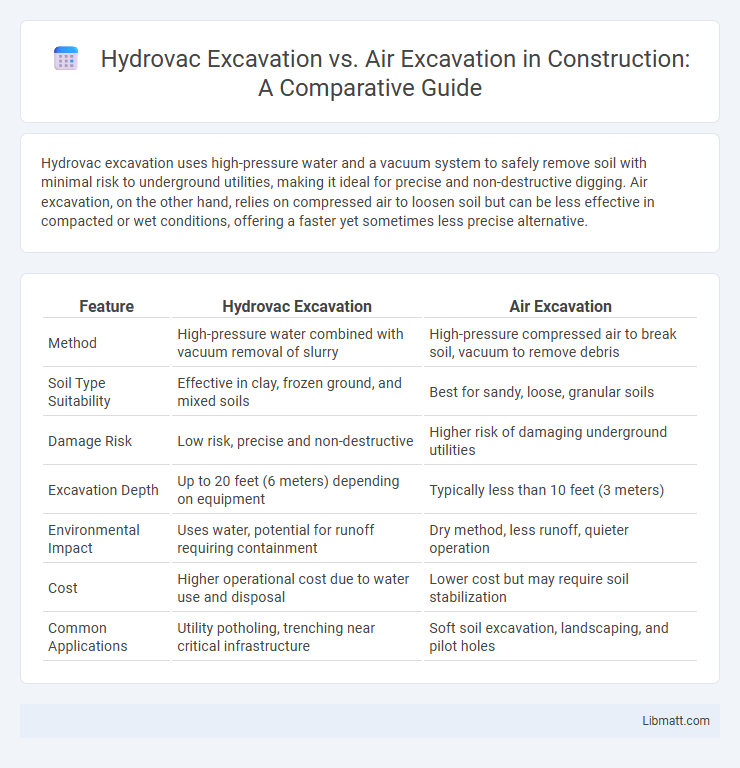
Hydrovac excavation uses high-pressure water and a vacuum system to safely remove soil with minimal risk to underground utilities, making it ideal for precise and non-destructive digging. Air excavation, on the other hand, relies on compressed air to loosen soil but can be less effective in compacted or wet conditions, offering a faster yet sometimes less precise alternative.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydrovac Excavation | Air Excavation |
|---|---|---|
| Method | High-pressure water combined with vacuum removal of slurry | High-pressure compressed air to break soil, vacuum to remove debris |
| Soil Type Suitability | Effective in clay, frozen ground, and mixed soils | Best for sandy, loose, granular soils |
| Damage Risk | Low risk, precise and non-destructive | Higher risk of damaging underground utilities |
| Excavation Depth | Up to 20 feet (6 meters) depending on equipment | Typically less than 10 feet (3 meters) |
| Environmental Impact | Uses water, potential for runoff requiring containment | Dry method, less runoff, quieter operation |
| Cost | Higher operational cost due to water use and disposal | Lower cost but may require soil stabilization |
| Common Applications | Utility potholing, trenching near critical infrastructure | Soft soil excavation, landscaping, and pilot holes |
Introduction to Hydrovac and Air Excavation
Hydrovac excavation uses high-pressure water to liquefy soil and a powerful vacuum to remove debris, making it ideal for precise, non-destructive digging around underground utilities. Air excavation employs compressed air to dislodge soil, allowing quick and safe exposure of buried structures without damaging sensitive infrastructure. Your choice between hydrovac and air excavation depends on soil type, site conditions, and the level of precision required for the project.
How Hydrovac Excavation Works
Hydrovac excavation uses high-pressure water to liquefy soil, followed by a powerful vacuum hose that removes the slurry and debris from the site, ensuring precise and non-destructive digging. This method reduces the risk of damaging underground utilities compared to air excavation, which uses compressed air to break up soil but can be less effective in dense or frozen ground. Your project benefits from hydrovac's accuracy and safety, especially in urban areas with complex underground infrastructure.
How Air Excavation Works
Air excavation uses highly pressurized air to loosen soil while minimizing damage to underground utilities and surrounding infrastructure. The process involves directing a powerful stream of compressed air through a specialized nozzle to break up compacted soil, which is then vacuumed away for debris removal. This technique offers precise, non-destructive digging, making it ideal for sensitive environments and densely populated areas.
Efficiency Comparison: Hydrovac vs Air Excavation
Hydrovac excavation offers superior efficiency compared to air excavation by using high-pressure water to liquefy soil and a powerful vacuum to remove debris, enabling faster and more precise digging with minimal ground disturbance. Air excavation relies on compressed air to loosen soil, which can be slower and less effective in clay or dense soils, leading to increased project time and labor costs. Your choice of hydrovac excavation optimizes operational speed and accuracy, especially in urban or sensitive environments where precision is critical.
Safety Considerations for Each Method
Hydrovac excavation uses high-pressure water and a vacuum system, reducing the risk of damaging underground utilities and minimizing worker injury compared to traditional methods. Air excavation employs compressed air to loosen soil, which is safer than mechanical digging but can risk underground utility damage if not carefully managed. Your choice should consider the specific subsurface conditions and safety protocols to ensure optimal protection for workers and nearby infrastructure.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Hydrovac excavation minimizes soil disturbance and reduces the risk of contaminant spread by using pressurized water and vacuum technology, making it more environmentally friendly compared to air excavation, which can cause significant dust generation and soil erosion. The precise nature of hydrovac reduces groundwater contamination and protects underground utilities, while air excavation's aggressive air pressure may lead to longer recovery times for the affected environment. Choosing hydrovac excavation over air excavation can help you ensure compliance with environmental regulations and promote sustainable site cleanup practices.
Cost Differences Between Hydrovac and Air Excavation
Hydrovac excavation typically involves higher initial costs due to specialized equipment and water usage, whereas air excavation tends to be more cost-effective for dry, non-sensitive environments. Your project's soil type, utility sensitivity, and depth requirements significantly influence the overall expense, with hydrovac preferred for its precision and reduced risk of utility damage. Choosing the right method balances budget considerations against safety and project complexity to optimize excavation efficiency.
Best Applications for Hydrovac Excavation
Hydrovac excavation is best suited for digging in urban environments with underground utilities, as it uses high-pressure water and a vacuum to safely expose pipes and cables without damaging them. This method excels in precise potholing, daylighting utilities, and working in confined spaces where traditional mechanical digging poses risks. Your project benefits from hydrovac excavation when soil conditions are challenging, such as frozen ground or clay, due to its clean, non-destructive process.
Ideal Scenarios for Air Excavation
Air excavation is ideal for delicate underground utility work where precision and minimal disturbance to surrounding soil are essential. It works best in areas with sandy or loose soil, reducing the risk of damaging fragile pipes, cables, or conduits. Your project benefits from increased accuracy and a lower chance of accidental utility strikes when using air excavation in these controlled environments.
Choosing the Right Excavation Method for Your Project
Hydrovac excavation uses high-pressure water and a vacuum system to safely expose underground utilities with minimal risk of damage, ideal for sensitive or congested areas. Air excavation employs compressed air to loosen soil, offering faster digging in dry, non-cohesive soils but with higher risk to fragile utilities. Assess your project's soil conditions, utility density, and safety requirements to determine whether hydrovac or air excavation best suits your needs.
Hydrovac excavation vs air excavation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com