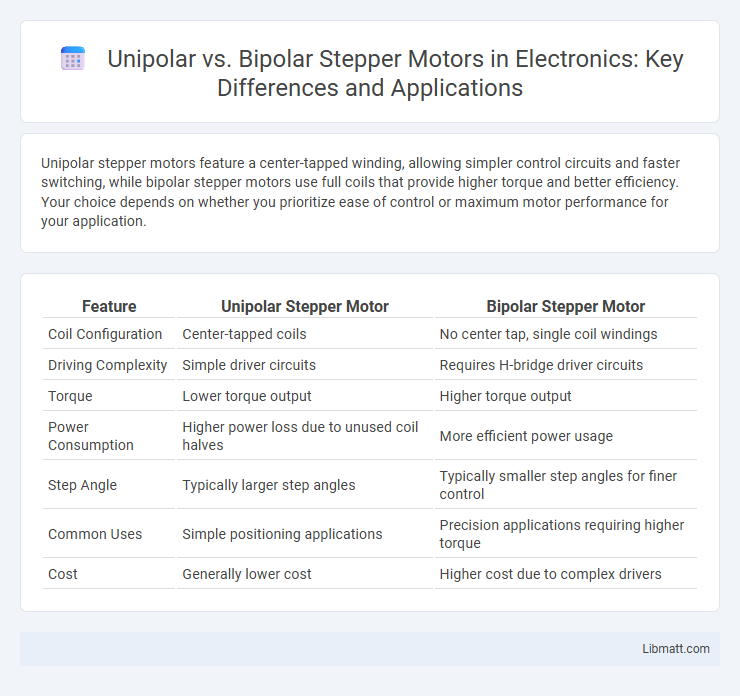
Unipolar stepper motors feature a center-tapped winding, allowing simpler control circuits and faster switching, while bipolar stepper motors use full coils that provide higher torque and better efficiency. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of control or maximum motor performance for your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Unipolar Stepper Motor | Bipolar Stepper Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Coil Configuration | Center-tapped coils | No center tap, single coil windings |
| Driving Complexity | Simple driver circuits | Requires H-bridge driver circuits |
| Torque | Lower torque output | Higher torque output |
| Power Consumption | Higher power loss due to unused coil halves | More efficient power usage |
| Step Angle | Typically larger step angles | Typically smaller step angles for finer control |
| Common Uses | Simple positioning applications | Precision applications requiring higher torque |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex drivers |
Introduction to Stepper Motors
Stepper motors convert electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements by dividing a full rotation into equal steps. Unipolar stepper motors feature a center-tapped winding allowing simpler control with fewer transistors, while bipolar stepper motors have windings without center taps, providing higher torque due to current flowing in both directions. Understanding the distinction helps you select the right motor type for applications requiring precise position control and varying torque needs.
Overview of Unipolar Stepper Motors
Unipolar stepper motors feature a center-tapped winding on each phase, enabling simplified control by energizing only half of the coil windings at a time. This configuration reduces the complexity of the driver circuit and allows for faster switching speeds, making unipolar motors suitable for low to medium torque applications. Commonly used in precision devices such as printers and disk drives, unipolar stepper motors offer easier winding arrangements but generally lower torque compared to bipolar counterparts.
Overview of Bipolar Stepper Motors
Bipolar stepper motors feature two windings per phase, allowing current to flow in both directions, which provides greater torque and efficiency compared to unipolar motors. The absence of a center tap in their coils requires more complex driving circuits, typically using an H-bridge configuration for current reversal. Commonly used in precision applications such as 3D printers and CNC machines, bipolar stepper motors deliver improved performance in variable load conditions and higher power density.
Key Differences Between Unipolar and Bipolar Stepper Motors
Unipolar stepper motors feature center-tapped windings allowing simpler drive circuitry and faster switching speeds, while bipolar motors use a single winding per phase requiring H-bridge drives but offering higher torque and efficiency. Unipolar motors typically provide lower torque due to partial coil utilization, whereas bipolar motors utilize full coil current, maximizing magnetic force and precision. The choice between unipolar and bipolar hinges on desired torque, control complexity, and application-specific performance requirements.
Wiring and Circuit Complexity Comparison
Unipolar stepper motors feature simpler wiring with a center-tapped coil configuration, allowing easy control with fewer transistors and simpler driver circuits. Bipolar stepper motors require a more complex H-bridge circuit for reversing current in coils, resulting in more intricate wiring and higher control circuit complexity. The reduced circuitry in unipolar motors often leads to cost-efficient and straightforward designs, while bipolar motors offer higher torque at the expense of greater wiring and driver complexity.
Performance and Torque Analysis
Unipolar stepper motors generally offer simpler control and faster response but produce lower torque compared to bipolar motors due to their coil design, which limits current flow through each winding. Bipolar stepper motors deliver higher torque and better efficiency because current reverses through the coils, maximizing the magnetic field strength for each phase. Your choice depends on the required torque and performance in applications, with bipolar motors preferred for high-torque needs and unipolar for simpler, lower-torque tasks.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Unipolar stepper motors typically consume more power due to their simpler winding design, which results in continuous current flow through part of the coil even when not generating torque, reducing overall efficiency. Bipolar stepper motors use the entire coil for each phase, delivering higher torque per current and thus improving power efficiency and performance. As a result, bipolar motors are generally preferred in applications demanding lower power consumption and greater energy efficiency.
Applications of Unipolar Stepper Motors
Unipolar stepper motors are commonly used in applications requiring moderate torque and simple control, such as 3D printers, fax machines, and small robotics. Their ease of drive circuit design and ability to operate at higher speeds make them ideal for office automation and CNC machines. Unipolar motors also find use in textile and servo systems where quick, precise positioning is essential.
Applications of Bipolar Stepper Motors
Bipolar stepper motors find extensive applications in CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics due to their higher torque and efficiency compared to unipolar motors. These motors are ideal for precise positioning and speed control in automation systems, making them essential in medical devices and textile machinery as well. Your projects benefit from the robust performance and compact design of bipolar stepper motors, especially where high torque and accuracy are critical.
Choosing the Right Stepper Motor for Your Project
Selecting between unipolar and bipolar stepper motors depends on torque requirements, wiring complexity, and control precision needed for your project. Bipolar stepper motors offer higher torque and efficiency with simpler winding, ideal for applications demanding strong performance and precise control. Unipolar motors provide easier wiring and simpler driver circuits, making them suitable for low-torque or beginner-level projects with limited hardware capabilities.
Unipolar vs Bipolar stepper motor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com