A socket is a physical interface on a motherboard designed to hold and connect a CPU, providing power and communication pathways, while a slot refers to a connector slot that allows expansion cards like graphics or memory modules to be inserted. Understanding the difference helps you optimize your computer's upgrade possibilities based on compatibility with CPUs or expansion cards.
Table of Comparison
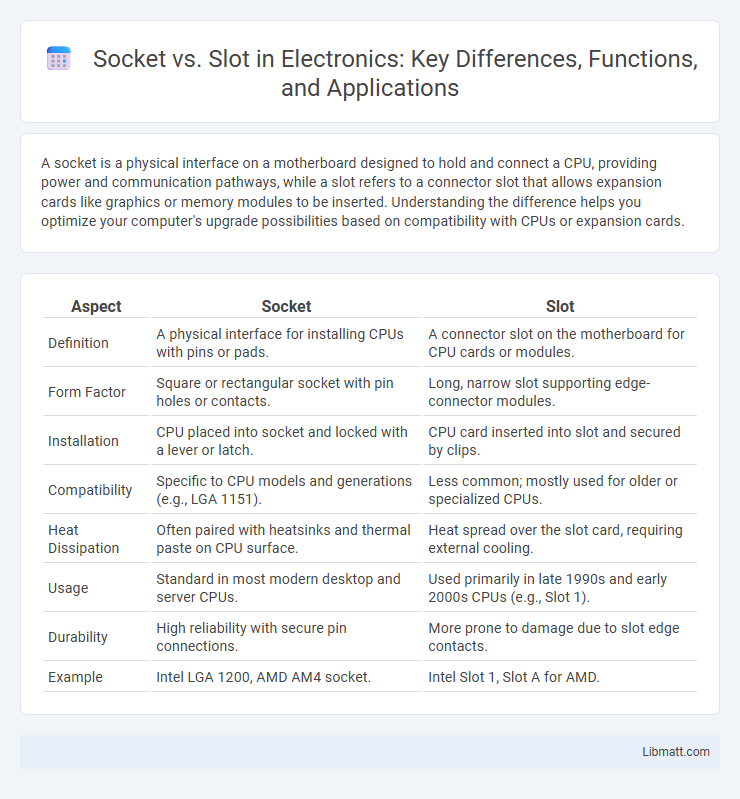
| Aspect | Socket | Slot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A physical interface for installing CPUs with pins or pads. | A connector slot on the motherboard for CPU cards or modules. |
| Form Factor | Square or rectangular socket with pin holes or contacts. | Long, narrow slot supporting edge-connector modules. |
| Installation | CPU placed into socket and locked with a lever or latch. | CPU card inserted into slot and secured by clips. |
| Compatibility | Specific to CPU models and generations (e.g., LGA 1151). | Less common; mostly used for older or specialized CPUs. |
| Heat Dissipation | Often paired with heatsinks and thermal paste on CPU surface. | Heat spread over the slot card, requiring external cooling. |
| Usage | Standard in most modern desktop and server CPUs. | Used primarily in late 1990s and early 2000s CPUs (e.g., Slot 1). |
| Durability | High reliability with secure pin connections. | More prone to damage due to slot edge contacts. |
| Example | Intel LGA 1200, AMD AM4 socket. | Intel Slot 1, Slot A for AMD. |
Introduction to Sockets and Slots
Sockets are physical connectors on a motherboard designed to house a CPU, ensuring proper electrical and thermal contact for processor operation. Slots refer to expansion connectors allowing peripheral cards, like GPUs or RAM modules, to interface with the motherboard and enhance system capabilities. Understanding the distinction between sockets and slots is essential for assembling and upgrading computer hardware effectively.
Definition: What is a Socket?
A socket is a physical interface on a motherboard designed to house and connect a CPU, enabling direct electrical communication between the processor and the system. It consists of a grid of pins or pads that align with corresponding contacts on the CPU, ensuring secure placement and proper signal transmission. Understanding the specific socket type is crucial for compatibility when upgrading or replacing your processor.
Definition: What is a Slot?
A slot is a physical or virtual connector on a motherboard or device designed to hold and interface expansion cards, such as RAM or graphics cards. It provides a dedicated pathway for data transfer between the device and the system, ensuring proper electrical and communication connections. Slots vary by type, including PCI, PCIe, and DIMM, each supporting specific hardware functions and compatibility.
Key Differences Between Socket and Slot
Sockets serve as physical connectors on motherboards designed to house CPUs, enabling direct electrical contact, while slots are primarily used for connecting expansion cards or memory modules. Socket types vary by pin configuration and CPU compatibility, affecting system upgrade options, whereas slots differ by form factor and supported device type, influencing peripheral connectivity. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate interface for installing or upgrading essential hardware components.
Common Applications of Sockets
Sockets are commonly used in network communication to establish connections between devices, enabling data exchange in applications such as web browsing, email, and online gaming. They facilitate client-server interactions by providing endpoints for sending and receiving data packets over TCP/IP or UDP protocols. You rely on sockets for real-time communication in instant messaging apps, streaming services, and remote access tools.
Common Applications of Slots
Slots are commonly used in computers and electronic devices to provide expansion capabilities, such as PCI, PCIe, and RAM slots that allow you to add graphics cards, sound cards, or additional memory modules. They are integral to enhancing system performance and customization by enabling easy hardware upgrades without soldering. These standardized connectors streamline compatibility and future-proof your devices for evolving technological needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sockets
Sockets offer flexibility by allowing CPUs to be easily upgraded or replaced without soldering, making them ideal for desktop PCs. They provide better cooling options and simpler installation, but can create electrical resistance and potential connection issues compared to soldered slots. Your choice of sockets impacts system maintainability and future upgrade potential, balancing convenience against performance stability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Slots
Slots offer advantages such as simplified hardware design and easy replacement or upgrading of components like memory modules or expansion cards without soldering. However, their disadvantages include limited compatibility due to varying slot types and potential wear over time from repeated insertions and removals. Slots can also restrict performance compared to soldered connections, which provide more stable and reliable electrical pathways.
Socket vs Slot: Compatibility Considerations
Socket and slot compatibility hinges on the physical and electrical interfaces designed for specific processors and motherboards. Your choice must ensure the CPU fits the motherboard socket type, such as LGA, PGA, or BGA, while slots like PCIe support expansion cards with specific keying and bandwidth requirements. Understanding these compatibility considerations prevents hardware conflicts and maximizes system performance.
Socket vs Slot: Which Should You Choose?
Choosing between a socket and a slot depends on your hardware requirements and compatibility needs. Sockets provide a stable, secure connection for CPUs, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and easier upgrades, while slots are typically used for expansion cards, offering flexibility in adding peripherals like graphics cards or network adapters. Assess your specific device compatibility and upgrade plans to determine whether a socket or slot is the best fit for your system.
Socket vs Slot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com