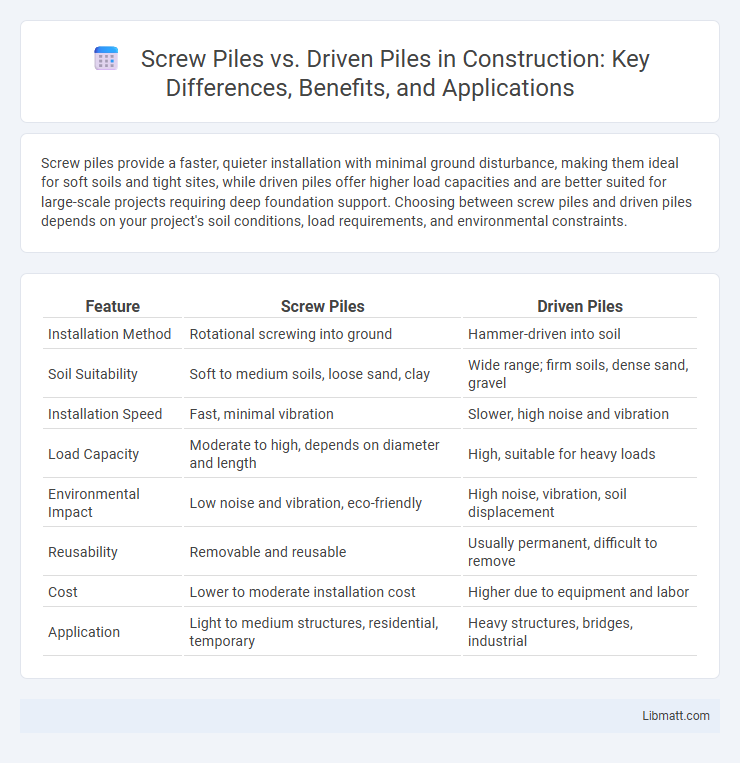
Screw piles provide a faster, quieter installation with minimal ground disturbance, making them ideal for soft soils and tight sites, while driven piles offer higher load capacities and are better suited for large-scale projects requiring deep foundation support. Choosing between screw piles and driven piles depends on your project's soil conditions, load requirements, and environmental constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screw Piles | Driven Piles |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Rotational screwing into ground | Hammer-driven into soil |
| Soil Suitability | Soft to medium soils, loose sand, clay | Wide range; firm soils, dense sand, gravel |
| Installation Speed | Fast, minimal vibration | Slower, high noise and vibration |
| Load Capacity | Moderate to high, depends on diameter and length | High, suitable for heavy loads |
| Environmental Impact | Low noise and vibration, eco-friendly | High noise, vibration, soil displacement |
| Reusability | Removable and reusable | Usually permanent, difficult to remove |
| Cost | Lower to moderate installation cost | Higher due to equipment and labor |
| Application | Light to medium structures, residential, temporary | Heavy structures, bridges, industrial |
Introduction to Screw Piles and Driven Piles
Screw piles are deep foundation solutions featuring a helical steel shaft that is twisted into the ground, providing stability through torque and soil displacement. Driven piles consist of pre-formed concrete, steel, or timber elements hammered or pressed into the soil to transfer structural loads through friction and end-bearing. Understanding the differences between screw piles and driven piles helps you select the optimal foundation method based on soil conditions, load requirements, and installation constraints.
Key Differences Between Screw and Driven Piles
Screw piles are installed by rotating them into the ground, causing minimal noise and vibration, while driven piles are hammer-driven, often creating significant noise and ground disturbance. Screw piles offer immediate load-bearing capacity upon installation, whereas driven piles require impact driving, which can cause soil displacement affecting surrounding structures. Your choice between screw and driven piles should consider site conditions, environmental impact, and installation speed.
Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Screw piles are typically made from high-strength steel with helical plates welded onto the shaft, manufactured through precision welding and galvanization to enhance corrosion resistance. Driven piles often consist of concrete, steel, or timber, fabricated by casting for concrete, rolling and welding for steel, or treatment processes for timber to ensure durability. Your choice between screw piles and driven piles should consider the specific material properties and manufacturing quality, which impact load-bearing capacity and longevity.
Installation Methods: Screw vs Driven Piles
Screw piles are installed by rotating them into the ground using hydraulic machinery, minimizing soil disturbance and noise, and allowing for precise control during installation. Driven piles are hammered or vibrated into the soil using heavy machinery, which can be faster but often causes more vibration, noise, and potential soil displacement. Your choice between these installation methods depends on site conditions, noise restrictions, and soil type for optimal foundation performance.
Load Capacity and Performance
Screw piles deliver high load capacity by transferring structural loads deep into stable soil layers through helical plates, providing excellent performance in both tension and compression. Driven piles achieve substantial load capacity by displacement and compaction of surrounding soil, enhancing lateral stability and bearing capacity, especially in dense or layered soils. Performance of screw piles excels in installations with minimal vibration and noise, while driven piles are preferred for applications requiring high axial load resistance in dense substrates.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Screw piles have a lower environmental impact compared to driven piles due to their minimal soil displacement and reduced noise pollution during installation. Driven piles cause significant vibration and disturbance to surrounding soil and ecosystems, often leading to habitat disruption and increased carbon emissions. Your choice of screw piles supports eco-friendly construction practices by preserving soil structure and reducing environmental footprint.
Cost Analysis: Screw Piles vs Driven Piles
Screw piles generally offer lower installation costs compared to driven piles due to faster deployment and minimal site preparation requirements. Driven piles often incur higher expenses because of specialized equipment, longer installation times, and noise or vibration mitigation measures. Your project budget can benefit significantly from screw piles' cost efficiency while maintaining structural integrity.
Suitability for Different Soil Conditions
Screw piles perform exceptionally well in soft or unstable soils such as clay, silt, and loose sand due to their helical design that anchors firmly without extensive soil displacement. Driven piles are better suited for dense, load-bearing soils and can penetrate through hard layers, making them ideal for sites with compacted gravel or rock formations. Your choice between screw piles and driven piles should depend on the soil type and load requirements to ensure optimal foundation stability and cost-efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Screw piles offer quick installation with minimal soil disturbance and are reusable, making them ideal for lightweight to medium-load structures, though they may have limited capacity in dense or rocky soils. Driven piles provide high load-bearing capacity and excellent performance in a variety of soil conditions but require heavy equipment and can cause noise and vibration during installation. Cost efficiency for screw piles favors smaller projects, while driven piles are better suited for large-scale developments requiring deep foundations.
Choosing the Right Piling Solution
Screw piles offer rapid installation with minimal soil displacement, making them ideal for projects requiring low environmental impact and immediate load bearing capacity. Driven piles provide high load capacity and are suited for heavy structural support in dense or challenging soil conditions, often used in large-scale infrastructure projects. Evaluating soil type, load requirements, and environmental constraints ensures selecting the optimal piling solution for project longevity and performance.
Screw piles vs driven piles Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com