Spray foam insulation provides superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch compared to batt insulation, offering enhanced energy efficiency and moisture resistance. Your choice depends on budget, installation area, and desired performance, with spray foam ideal for hard-to-reach spaces and batt insulation suitable for DIY projects and budget-conscious upgrades.
Table of Comparison
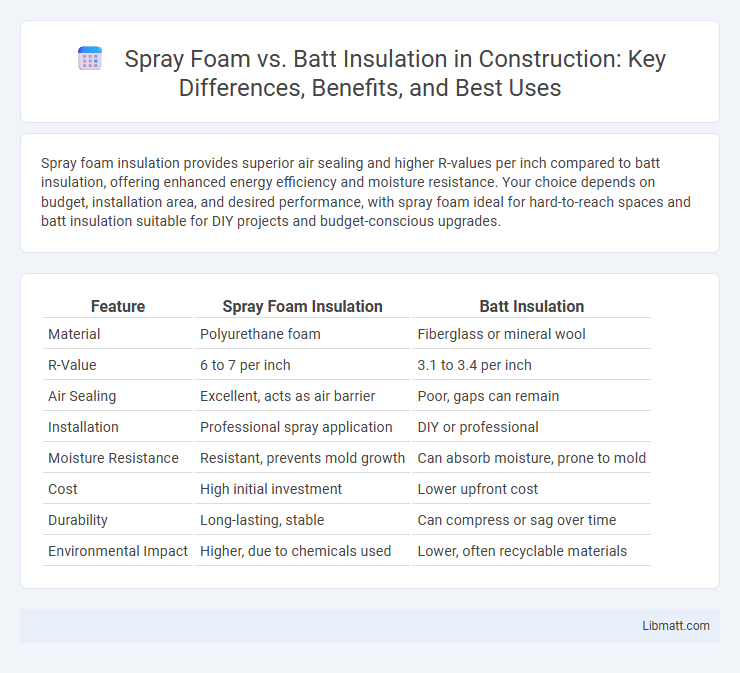
| Feature | Spray Foam Insulation | Batt Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyurethane foam | Fiberglass or mineral wool |
| R-Value | 6 to 7 per inch | 3.1 to 3.4 per inch |
| Air Sealing | Excellent, acts as air barrier | Poor, gaps can remain |
| Installation | Professional spray application | DIY or professional |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant, prevents mold growth | Can absorb moisture, prone to mold |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Durability | Long-lasting, stable | Can compress or sag over time |
| Environmental Impact | Higher, due to chemicals used | Lower, often recyclable materials |
Introduction to Spray Foam and Batt Insulation
Spray foam insulation expands upon application, forming an air-tight seal that enhances energy efficiency and moisture resistance, ideal for irregular spaces. Batt insulation, typically made of fiberglass or mineral wool, consists of pre-cut panels that fit between studs or joists, providing thermal resistance while allowing for easier installation. Both types address thermal performance but differ significantly in air sealing capabilities and installation methods.
Key Differences Between Spray Foam and Batt Insulation
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch compared to batt insulation, making it more effective at preventing heat loss and moisture intrusion. Batt insulation, commonly made from fiberglass or mineral wool, is easier to install and more cost-effective but lacks the ability to provide an airtight barrier. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right insulation type for improved energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
R-Value Comparison: Spray Foam vs Batt Insulation
Spray foam insulation typically offers an R-value between 6 and 7 per inch, significantly higher than batt insulation, which averages around R-3.5 to R-4.3 per inch. This higher R-value means spray foam provides superior thermal resistance, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. Choosing spray foam insulation for your home can result in better temperature regulation and long-term savings on utility bills.
Installation Process: What to Expect
Spray foam insulation requires professional installation involving specialized equipment to spray and expand the foam, creating an airtight seal that fills gaps and cracks effectively. Batt insulation is generally easier and faster to install, often using pre-cut fiberglass or mineral wool panels that fit between studs or joists but may leave small gaps if not tightly placed. Homeowners should expect higher upfront labor costs for spray foam due to its complexity, while batt insulation offers more DIY-friendly installation with variable performance based on accuracy and material quality.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Savings
Spray foam insulation typically has a higher upfront cost compared to batt insulation due to material and installation expenses, but it offers superior air sealing and higher R-values that lead to significant long-term energy savings. Batt insulation is more affordable initially but may result in higher heating and cooling costs over time due to gaps and less effective thermal performance. Your investment in spray foam can yield greater overall cost efficiency by reducing utility bills and improving home comfort.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Spray foam insulation offers superior energy efficiency by creating an airtight seal that minimizes heat loss and prevents air leakage, outperforming traditional batt insulation in thermal resistance. Batt insulation, typically made from fiberglass or mineral wool, can leave gaps and settle over time, reducing its effectiveness and allowing drafts that increase energy costs. Choosing spray foam can enhance your home's performance by providing durable insulation that maintains consistent temperatures and lowers utility bills.
Moisture Resistance and Air Sealing Capabilities
Spray foam insulation offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water infiltration and reducing the risk of mold growth. Its expansive nature creates a seamless air barrier, minimizing air leaks and enhancing energy efficiency compared to batt insulation, which often has gaps that allow air and moisture penetration. This makes spray foam the preferred choice for environments with high humidity or where airtight sealing is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing, reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions more effectively than batt insulation, which has gaps that allow air leaks. Although spray foam uses petroleum-based chemicals, advancements in eco-friendly formulas and higher insulation R-values contribute to long-term sustainability by lowering heating and cooling demands. Batt insulation is made from natural or recycled materials like fiberglass or mineral wool, but its lower efficiency can lead to increased energy use, offsetting some environmental benefits.
Best Applications for Spray Foam and Batt Insulation
Spray foam insulation excels in sealing air leaks and insulating irregular spaces, making it ideal for attics, crawl spaces, and areas with complex architectural features. Batt insulation is best suited for straightforward applications such as standard wall cavities, floors, and ceilings in framed construction where ease of installation and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Choosing between spray foam and batt depends on factors like desired R-value, moisture resistance, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing and higher R-values per inch compared to batt insulation, making it ideal for maximizing energy efficiency in tight or irregular spaces. Batt insulation, typically made from fiberglass or mineral wool, provides a cost-effective solution for standard wall cavities and simple framing structures. Assess project requirements such as thermal performance, moisture control, budget constraints, and installation complexity to determine the most suitable insulation type.
Spray foam vs Batt insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com