FIFO memory operates on a first-in, first-out basis, ensuring data is processed in the exact order it was received, which is ideal for buffering and queue management. LIFO memory, or stack memory, retrieves the most recently stored data first, making it suitable for tasks requiring reverse-order processing such as function calls and recursion.
Table of Comparison
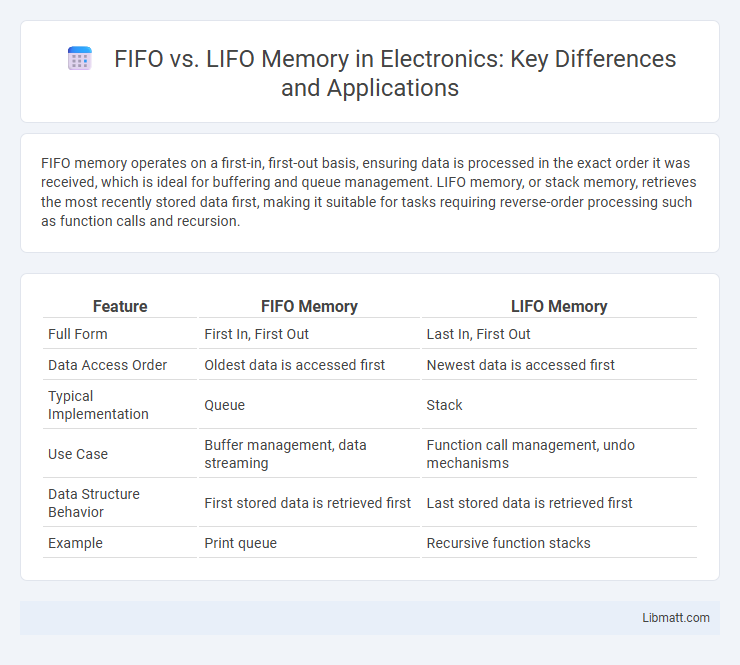
| Feature | FIFO Memory | LIFO Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | First In, First Out | Last In, First Out |
| Data Access Order | Oldest data is accessed first | Newest data is accessed first |
| Typical Implementation | Queue | Stack |
| Use Case | Buffer management, data streaming | Function call management, undo mechanisms |
| Data Structure Behavior | First stored data is retrieved first | Last stored data is retrieved first |
| Example | Print queue | Recursive function stacks |
Introduction to Memory Management Techniques
FIFO and LIFO are fundamental memory management techniques used to organize data storage and retrieval effectively. FIFO (First-In-First-Out) manages memory by removing the oldest data first, ensuring that the earliest stored information is accessed prior to newer entries. LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) prioritizes the most recent data, making it ideal for scenarios where recent information requires immediate attention, directly influencing your system's efficiency and performance.
Understanding FIFO (First-In, First-Out) Memory
FIFO (First-In, First-Out) memory operates by processing data in the exact order it was received, ensuring the earliest input is output first, which is crucial for applications requiring sequential data handling like buffers and queues. This memory type is implemented using shift registers or circular buffers to maintain data integrity and timing consistency. Understanding FIFO helps you optimize system performance by selecting the appropriate memory management method for data flow control and latency reduction.
Exploring LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) Memory
LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) memory operates by accessing the most recently stored data first, making it ideal for scenarios such as function call management and recursive algorithms. This stack-based memory structure ensures efficient temporary data storage, facilitating quick retrieval and reducing overhead in program execution. Understanding LIFO can optimize your application's performance by leveraging its principle for controlled data flow and memory usage.
Key Differences Between FIFO and LIFO
FIFO (First-In, First-Out) memory processes data in the order it was received, ensuring that the earliest input is accessed first, which is ideal for queue management and buffering applications. LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) memory retrieves the most recent data first, making it suitable for stack-based operations like function call management and undo mechanisms. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the optimal memory structure for your application's data handling and retrieval needs.
Use Cases for FIFO Memory Management
FIFO memory management excels in scenarios requiring orderly processing, such as task scheduling, buffering data streams, and handling printer queues where the first request must be serviced first. It is ideal for managing resources in real-time systems, network packet processing, and situations where data integrity depends on strict chronological order. FIFO ensures predictable performance by maintaining a clear sequence, reducing complexity in applications like cache management and inter-process communication.
Use Cases for LIFO Memory Management
LIFO memory management is widely used in function call stacks where the most recent function call must be completed before returning to the previous state. It is ideal for managing temporary data storage during recursive programming and expression evaluation in compilers. The stack structure of LIFO memory allows efficient handling of nested function calls and local variable allocation.
Performance Comparison: FIFO vs LIFO
FIFO memory management processes data by accessing the oldest stored elements first, ensuring predictable and fair performance at the cost of potential delays in retrieving recent data. LIFO memory management, on the other hand, accesses the most recently stored data immediately, which often results in faster data retrieval and better cache performance for your applications. Choosing between FIFO and LIFO directly affects your system's efficiency, with LIFO typically delivering superior speed in scenarios requiring quick access to the latest information.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FIFO
FIFO (First In, First Out) memory ensures data is accessed in the order it was stored, providing predictable and straightforward data management ideal for buffering and queue operations. Its advantages include simplicity, fast access times for sequential data processing, and prevention of data starvation. However, FIFO may lead to inefficiencies in scenarios requiring quick access to the most recent data, as older entries must be accessed first, potentially causing increased latency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LIFO
LIFO memory, or Last-In-First-Out, provides advantages such as efficient management of temporary data and function call stacks, enabling quick access to the most recently stored information which is crucial in recursive algorithms and interrupt handling. However, LIFO's disadvantages include potential difficulties in accessing older data since only the last stored item can be retrieved first, which may lead to inefficiencies in applications requiring random access or processing of long sequences. Moreover, improper use of LIFO can cause stack overflow errors if memory allocation exceeds limits, impacting system stability.
Choosing the Right Memory Management Approach
Choosing the right memory management approach depends on the specific application requirements for data processing speed and resource efficiency. FIFO (First-In, First-Out) memory is ideal for scenarios needing chronological data handling, such as buffering streaming data or task scheduling, ensuring orderly data retrieval. LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) memory is better suited for recursive algorithms or undo mechanisms where the most recently added data must be accessed first, optimizing stack operations and temporary storage management.
FIFO vs LIFO Memory Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com