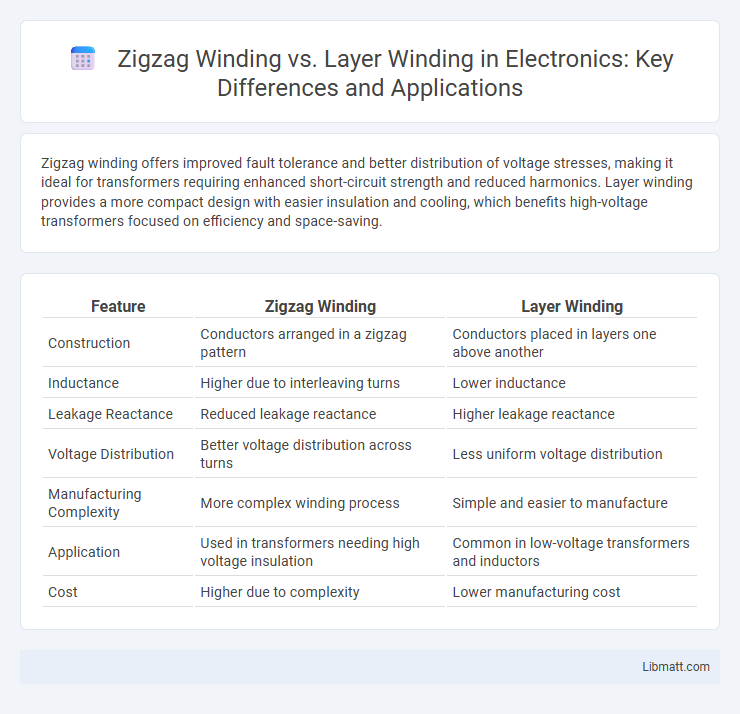
Zigzag winding offers improved fault tolerance and better distribution of voltage stresses, making it ideal for transformers requiring enhanced short-circuit strength and reduced harmonics. Layer winding provides a more compact design with easier insulation and cooling, which benefits high-voltage transformers focused on efficiency and space-saving.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zigzag Winding | Layer Winding |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Conductors arranged in a zigzag pattern | Conductors placed in layers one above another |
| Inductance | Higher due to interleaving turns | Lower inductance |
| Leakage Reactance | Reduced leakage reactance | Higher leakage reactance |
| Voltage Distribution | Better voltage distribution across turns | Less uniform voltage distribution |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex winding process | Simple and easier to manufacture |
| Application | Used in transformers needing high voltage insulation | Common in low-voltage transformers and inductors |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower manufacturing cost |
Introduction to Transformer Winding Techniques
Transformer winding techniques, including Zigzag and Layer Winding, play crucial roles in electrical engineering by influencing transformer performance and efficiency. Zigzag winding provides excellent harmonic reduction and fault tolerance by connecting windings in a zigzag pattern, while Layer Winding arranges coils in successive layers to optimize voltage distribution and minimize leakage reactance. Understanding these methods helps you select the appropriate winding design that meets specific transformer requirements and operational conditions.
What is Zigzag Winding?
Zigzag winding is a transformer winding technique where conductor segments are connected in a zigzag pattern across multiple limbs, enhancing phase shifting and reducing harmonics. This winding type is used in earthing transformers and helps improve grounding by providing neutral points in three-phase systems. Zigzag winding offers better fault current distribution and superior harmonic suppression compared to standard layer winding, making it ideal for power system stability and noise reduction.
What is Layer Winding?
Layer winding is a method used in electrical coil construction where wire is wound in consecutive, flat layers directly on top of each other, creating a uniform and compact coil structure. This technique enhances magnetic efficiency and reduces leakage inductance, making it ideal for transformers and inductors requiring precise voltage regulation. Your choice of layer winding impacts thermal management and insulation, crucial for optimizing coil performance in various electrical applications.
Structural Differences Between Zigzag and Layer Winding
Zigzag winding consists of coil groups connected in a zigzag pattern, increasing the number of parallel paths and improving short-circuit current capacity, whereas layer winding involves consecutive coil turns placed side by side in distinct layers, optimizing voltage distribution and reducing insulation stress. The structural arrangement of zigzag winding results in a more complex coil geometry with increased mutual inductance, while layer winding features simpler, uniform coil sections aligned to facilitate better heat dissipation. Zigzag windings are typically used in high-power transformers for enhanced thermal and electrical performance, whereas layer windings are preferred in precision applications requiring reduced leakage inductance and uniform distribution of the magnetic field.
Electrical Performance: Zigzag Winding vs Layer Winding
Zigzag winding offers improved fault tolerance and better handling of unbalanced loads due to its unique phase displacement and interconnection, enhancing overall electrical performance in transformers. Layer winding provides lower leakage reactance and higher voltage withstand capability, leading to efficient energy transfer in high-voltage applications. Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs for voltage stability and fault resilience in electrical systems.
Advantages of Zigzag Winding
Zigzag winding offers superior short-circuit current capacity and excellent current distribution, enhancing transformer reliability and performance. Its design reduces leakage reactance and improves voltage regulation, making it suitable for applications requiring robust fault tolerance. You benefit from increased mechanical strength and better thermal management compared to traditional layer winding.
Advantages of Layer Winding
Layer winding offers improved insulation and better heat dissipation compared to zigzag winding, enhancing the overall efficiency of electrical machines. Its uniform coil distribution minimizes leakage inductance and voltage stress, leading to increased reliability and longer lifespan of transformers and motors. You benefit from easier manufacturing and maintenance processes due to the straightforward coil arrangement in layer winding designs.
Applications of Zigzag and Layer Winding
Zigzag winding is commonly used in transformers for high-frequency applications and distribution transformers, where better magnetic flux distribution and fault tolerance are essential. Layer winding is preferred in power transformers and large electrical machines due to its efficient insulation and superior heat dissipation properties. You can optimize your transformer design by selecting zigzag winding for improved fault handling or layer winding for enhanced thermal performance.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Winding Type
Factors influencing the choice between zigzag winding and layer winding include voltage level, application requirements, and space constraints. Zigzag winding is favored for applications demanding better harmonic suppression and fault tolerance, while layer winding provides improved insulation and easier manufacturing for high voltage transformers. Your selection depends on balancing electrical performance, thermal management, and mechanical stability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Winding Method
Choosing between zigzag winding and layer winding depends on the specific application and performance requirements of electrical transformers. Zigzag winding offers superior grounding and harmonic mitigation, making it ideal for power distribution systems with unbalanced loads. Layer winding provides better insulation and simpler construction, preferred for high-voltage transformers requiring reliable voltage regulation and mechanical stability.
Zigzag Winding vs Layer Winding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com