Board-to-board connectors provide a direct electrical connection between two printed circuit boards, enabling high-density signal transfer and compact device design. Wire-to-board connectors link wires to PCBs, offering flexible wiring options for external components or power sources, making your system easier to assemble and maintain.
Table of Comparison
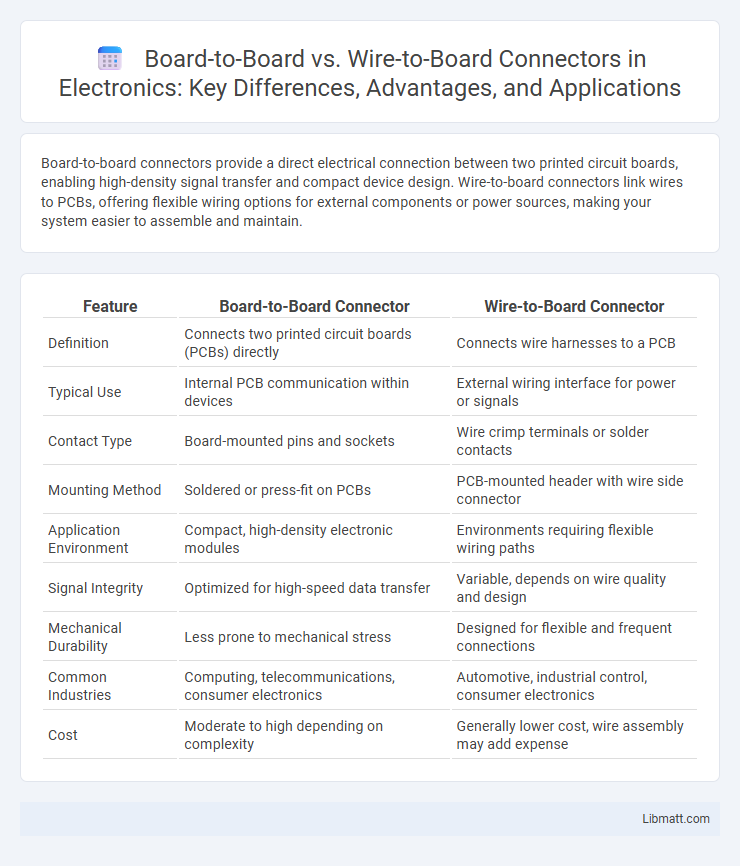
| Feature | Board-to-Board Connector | Wire-to-Board Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connects two printed circuit boards (PCBs) directly | Connects wire harnesses to a PCB |
| Typical Use | Internal PCB communication within devices | External wiring interface for power or signals |
| Contact Type | Board-mounted pins and sockets | Wire crimp terminals or solder contacts |
| Mounting Method | Soldered or press-fit on PCBs | PCB-mounted header with wire side connector |
| Application Environment | Compact, high-density electronic modules | Environments requiring flexible wiring paths |
| Signal Integrity | Optimized for high-speed data transfer | Variable, depends on wire quality and design |
| Mechanical Durability | Less prone to mechanical stress | Designed for flexible and frequent connections |
| Common Industries | Computing, telecommunications, consumer electronics | Automotive, industrial control, consumer electronics |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on complexity | Generally lower cost, wire assembly may add expense |
Introduction to Board-to-Board and Wire-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors electrically link two printed circuit boards (PCBs) directly, enabling compact and reliable communication between multiple PCB assemblies within electronic devices. Wire-to-board connectors facilitate the connection of individual wires or cables to a PCB, providing secure and easy-to-install interfaces for external power or signal input. Understanding the differences in design and application helps you select the most efficient connector type for your specific electronic system requirements.
Key Differences Between Board-to-Board and Wire-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors provide direct electrical connections between two printed circuit boards, enabling compact and reliable inter-board communication with consistent signal integrity. Wire-to-board connectors, on the other hand, facilitate connections between a wire harness and a PCB, offering flexibility in routing and ease of assembly in diverse electronic applications. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right connector type based on design requirements, space constraints, and electrical performance needs.
Common Applications of Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors are commonly used in applications requiring compact, high-density connections such as computer motherboards, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics. They facilitate direct, perpendicular or parallel connections between two printed circuit boards, enhancing signal integrity and reducing space. Your device's reliable performance often depends on selecting the appropriate board-to-board connector tailored to specific power, signal, and environmental requirements.
Typical Uses for Wire-to-Board Connectors
Wire-to-board connectors are commonly used in electronic devices to link individual wires directly to a printed circuit board (PCB), facilitating secure electrical connections in compact spaces. They are prevalent in consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial equipment, and household appliances, where reliable signal and power transmission are critical. These connectors simplify assembly and maintenance by enabling quick disconnects and ensuring stable contact in diverse environmental conditions.
Mechanical and Electrical Considerations
Board-to-board connectors offer high-density interconnections with precise mechanical alignment and enhanced signal integrity, optimal for compact electronic assemblies requiring multi-layer PCB stacking. Wire-to-board connectors provide flexibility in wiring configurations, designed to withstand mechanical stress and vibration, ensuring secure electrical connections with varied current and voltage ratings. Both connector types require careful evaluation of contact resistance, mating cycles, and environmental durability to maintain reliable performance in their respective applications.
Space Efficiency and Design Flexibility
Board-to-board connectors offer superior space efficiency by enabling direct PCB stacking, which minimizes signal path length and reduces overall device footprint. Wire-to-board connectors provide greater design flexibility through customizable wiring harnesses that accommodate varied routing and external component integration. Selecting between these connectors involves balancing compact PCB layout needs against adaptable system configuration requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Board-to-board connectors offer streamlined installation with precise alignment features that reduce the risk of damage during mating, enabling easier maintenance through quick disconnect capabilities. Wire-to-board connectors require careful wire termination and secure fastening to ensure stable electrical connections, often involving additional tools or soldering for installation and maintenance. The simplified mechanical process of board-to-board connectors generally results in lower maintenance efforts compared to the more involved procedures needed for wire-to-board connector upkeep.
Signal Integrity and Performance Comparison
Board-to-board connectors provide superior signal integrity by minimizing impedance discontinuities and crosstalk through direct mating interfaces, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission in compact electronic assemblies. Wire-to-board connectors can introduce additional signal loss and noise due to wire harnesses and solder joints, potentially degrading performance in sensitive signal applications. Optimizing connector geometry and contact materials in board-to-board systems enhances performance stability across varying frequencies compared to wire-to-board alternatives.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Board-to-board connectors typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to simpler assembly processes and fewer components, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects. Wire-to-board connectors often incur higher expenses because of the added labor and materials required for wire harnessing and assembly, impacting your overall budget. Evaluating these cost implications helps optimize your design while maintaining financial efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Connector for Your Project
Choosing the right connector for your project depends on factors such as space constraints, signal integrity, and assembly method. Board-to-board connectors are ideal for compact designs requiring high-density connections and precise alignment between PCBs. Wire-to-board connectors are better suited for applications needing flexible wiring options and easier maintenance or replacement.
Board-to-Board vs Wire-to-Board Connector Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com