Network-centric warfare leverages interconnected systems and real-time data sharing to enhance situational awareness, decision-making, and operational effectiveness across different units. In contrast, platform-centric warfare focuses on the individual capabilities and strengths of specific machines or units, often limiting coordination and information flow compared to a network-centric approach.
Table of Comparison
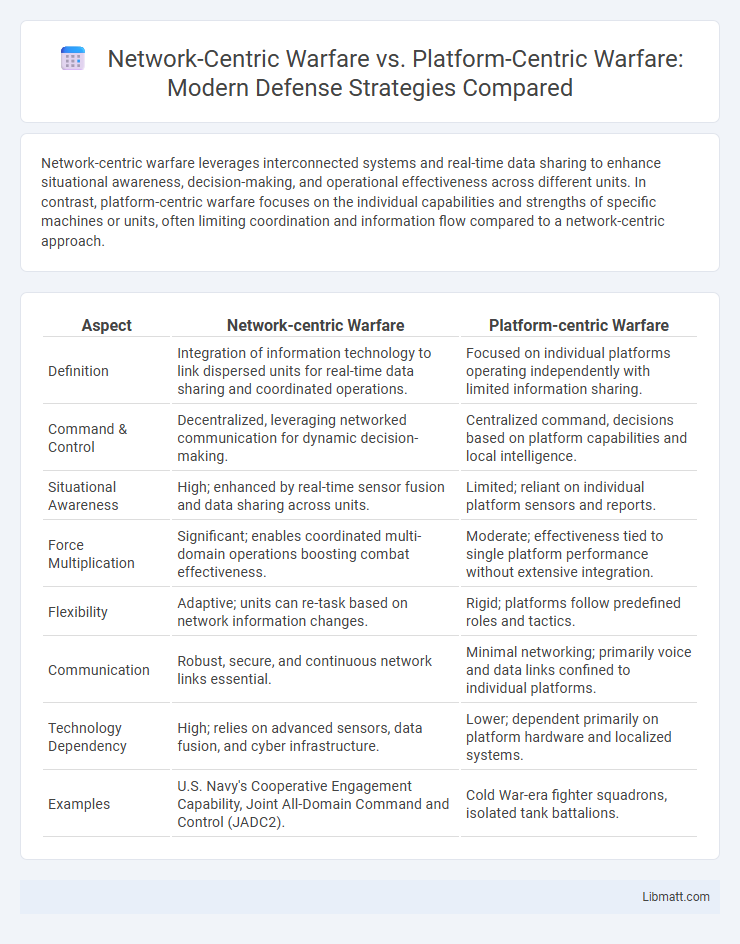
| Aspect | Network-centric Warfare | Platform-centric Warfare |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of information technology to link dispersed units for real-time data sharing and coordinated operations. | Focused on individual platforms operating independently with limited information sharing. |
| Command & Control | Decentralized, leveraging networked communication for dynamic decision-making. | Centralized command, decisions based on platform capabilities and local intelligence. |
| Situational Awareness | High; enhanced by real-time sensor fusion and data sharing across units. | Limited; reliant on individual platform sensors and reports. |
| Force Multiplication | Significant; enables coordinated multi-domain operations boosting combat effectiveness. | Moderate; effectiveness tied to single platform performance without extensive integration. |
| Flexibility | Adaptive; units can re-task based on network information changes. | Rigid; platforms follow predefined roles and tactics. |
| Communication | Robust, secure, and continuous network links essential. | Minimal networking; primarily voice and data links confined to individual platforms. |
| Technology Dependency | High; relies on advanced sensors, data fusion, and cyber infrastructure. | Lower; dependent primarily on platform hardware and localized systems. |
| Examples | U.S. Navy's Cooperative Engagement Capability, Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2). | Cold War-era fighter squadrons, isolated tank battalions. |
Introduction to Network-Centric and Platform-Centric Warfare
Network-centric warfare leverages advanced information technologies to connect various military units, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making speed. Platform-centric warfare centers on individual combat systems operating independently, relying primarily on the capabilities of each platform rather than integrated networked coordination. Understanding the shift from platform-centric to network-centric strategies highlights how your forces can achieve greater operational effectiveness through real-time data sharing and collaborative engagement.
Historical Evolution of Warfare Concepts
Network-centric warfare evolved from the limitations of platform-centric warfare, which focused on individual military assets operating independently during the Cold War era. The shift toward network-centric warfare began in the late 20th century with the advent of advanced communications and information technologies, enabling real-time data sharing and coordinated operations across multiple platforms. This evolution transformed battlefield dynamics by prioritizing information superiority and collaborative force integration over isolated platform capabilities.
Core Principles of Platform-Centric Warfare
Platform-centric warfare emphasizes individual combat platforms such as tanks, ships, and aircraft as independent units designed for specific missions with centralized command and control. Key principles include robust platform survivability, firepower concentrated within each unit, and compartmentalized operations that limit real-time information sharing across units. This approach prioritizes the technical superiority and self-sufficiency of each platform over integrated networked collaboration.
Key Features of Network-Centric Warfare
Network-centric warfare integrates real-time data sharing across multiple platforms, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making speed through interconnected sensors and communication systems. It relies on decentralized command structures and collaborative engagement, allowing your forces to operate cohesively in dynamic combat environments. This approach contrasts platform-centric warfare, which emphasizes individual systems operating in isolation with limited information flow.
Comparative Analysis: Communication and Data Integration
Network-centric warfare enhances communication and data integration by enabling real-time information sharing across multiple units through advanced satellite links, secure networks, and interoperable systems. Platform-centric warfare relies primarily on isolated communication channels, limiting data exchange to individual platforms and reducing overall situational awareness. Your operational effectiveness increases significantly with network-centric approaches that synchronize intelligence, surveillance, and command capabilities for coordinated, adaptive decision-making.
Impact on Battlefield Effectiveness
Network-centric warfare enhances battlefield effectiveness by integrating real-time data sharing among multiple units, leading to improved situational awareness and faster decision-making. Platform-centric warfare relies heavily on individual platforms' capabilities, often resulting in isolated operations with limited coordination. Your ability to leverage network-centric systems can significantly increase operational efficiency and tactical superiority in complex combat environments.
Technological Requirements and Infrastructure
Network-centric warfare demands advanced communication systems, real-time data sharing platforms, and robust cyber infrastructure to enable seamless information exchange among dispersed units. Platform-centric warfare relies heavily on individual weapon platforms equipped with specialized sensors and weapons, requiring less integrated communication networks but more sophisticated standalone technology. Your military operations benefit from evaluating these technological requirements to determine whether a highly interconnected network or focused platform capabilities better suit mission objectives.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Network-centric warfare faces challenges such as vulnerability to cyber-attacks, dependency on reliable communication infrastructure, and complexities in real-time data integration across diverse systems. Platform-centric warfare struggles with limited situational awareness, slower decision-making processes, and higher risks of isolated operational failures due to lack of interconnectedness. Both approaches encounter limitations in scalability, adaptability to evolving threats, and balancing technological investments with tactical effectiveness.
Case Studies and Real-World Implementations
Network-centric warfare demonstrates superior battlefield coordination and situational awareness, exemplified by the U.S. military's implementation during Operation Iraqi Freedom, where data-sharing across sensors, command centers, and units enhanced decision-making speed and precision strikes. In contrast, platform-centric warfare, as observed in traditional Cold War-era conflicts, relied heavily on isolated, individually operated military assets such as standalone tanks and fighter jets, often resulting in slower communication and less adaptive responses. The effectiveness of network-centric approaches is further validated in joint NATO exercises, where integrated digital networks facilitated real-time adaptation and interoperability across multinational forces.
Future Trends in Military Strategy and Warfare
Future trends in military strategy emphasize the transition from platform-centric warfare, where individual weapon systems operate independently, to network-centric warfare that integrates sensors, communication systems, and weapons into a cohesive information network. This shift enhances situational awareness, decision-making speed, and force efficiency by leveraging real-time data sharing and collaborative targeting across multiple platforms. Advances in artificial intelligence, cyber warfare, and autonomous systems are key drivers accelerating the adoption of network-centric operations in modern and future battlefields.
Network-centric warfare vs Platform-centric warfare Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com