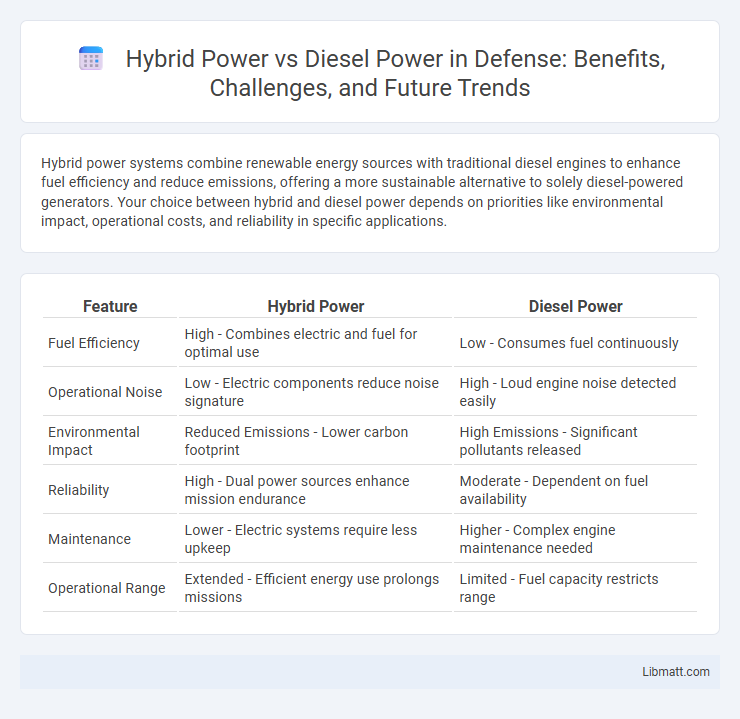
Hybrid power systems combine renewable energy sources with traditional diesel engines to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, offering a more sustainable alternative to solely diesel-powered generators. Your choice between hybrid and diesel power depends on priorities like environmental impact, operational costs, and reliability in specific applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hybrid Power | Diesel Power |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | High - Combines electric and fuel for optimal use | Low - Consumes fuel continuously |
| Operational Noise | Low - Electric components reduce noise signature | High - Loud engine noise detected easily |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced Emissions - Lower carbon footprint | High Emissions - Significant pollutants released |
| Reliability | High - Dual power sources enhance mission endurance | Moderate - Dependent on fuel availability |
| Maintenance | Lower - Electric systems require less upkeep | Higher - Complex engine maintenance needed |
| Operational Range | Extended - Efficient energy use prolongs missions | Limited - Fuel capacity restricts range |
Introduction to Hybrid Power and Diesel Power
Hybrid power systems combine renewable energy sources like solar or wind with conventional diesel generators to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Diesel power relies solely on combustion engines fueled by diesel, known for reliability and high energy density but with higher greenhouse gas emissions. Hybrid power solutions offer enhanced sustainability by integrating battery storage and smart controls, lowering operational costs compared to traditional diesel-only setups.
How Hybrid Power Systems Work
Hybrid power systems combine internal combustion engines with electric motors, using energy from fuel and stored batteries to optimize efficiency. These systems capture energy during braking and convert it into electrical power, which recharges the batteries and reduces fuel consumption. Advanced control units manage the power flow, ensuring seamless transitions between diesel and electric modes for enhanced performance and lower emissions.
Diesel Power: Mechanism and Applications
Diesel power operates through internal combustion engines that ignite diesel fuel to generate mechanical energy, powering generators, vehicles, and heavy machinery with high torque and fuel efficiency. Its widespread applications include shipping, construction equipment, and backup power systems where reliability and long-running operation are critical. Understanding your energy needs is essential to determine if diesel power's robustness and fuel availability align better than hybrid systems for your specific use case.
Environmental Impact: Hybrid vs Diesel
Hybrid power systems significantly reduce environmental impact compared to diesel power by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing fuel consumption. Diesel engines emit higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and health hazards. Your choice of hybrid technology supports cleaner air quality and aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Hybrid power systems significantly outperform diesel power in fuel efficiency by combining an internal combustion engine with electric motors to optimize energy use and reduce fuel consumption. Diesel engines rely solely on combustion, leading to higher fuel use and emissions, especially under varying load conditions. Your choice of hybrid power can result in substantial fuel savings and lower operational costs compared to traditional diesel power solutions.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Hybrid power systems typically incur a higher initial investment compared to diesel power due to advanced technology and battery components. Long-term savings arise from lower fuel consumption and reduced maintenance expenses, with hybrid systems offering up to 40% savings on operational costs over 10 years. Diesel power systems have lower upfront costs but face rising fuel prices and higher emissions-related expenses, making hybrids more cost-efficient in the long run.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Hybrid power systems typically require less frequent maintenance than diesel power units due to fewer mechanical parts subject to wear and the inclusion of advanced electronic controls that optimize engine performance. Diesel power generators demand regular oil changes, filter replacements, and fuel system checks to maintain efficiency and prevent breakdowns, which can increase long-term maintenance costs. The longevity of hybrid systems is often enhanced by reduced engine strain and optimized operating conditions, while diesel engines have a well-established lifespan contingent on rigorous maintenance schedules and operating practices.
Performance and Reliability in Real-World Use
Hybrid power systems offer superior fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to traditional diesel power, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance with environmental considerations. Diesel engines provide robust reliability and high torque output, maintaining steady power delivery in harsh conditions and heavy-duty real-world use. Hybrid configurations enhance operational flexibility by combining electric motors with diesel engines, reducing fuel consumption while ensuring dependable performance in diverse environments.
Regulatory Trends and Market Adoption
Hybrid power systems align with increasing regulatory trends targeting carbon emission reductions and fuel consumption limits in transportation and industrial sectors. Governments worldwide, including the European Union and California Air Resources Board, implement stricter emissions standards favoring hybrid technology adoption over traditional diesel engines. Market adoption reflects these policies as fleets and manufacturers invest in hybrid solutions to comply with regulations, optimize operational costs, and reduce environmental impact.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Power Solutions
Hybrid power systems, integrating renewable energy sources with battery storage, are projected to dominate future energy landscapes due to increasing environmental regulations and cost efficiencies. Diesel power, while reliable for current high-demand applications, faces declining adoption as stricter emission standards and fuel expenses rise. Your investment in hybrid technology aligns with the global transition towards sustainable and resilient power solutions.
hybrid power vs diesel power Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com