Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, are capable of amplifying signals and controlling electrical power, making them essential for dynamic functions in electronic circuits. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors cannot generate energy but influence current and voltage by storing or dissipating electrical energy, providing stability and filtering in your circuits.
Table of Comparison
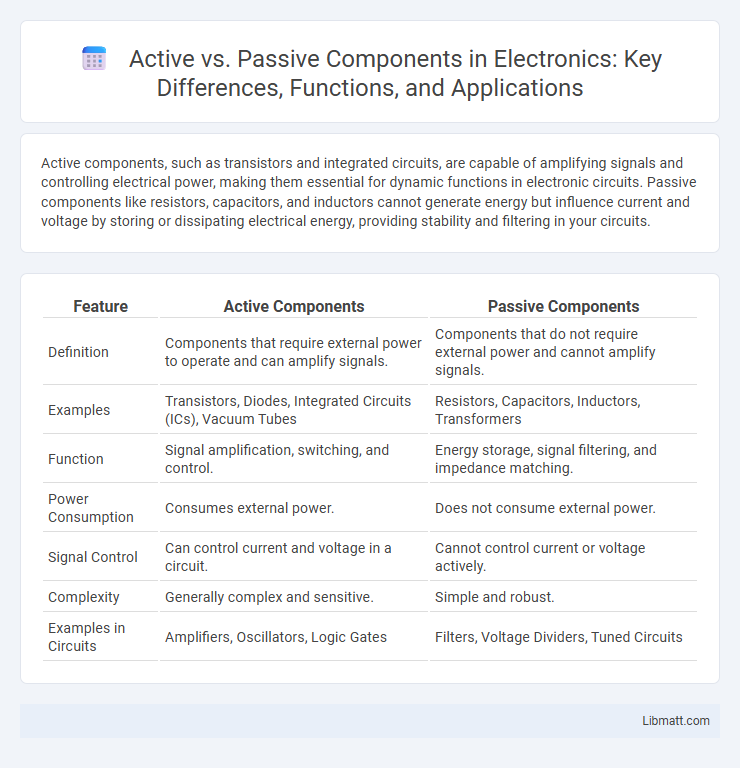
| Feature | Active Components | Passive Components |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Components that require external power to operate and can amplify signals. | Components that do not require external power and cannot amplify signals. |
| Examples | Transistors, Diodes, Integrated Circuits (ICs), Vacuum Tubes | Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors, Transformers |
| Function | Signal amplification, switching, and control. | Energy storage, signal filtering, and impedance matching. |
| Power Consumption | Consumes external power. | Does not consume external power. |
| Signal Control | Can control current and voltage in a circuit. | Cannot control current or voltage actively. |
| Complexity | Generally complex and sensitive. | Simple and robust. |
| Examples in Circuits | Amplifiers, Oscillators, Logic Gates | Filters, Voltage Dividers, Tuned Circuits |
Understanding Active and Passive Components
Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, require an external power source to control current flow and amplify signals, playing a crucial role in electronic circuits. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors do not generate energy but influence current and voltage by storing or dissipating energy. Understanding these distinctions helps you design and troubleshoot circuits effectively, ensuring optimal performance in your electronic projects.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Components
Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, require an external power source to operate and can amplify or control electrical signals. Passive components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not need power to function and primarily store or dissipate energy. Understanding these key differences helps you design efficient electronic circuits by selecting the appropriate components based on their roles and power requirements.
Common Examples of Active Components
Common examples of active components include transistors, diodes, and operational amplifiers, which are essential for amplifying signals and controlling current flow in electronic circuits. These components rely on an external power source to operate and enable functionalities such as switching, amplification, and signal modulation. Understanding how your circuits utilize these active devices is crucial for designing efficient and responsive electronic systems.
Common Examples of Passive Components
Common examples of passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which do not generate energy but instead store or dissipate it within electronic circuits. Resistors control current flow and voltage levels, capacitors store and release electrical energy, while inductors store energy in magnetic fields. These components are essential in filtering, tuning, and signal processing applications across various electronic devices.
Functions of Active Components in Circuits
Active components in circuits primarily function to amplify electrical signals, control current flow, and provide power gain essential for signal processing tasks. Devices such as transistors, integrated circuits, and vacuum tubes enable switching, modulation, and oscillation operations critical to electronic communication and computing systems. Their capability to inject energy into the circuit distinguishes them from passive components, making them indispensable for amplification and active control in modern electronics.
Roles of Passive Components in Electronics
Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors play crucial roles in electronics by controlling voltage, current, and signal flow without requiring external power. These components enable functions like filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching, ensuring circuit stability and performance. Incorporating high-quality passive components in your designs enhances overall device reliability and efficiency.
Advantages of Active Components
Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, provide amplification and signal control, enabling complex functionalities in electronic devices. They can power and regulate circuits, making them essential for creating dynamic systems like amplifiers, oscillators, and digital electronics. Your electronic designs benefit from enhanced performance and versatility when using active components.
Benefits and Limitations of Passive Components
Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors offer benefits such as reliability, simplicity, and low cost due to their lack of power sources or active devices. These components provide stable performance with minimal maintenance and do not introduce noise or distortion into circuits. However, passive components cannot amplify signals or provide power gain, limiting their function to energy storage, dissipation, or filtering in your electronic designs.
Applications of Active and Passive Components
Active components such as transistors and integrated circuits are essential in amplifiers, oscillators, and signal processing devices, enabling control and modulation of electrical signals in communication and computing systems. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors are crucial for filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching in power supplies, RF circuits, and audio equipment. Both component types are integral in designing electronic circuits for applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Project
Selecting the right component between active and passive types depends on the project's functional requirements and power needs. Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, amplify signals and require external power, making them essential for dynamic electronic functions. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors manage energy flow without power consumption, ideal for signal tuning and energy storage.
Active vs Passive Components Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com