement joint. Dowel bars are typically used to transfer load across expansion joints, allowing for horizontal movement while maintaining alignment and load transfer efficiency. Tie bars, on the other hand, are designed to hold adjacent concrete slabs together and prevent longitudinal joint separation, providing structural integrity without accommodating movement.
Dowel bar vs tie bar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com