Self-compacting concrete flows effortlessly into molds without mechanical vibration, ideal for complex forms and congested reinforcement areas, while high-performance concrete prioritizes enhanced durability, strength, and long-term performance under extreme conditions. Your choice depends on construction requirements, whether ease of placement or superior mechanical properties is the priority.
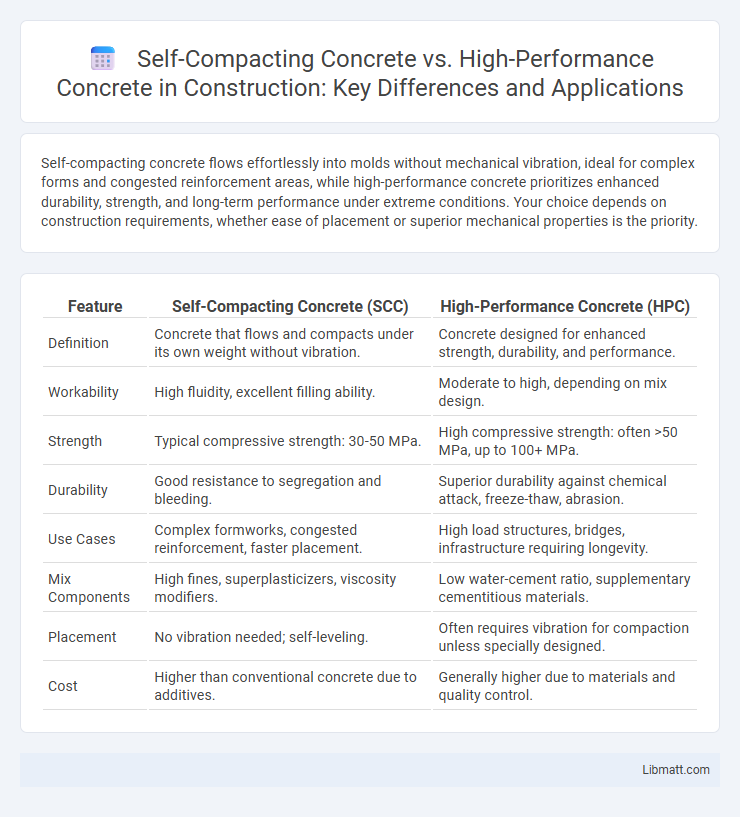
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC) | High-Performance Concrete (HPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete that flows and compacts under its own weight without vibration. | Concrete designed for enhanced strength, durability, and performance. |
| Workability | High fluidity, excellent filling ability. | Moderate to high, depending on mix design. |
| Strength | Typical compressive strength: 30-50 MPa. | High compressive strength: often >50 MPa, up to 100+ MPa. |
| Durability | Good resistance to segregation and bleeding. | Superior durability against chemical attack, freeze-thaw, abrasion. |
| Use Cases | Complex formworks, congested reinforcement, faster placement. | High load structures, bridges, infrastructure requiring longevity. |
| Mix Components | High fines, superplasticizers, viscosity modifiers. | Low water-cement ratio, supplementary cementitious materials. |
| Placement | No vibration needed; self-leveling. | Often requires vibration for compaction unless specially designed. |
| Cost | Higher than conventional concrete due to additives. | Generally higher due to materials and quality control. |
Introduction to Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC) and High-Performance Concrete (HPC)
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is a highly flowable material designed to spread into place and encapsulate reinforcement without mechanical vibration, improving placement efficiency and surface finish quality. High-performance concrete (HPC) combines enhanced properties such as high strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors through optimized mix design and advanced admixtures. While SCC emphasizes workability and ease of placement, HPC focuses on achieving superior mechanical and durability characteristics for demanding structural applications.
Key Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) exhibits high flowability, allowing it to fill complex formworks without mechanical vibration, thanks to its superior workability and segregation resistance. Its key properties include enhanced viscosity, stability against bleeding, and excellent cohesiveness, ensuring uniform density and surface finish. Your construction projects benefit from SCC's rapid placement and reduced labor costs while maintaining comparable strength and durability to high-performance concrete.
Defining Characteristics of High-Performance Concrete
High-performance concrete (HPC) is defined by its superior strength, durability, and workability compared to conventional concrete. It typically features a carefully designed mix with low water-cement ratio, specialized admixtures, and high-quality aggregates to achieve enhanced mechanical properties and resistance to environmental attacks. Your construction projects benefit from HPC's ability to withstand harsh conditions while maintaining structural integrity over time.
Mix Design Differences: SCC vs HPC
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) features a mix design rich in fine fillers, superplasticizers, and viscosity-modifying agents to ensure flowability without segregation or bleeding. High-performance concrete (HPC) emphasizes a low water-cement ratio and optimized aggregate gradation, incorporating supplementary cementitious materials like silica fume for enhanced strength and durability. The key mix design difference lies in SCC's focus on rheology for self-compaction, whereas HPC prioritizes mechanical properties and longevity through material enhancement.
Workability and Placement: A Comparative Analysis
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) offers superior workability due to its high flowability and ability to consolidate under its own weight, eliminating the need for mechanical vibration during placement. In contrast, high-performance concrete (HPC) prioritizes strength and durability but often requires external vibration to ensure proper compaction and reduce voids. The enhanced fresh-state properties of SCC improve placement efficiency in complex formworks, while HPC's focus remains on achieving specific structural performance parameters.
Strength and Durability Performance
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) offers excellent flowability and uniformity, ensuring high strength through optimal compaction without compromising durability. High-performance concrete (HPC) is specifically engineered to achieve superior strength and enhanced durability, often exceeding traditional concrete properties with optimized mix designs and supplementary cementitious materials. Your choice between SCC and HPC should consider the specific project requirements for strength and long-term durability under environmental stressors.
Applications and Use Cases in Construction Industry
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is extensively used in complex formworks, prefabricated structures, and areas requiring rapid placement without vibration, such as high-rise buildings and heavily reinforced sections. High-performance concrete (HPC) is preferred for infrastructure projects demanding exceptional durability, strength, and resistance to environmental factors, including bridges, dams, and tunnels. Both SCC and HPC improve construction quality and efficiency but are selected based on specific project requirements like workability or performance criteria.
Cost Comparison and Resource Efficiency
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) typically incurs higher initial material costs due to specialized admixtures but reduces labor expenses through faster placement and improved workability. High-performance concrete (HPC) often demands premium raw materials and stringent quality control, increasing production costs, yet it provides superior durability that lowers long-term maintenance expenditures. SCC enhances resource efficiency by minimizing waste and energy consumption during construction, whereas HPC optimizes lifecycle resource utilization through enhanced structural longevity.
Challenges and Limitations of SCC and HPC
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) faces challenges such as high material costs and sensitivity to mix composition, leading to potential segregation and reduced durability if not properly controlled. High-performance concrete (HPC) often requires specialized curing and admixtures to achieve its superior strength and durability, which can complicate construction schedules and increase costs. Your project must consider these limitations to balance performance benefits with practical application constraints.
Future Trends in Advanced Concrete Technologies
Future trends in advanced concrete technologies emphasize the integration of self-compacting concrete (SCC) and high-performance concrete (HPC) to enhance construction efficiency and structural durability. Innovations focus on nano-engineered additives and tailored mix designs that improve flowability in SCC while boosting the mechanical strength and longevity of HPC. Sustainable development drives the incorporation of recycled materials and smart sensing capabilities for real-time monitoring of concrete performance in both SCC and HPC applications.
Self-compacting concrete vs high-performance concrete Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com