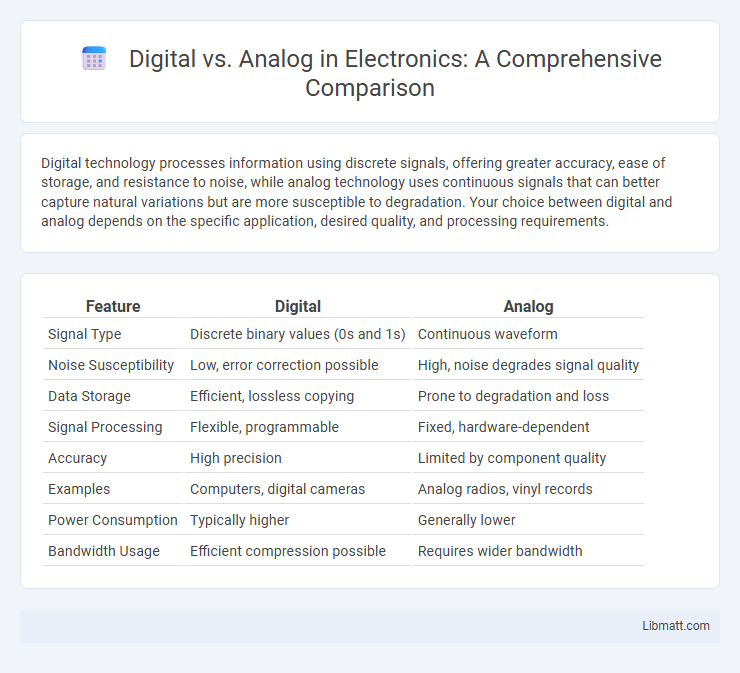
Digital technology processes information using discrete signals, offering greater accuracy, ease of storage, and resistance to noise, while analog technology uses continuous signals that can better capture natural variations but are more susceptible to degradation. Your choice between digital and analog depends on the specific application, desired quality, and processing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital | Analog |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Discrete binary values (0s and 1s) | Continuous waveform |
| Noise Susceptibility | Low, error correction possible | High, noise degrades signal quality |
| Data Storage | Efficient, lossless copying | Prone to degradation and loss |
| Signal Processing | Flexible, programmable | Fixed, hardware-dependent |
| Accuracy | High precision | Limited by component quality |
| Examples | Computers, digital cameras | Analog radios, vinyl records |
| Power Consumption | Typically higher | Generally lower |
| Bandwidth Usage | Efficient compression possible | Requires wider bandwidth |
Introduction to Digital vs Analog
Digital systems process information using discrete binary codes, enabling high precision and noise resistance in data transmission and storage. Analog systems represent data through continuous signals, closely mirroring real-world phenomena but are more susceptible to distortion and degradation. Understanding the fundamental differences between digital and analog technologies is crucial for applications in electronics, communication, and signal processing.
Defining Digital and Analog Systems
Digital systems process information using discrete signals, representing data in binary format (0s and 1s) to enable precise computation and error correction. Analog systems handle continuous signals that vary smoothly over time, directly correlating to physical quantities like sound, light, or temperature. The fundamental difference lies in the representation and manipulation of data, where digital systems offer robustness and scalability, while analog systems provide real-time processing of natural phenomena.
Key Differences Between Digital and Analog
Digital signals use discrete values for data representation, offering higher precision and noise resistance compared to analog's continuous signal variations. Analog signals vary smoothly over time, reflecting real-world phenomena but are more susceptible to distortion and signal degradation. Your choice between digital and analog impacts system performance, with digital preferred for accuracy and analog favored for natural signal replication.
Examples of Digital Technologies
Digital technologies include devices such as smartphones, computers, digital cameras, and streaming services that operate using binary code to process and transmit information efficiently. These technologies enable data encryption, cloud computing, and real-time communication, providing greater accuracy and flexibility compared to analog systems. Your interaction with digital voice assistants, social media platforms, and online banking exemplifies the widespread adoption of digital technology in everyday life.
Examples of Analog Technologies
Analog technologies include devices such as vinyl record players, which use continuous waveforms to reproduce sound, and traditional television sets that receive analog broadcast signals. Analog clocks with moving hands, film cameras capturing images on chemical film, and landline telephones employing continuous electrical signals also exemplify analog systems. These technologies rely on continuous data representation, contrasting with the discrete states found in digital systems.
Advantages of Digital Technology
Digital technology offers higher precision and consistency compared to analog systems due to its ability to represent data in binary format, reducing noise and signal degradation. It enables easier storage, replication, and transmission of information without quality loss, enhancing efficiency in communication and computing. Your devices benefit from faster processing speeds and improved compatibility with modern software, driving innovation and user-friendly experiences.
Benefits of Analog Systems
Analog systems offer continuous signal processing, providing higher fidelity and natural representation of audio and visual information compared to digital systems. These systems excel in real-time applications, minimizing latency and preserving waveform integrity, which is crucial in audio engineering and instrumentation. Their simplicity and robustness also result in lower power consumption and easier troubleshooting in environments with electromagnetic interference.
Limitations of Both Technologies
Digital technology faces limitations such as limited resolution due to discrete sampling rates and potential data loss during conversion, while analog systems suffer from signal degradation, noise interference, and lower precision over long distances. Both technologies require careful consideration of bandwidth and fidelity constraints to optimize performance. Hybrid systems often emerge to leverage digital accuracy with analog's continuous signal advantages.
Current Applications in Various Industries
Digital technology dominates telecommunications, enabling fast data transmission and real-time communication in industries like finance and healthcare. Analog systems remain relevant in audio production and broadcasting for their warmth and sound quality. Manufacturing leverages digital sensors for precision, while analog gauges persist in legacy equipment for simple, reliable readings.
The Future of Digital and Analog Technologies
Digital technologies are rapidly advancing with innovations like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 5G networks driving unprecedented connectivity and data processing capabilities. Analog systems, known for their simplicity and reliability, continue to hold relevance in niche applications such as audio equipment, sensors, and certain medical devices where signal fidelity and continuous data representation are crucial. Your choice between digital and analog will depend on specific requirements, balancing the precision and scalability of digital with the nuanced performance of analog technologies.
Digital vs Analog Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com