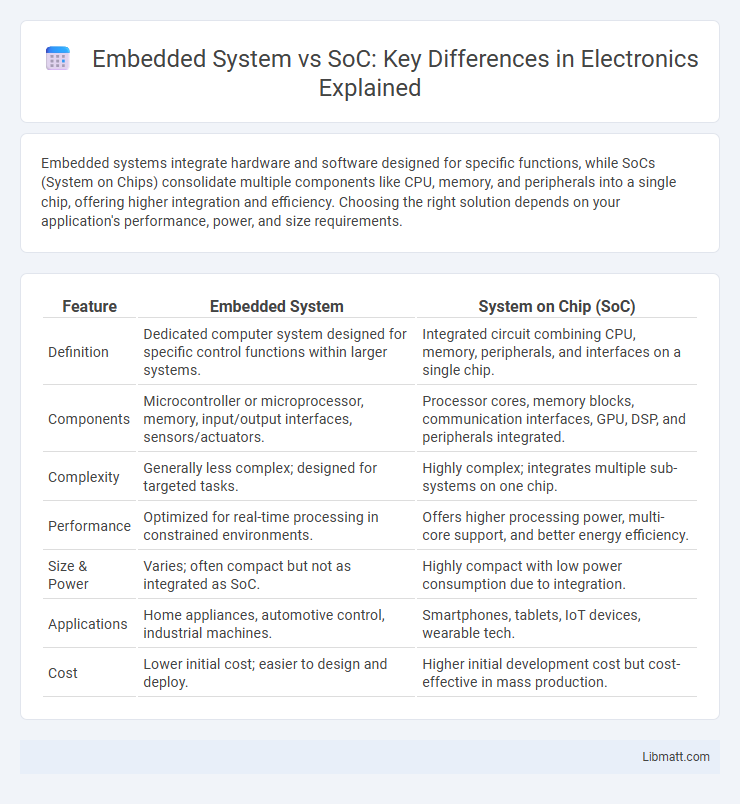
Embedded systems integrate hardware and software designed for specific functions, while SoCs (System on Chips) consolidate multiple components like CPU, memory, and peripherals into a single chip, offering higher integration and efficiency. Choosing the right solution depends on your application's performance, power, and size requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Embedded System | System on Chip (SoC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated computer system designed for specific control functions within larger systems. | Integrated circuit combining CPU, memory, peripherals, and interfaces on a single chip. |
| Components | Microcontroller or microprocessor, memory, input/output interfaces, sensors/actuators. | Processor cores, memory blocks, communication interfaces, GPU, DSP, and peripherals integrated. |
| Complexity | Generally less complex; designed for targeted tasks. | Highly complex; integrates multiple sub-systems on one chip. |
| Performance | Optimized for real-time processing in constrained environments. | Offers higher processing power, multi-core support, and better energy efficiency. |
| Size & Power | Varies; often compact but not as integrated as SoC. | Highly compact with low power consumption due to integration. |
| Applications | Home appliances, automotive control, industrial machines. | Smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, wearable tech. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; easier to design and deploy. | Higher initial development cost but cost-effective in mass production. |
Understanding Embedded Systems: A Brief Overview
Embedded systems integrate dedicated hardware and software designed for specific control functions within larger systems, often characterized by real-time operation and resource constraints. System on Chip (SoC) represents a form of embedded system where all components, including processor cores, memory, and peripherals, are integrated into a single chip, enhancing performance and reducing power consumption. Understanding the distinction between embedded systems and SoC lies in recognizing that SoCs are a highly integrated subset of embedded systems tailored for compact, efficient applications.
What is a System on Chip (SoC)?
A System on Chip (SoC) integrates all essential components of a computer or electronic system, including the processor, memory, input/output ports, and secondary storage, onto a single chip. This consolidation enables higher performance, lower power consumption, and reduced physical size compared to traditional embedded systems composed of separate components. Your choice between an embedded system and an SoC depends on the specific application requirements, such as processing power, integration level, and cost constraints.
Key Differences Between Embedded Systems and SoCs
Embedded systems integrate dedicated hardware and software to perform specific tasks within larger devices, while System on Chips (SoCs) consolidate multiple components like CPU, memory, and peripherals onto a single silicon chip. The primary difference lies in scope: embedded systems encompass a broader combination of hardware and software, whereas SoCs represent a compact, integrated hardware solution designed for efficiency and performance. SoCs enable more compact designs and lower power consumption, making them ideal for modern embedded applications requiring high integration and processing capability.
Architecture Comparison: Embedded Systems vs. SoC
Embedded systems typically feature a microcontroller or microprocessor with dedicated peripherals tailored for specific tasks, emphasizing simplicity and real-time performance. Systems on Chip (SoC) integrate multiple components such as CPU cores, memory, input/output interfaces, and specialized accelerators onto a single silicon chip, enabling high functionality and power efficiency. Understanding the architectural differences helps you choose the right solution based on complexity, integration level, and application requirements.
Performance and Efficiency: SoC vs. Embedded Systems
System-on-Chip (SoC) integrates multiple components such as CPU, GPU, memory, and peripherals on a single chip, significantly enhancing performance by reducing data transfer latency and power consumption compared to traditional embedded systems, which often comprise separate components. SoCs offer higher efficiency through optimized silicon design and advanced fabrication technologies, enabling faster processing speeds and lower energy usage in compact form factors. Embedded systems, while flexible and customizable, generally exhibit lower performance and efficiency due to discrete hardware integration and limited scalability.
Applications: Where Are Embedded Systems Used vs. SoCs?
Embedded systems power specific functions in devices like home appliances, automotive controls, and industrial machines by integrating dedicated hardware and software. System on Chips (SoCs) are utilized in more complex applications requiring consolidated processing power, such as smartphones, tablets, and advanced IoT devices, combining multiple components like CPU, GPU, and memory on a single chip. Your choice between an embedded system and an SoC depends on the application's complexity, performance needs, and integration requirements.
Cost and Scalability: Pros and Cons
Embedded systems typically offer lower initial costs due to their simplicity and dedicated functionality, making them cost-effective for single-purpose applications. Systems on Chip (SoCs) provide greater scalability and integration by combining multiple components on one chip, which reduces overall system size and power consumption but may increase design complexity and upfront development expenses. The trade-off involves evaluating whether long-term flexibility and integration benefits of SoCs outweigh the lower immediate costs and limited scalability of traditional embedded systems.
Design Complexity and Integration
Embedded systems typically feature simpler design complexity with dedicated microcontrollers or processors tailored for specific tasks, resulting in easier integration of individual components. System on Chip (SoC) solutions integrate multiple functions--including CPU, memory, and peripherals--onto a single chip, significantly reducing physical space and power consumption while increasing design complexity due to advanced fabrication processes. Your choice between embedded systems and SoCs impacts the balance between ease of development and the level of integration required for your application.
Future Trends: Embedded Systems and SoC Evolution
Embedded systems and System on Chip (SoC) technologies are rapidly advancing with trends like increased integration of AI accelerators, enhanced low-power designs, and edge computing capabilities. You can expect future SoCs to deliver higher performance and energy efficiency, supporting diverse applications from IoT devices to autonomous systems. Emerging developments in heterogeneous computing and advanced semiconductor processes will shape the evolution of both embedded systems and SoCs.
Choosing the Right Solution: Embedded System or SoC?
Choosing between an embedded system and a System on Chip (SoC) depends on application requirements such as processing power, flexibility, and integration level. Embedded systems offer modularity and easy customization for specialized tasks, while SoCs provide high integration with multiple components like CPU, GPU, and memory on a single chip, reducing size and power consumption. Evaluating factors like development cost, performance needs, and power efficiency helps determine the optimal solution for IoT devices, automotive systems, or consumer electronics.
Embedded System vs SoC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com