D-sub connectors offer robust, multi-pin connections ideal for legacy serial and parallel devices, while USB connectors provide faster data transfer, hot-swapping capabilities, and widespread compatibility for modern peripherals. Your choice depends on the specific device requirements and the need for speed versus durability.
Table of Comparison
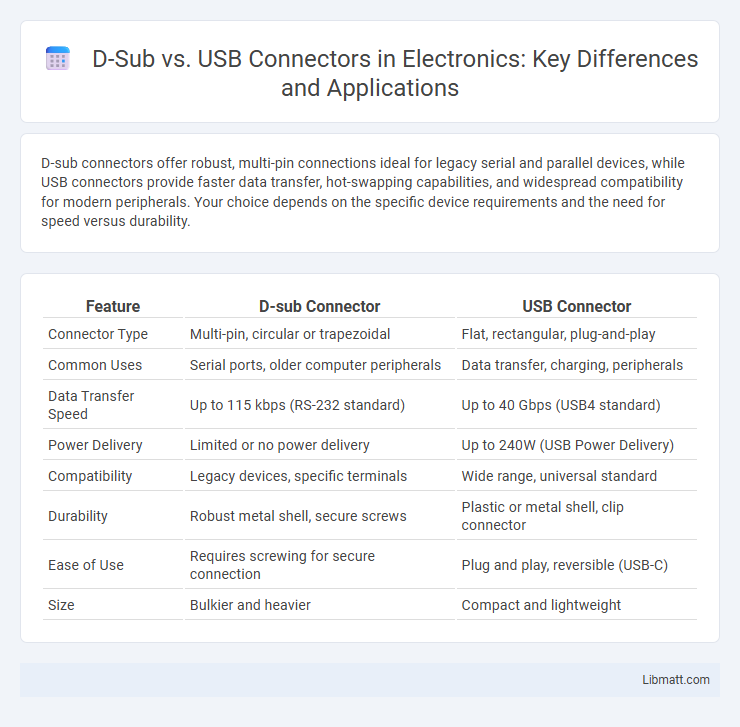
| Feature | D-sub Connector | USB Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | Multi-pin, circular or trapezoidal | Flat, rectangular, plug-and-play |
| Common Uses | Serial ports, older computer peripherals | Data transfer, charging, peripherals |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 115 kbps (RS-232 standard) | Up to 40 Gbps (USB4 standard) |
| Power Delivery | Limited or no power delivery | Up to 240W (USB Power Delivery) |
| Compatibility | Legacy devices, specific terminals | Wide range, universal standard |
| Durability | Robust metal shell, secure screws | Plastic or metal shell, clip connector |
| Ease of Use | Requires screwing for secure connection | Plug and play, reversible (USB-C) |
| Size | Bulkier and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
Introduction to D-sub and USB Connectors
D-sub connectors feature a D-shaped metal shield and multiple pins, commonly used for serial, parallel, and VGA connections in industrial and computer applications. USB connectors offer versatile, plug-and-play connectivity with standardized protocols supporting data transfer and power delivery across devices like smartphones, peripherals, and storage devices. The evolution from D-sub to USB reflects advancements in connector design emphasizing compact size, ease of use, and higher data transfer rates.
Historical Evolution of D-sub and USB
D-sub connectors, introduced in the 1950s, became widely used for early computer and communication interfaces due to their robust metal shell and multiple-pin configurations. USB connectors emerged in the mid-1990s as a standardized, versatile solution designed to simplify peripheral connectivity with faster data transfer and plug-and-play capabilities. Your choice between D-sub and USB reflects the evolution from legacy analog and serial connections to modern digital interfaces that prioritize speed, convenience, and broad compatibility.
Physical Design and Connector Types
D-sub connectors feature a trapezoidal metal shell and multiple pins arranged in rows, designed primarily for secure, robust connections in industrial and computer interfaces. USB connectors, available in various types like Type-A, Type-B, and the compact USB-C, emphasize user-friendly, reversible designs that support hot-swapping and high data transfer rates. Your choice depends on the required durability and compatibility, with D-sub preferred for legacy or heavy-duty environments and USB dominating modern consumer electronics.
Data Transmission Capabilities
D-sub connectors typically support slower data transmission rates, suitable for RS-232 serial communication and VGA signals, while USB connectors enable high-speed data transfer, ranging from USB 2.0's 480 Mbps to USB 3.2 and USB4 standards exceeding 40 Gbps. Your choice between D-sub and USB connectors impacts the efficiency of data exchange, especially when handling large files or real-time video streaming. USB connectors offer more advanced protocols and power delivery options, making them ideal for modern digital devices requiring fast and reliable communication.
Power Supply Features
D-sub connectors primarily support low-voltage signals and are not designed to provide significant power supply capabilities, limiting their use in power-intensive applications. USB connectors offer standardized power delivery, with USB 3.0 and USB-C versions supporting up to 100W power transfer, enabling device charging and power supply simultaneously with data transfer. Your choice between these connectors depends on whether power delivery is a critical factor in your application.
Compatibility and Device Support
D-sub connectors are commonly used in legacy equipment such as older computers, industrial machines, and audio-visual devices, offering robust compatibility with established hardware standards like VGA and serial interfaces. USB connectors support a vast range of modern devices including smartphones, printers, external drives, and keyboards, providing widespread compatibility across consumer electronics and peripherals due to universal industry adoption. Your choice between D-sub and USB should consider whether you need support for older equipment or broad compatibility with contemporary digital devices.
Speed and Performance Comparison
USB connectors significantly outperform D-sub connectors in speed and data transfer rates, with USB 3.2 achieving up to 20 Gbps compared to D-sub's maximum of around 115 kbps in traditional RS-232 implementations. USB supports full-duplex communication and plug-and-play functionality enhancing overall efficiency and user experience. D-sub connectors, primarily designed for serial communication, lack the bandwidth and versatility needed for modern high-speed data applications.
Durability and Reliability
D-sub connectors are known for their robust metal shell and secure locking mechanisms, providing superior durability and reliable connections in harsh environments. USB connectors, while convenient and widely compatible, generally offer less mechanical strength and may be prone to wear and loosening over time. Your choice should consider application demands where D-sub connectors excel in industrial settings requiring long-term durability and USB connectors suit everyday consumer electronic use.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
D-sub connectors are commonly used in industrial, automotive, and communication equipment for serial and parallel data transmission, ensuring durable and secure connections in harsh environments. USB connectors dominate consumer electronics and computer peripherals, enabling fast data transfer, power delivery, and plug-and-play functionality for devices like printers, external drives, and smartphones. Your choice between D-sub and USB connectors depends on the need for legacy interface compatibility or the benefits of modern, high-speed connectivity.
Future Trends and Market Adoption
USB connectors dominate current markets due to their compact design, faster data transfer speeds, and widespread compatibility with modern devices. D-sub connectors, primarily used in legacy systems, are gradually being phased out as industries shift toward streamlined, high-performance interfaces like USB-C and Thunderbolt. Your adoption decisions should consider USB's expanding ecosystem and its alignment with future technological trends in connectivity.
D-sub vs USB connector Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com