Shotcrete and gunite are both techniques for applying concrete pneumatically, but shotcrete mixes concrete before spraying, offering better control over mix consistency and faster application. Gunite involves dry mix delivery with water added at the nozzle, allowing for greater flexibility in adjustments on-site and is often preferred for complex or repair work where precision is essential.
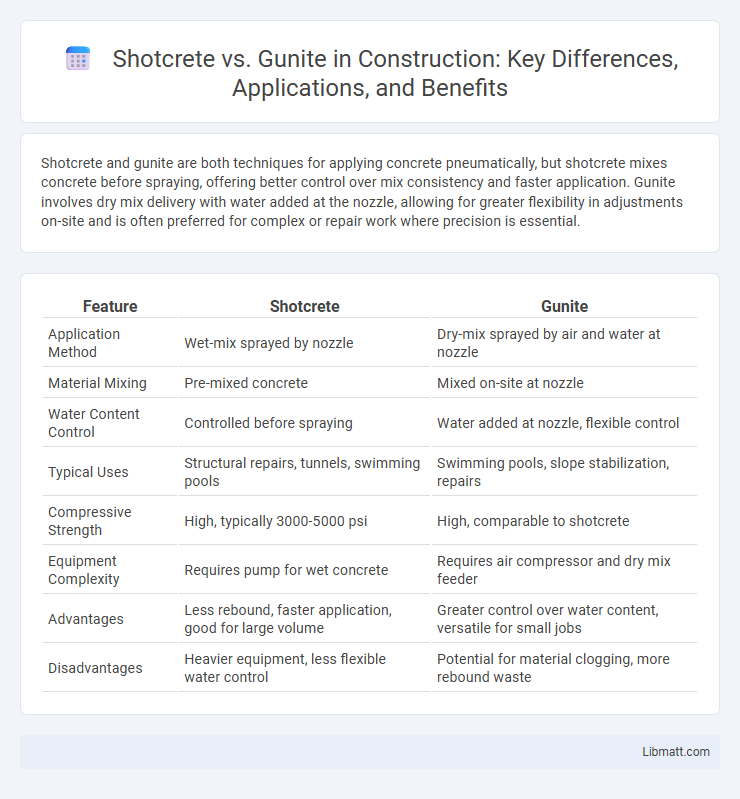
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shotcrete | Gunite |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Wet-mix sprayed by nozzle | Dry-mix sprayed by air and water at nozzle |
| Material Mixing | Pre-mixed concrete | Mixed on-site at nozzle |
| Water Content Control | Controlled before spraying | Water added at nozzle, flexible control |
| Typical Uses | Structural repairs, tunnels, swimming pools | Swimming pools, slope stabilization, repairs |
| Compressive Strength | High, typically 3000-5000 psi | High, comparable to shotcrete |
| Equipment Complexity | Requires pump for wet concrete | Requires air compressor and dry mix feeder |
| Advantages | Less rebound, faster application, good for large volume | Greater control over water content, versatile for small jobs |
| Disadvantages | Heavier equipment, less flexible water control | Potential for material clogging, more rebound waste |
Introduction to Shotcrete and Gunite
Shotcrete and Gunite are advanced methods of applying concrete that use high-pressure spraying to deliver material, enhancing strength and durability. Shotcrete involves pneumatically projecting a dry or wet mix, while Gunite specifically refers to the dry-mix process where water is added at the nozzle for application. Understanding these techniques helps you select the best option for projects requiring rapid setting and superior adhesion in construction or repair work.
Understanding the Key Differences
Shotcrete and Gunite are both methods of applying concrete pneumatically, but Shotcrete uses a wet mix sprayed through a hose while Gunite uses a dry mix that is combined with water at the nozzle. Shotcrete offers faster application and better control over moisture content, making it ideal for large-scale projects, whereas Gunite provides greater flexibility and is often preferred for smaller or more intricate tasks. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate technique based on project size, application speed, and desired material consistency.
Material Composition and Preparation
Shotcrete consists of pre-mixed concrete combined with water at the nozzle during spraying, using a ready-mix concrete mixture with selected aggregates and admixtures for enhanced strength and workability. Gunite involves dry cement and aggregate mixed prior to application, with water added at the nozzle, allowing for precise control of water content and consistency but requiring skilled operators to ensure proper mixing. Both methods utilize cementitious binders but differ in their preparation processes, impacting material properties and application techniques in shotcrete versus gunite projects.
Application Methods: Wet-Mix vs Dry-Mix
Shotcrete uses a wet-mix method where concrete is premixed with water before being sprayed through a hose at high velocity, allowing for consistent moisture control and better adhesion on surfaces. Gunite employs a dry-mix process where dry cement and aggregate are blown through a hose and water is added at the nozzle, enabling greater control over water content and reducing waste in complex applications. Both techniques are widely used in construction and repair projects, but the choice depends on factors like portability, curing time, and site conditions.
Structural Strength and Durability
Shotcrete and gunite both offer exceptional structural strength and durability, with shotcrete typically applied using a wet-mix method that ensures a more consistent concrete mixture, enhancing compressive strength. Gunite uses a dry-mix process, which can lead to slight variations in material density but provides excellent adhesion and flexibility for complex structures. Both methods achieve high durability in applications such as retaining walls, tunnels, and pools, but shotcrete often has an edge in uniformity and long-term performance due to controlled water content.
Surface Finish Quality
Shotcrete provides a smoother and more uniform surface finish compared to gunite due to its wet-mix application, which allows better control and compaction. Gunite's dry-mix method often results in a rougher texture with more variability in surface consistency. For Your project, choosing shotcrete can enhance aesthetic appeal and reduce finishing work.
Typical Uses in Construction Projects
Shotcrete is commonly used for structural reinforcement in tunnels, retaining walls, and swimming pools due to its high compressive strength and fast application. Gunite, often applied in curved or complex surfaces such as pool shells and architectural features, offers superior adaptability with dry-mix consistency allowing precise control in intricate projects. Both materials provide effective solutions for slope stabilization and repair work with varying moisture control methods suited to project-specific requirements.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Shotcrete typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its wet-mix process, which requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, making it ideal for projects with larger volumes or complex structural needs. Gunite, utilizing a dry-mix sprayed application, generally offers cost savings on smaller projects or repair jobs because of reduced material wastage and lower equipment expenses. Budget considerations should factor in project scale, labor expertise, and long-term durability, with shotcrete often favored for commercial and large-scale applications while gunite suits residential or patching work.
Maintenance and Longevity
Shotcrete offers superior durability and requires less maintenance due to its higher compressive strength and dense application method, which reduces the risk of cracks and water infiltration. Gunite, while versatile and cost-effective, often demands more frequent repairs and surface treatments to prevent deterioration over time. Proper curing and sealing are essential for both materials to maximize longevity and maintain structural integrity.
Which is Best: Shotcrete or Gunite?
Shotcrete and Gunite each offer distinct advantages depending on your construction needs, with Shotcrete typically preferred for its higher compressive strength achieved through pumped wet concrete, ensuring faster application and superior durability. Gunite uses dry-mix sprayed material requiring water at the nozzle, offering better control in intricate projects but often results in longer curing times. Your choice relies on project scale, complexity, surface contour, and speed requirements, with Shotcrete favored for large-scale, load-bearing structures and Gunite ideal for detailed, smaller applications.
Shotcrete vs Gunite Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com