Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by maintaining a constant voltage across electronic circuits during overvoltage conditions, while TVS diodes protect sensitive components by rapidly clamping transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge or lightning strikes. Choosing the right diode ensures your circuit's reliability and effective protection against voltage irregularities.
Table of Comparison
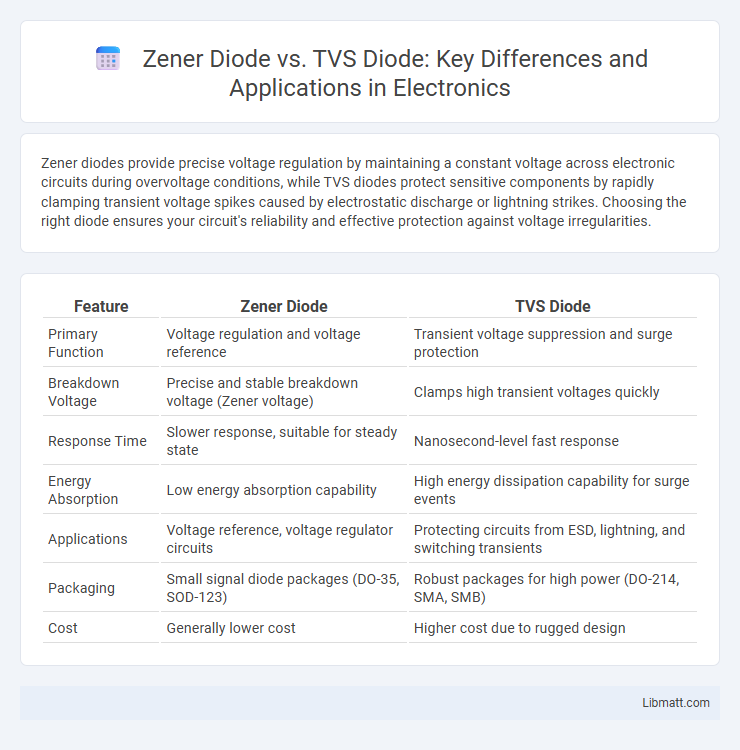
| Feature | Zener Diode | TVS Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Voltage regulation and voltage reference | Transient voltage suppression and surge protection |
| Breakdown Voltage | Precise and stable breakdown voltage (Zener voltage) | Clamps high transient voltages quickly |
| Response Time | Slower response, suitable for steady state | Nanosecond-level fast response |
| Energy Absorption | Low energy absorption capability | High energy dissipation capability for surge events |
| Applications | Voltage reference, voltage regulator circuits | Protecting circuits from ESD, lightning, and switching transients |
| Packaging | Small signal diode packages (DO-35, SOD-123) | Robust packages for high power (DO-214, SMA, SMB) |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to rugged design |
Introduction to Zener and TVS Diodes
Zener diodes are semiconductor devices designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region, providing voltage regulation and stable reference voltage in electronic circuits. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diodes protect sensitive electronics by clamping excessive voltage spikes during transient events such as electrostatic discharge or lightning strikes. Both components serve critical roles in safeguarding and stabilizing voltage levels but differ primarily in their intended applications and response characteristics.
Basic Functionality of Zener Diode
A Zener diode operates primarily as a voltage regulator by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds a specified breakdown level, known as the Zener voltage. It maintains a stable reference voltage in circuits, protecting sensitive components from voltage fluctuations. Unlike TVS diodes, Zener diodes are designed for continuous voltage regulation rather than transient voltage suppression.
Basic Functionality of TVS Diode
TVS diodes protect electronic circuits by clamping voltage spikes and transient surges, ensuring sensitive components remain safe from damage during electrostatic discharge or lightning events. Unlike Zener diodes that regulate voltage in steady-state conditions, TVS diodes respond instantly to transient voltage spikes, dissipating excess energy to prevent circuit failure. Your devices benefit from the rapid response and high power handling capability of TVS diodes, making them essential for robust surge protection.
Construction and Design Differences
Zener diodes are constructed with heavily doped p-n junctions to allow breakdown at a precise reverse voltage, optimizing voltage regulation in low-power circuits. TVS diodes feature a robust, avalanche-mode design with a thick semiconductor junction and fast response characteristics to protect sensitive electronics from transient voltage spikes. Your choice depends on whether precise voltage regulation (Zener diode) or high-energy pulse suppression (TVS diode) is required in the application.
Key Electrical Characteristics
Zener diodes are designed to operate in the breakdown region at a specific reverse voltage, providing precise voltage regulation with a tightly controlled breakdown voltage ranging from a few volts to several hundred volts. TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes are optimized for fast response times and high peak pulse power dissipation, commonly rated in the kilowatt range, to protect circuits from transient voltage spikes such as ESD or lightning surges. While Zener diodes maintain a stable voltage under steady-state conditions, TVS diodes excel in clamping voltage during transient events with response times in the picosecond to nanosecond range.
Typical Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are typically used for voltage regulation and reference applications, protecting circuits by maintaining a stable output voltage despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. They are commonly found in power supplies, voltage clamping circuits, and waveform clipping to safeguard sensitive electronic components from overvoltage. Unlike TVS diodes, which respond to transient voltage spikes with rapid energy absorption, Zener diodes provide steady voltage regulation under normal operating conditions.
Typical Applications of TVS Diodes
TVS diodes are primarily used for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and inductive load switching. Typical applications include safeguarding communication lines, power supply circuits, automotive electronics, and consumer devices. Your electronic designs benefit from the rapid response and high energy absorption capabilities of TVS diodes to prevent damage and ensure reliability.
Protection Mechanisms: Zener vs TVS
Zener diodes provide voltage regulation by clamping voltage to a specific breakdown level, protecting circuits from overvoltage in steady-state conditions. TVS diodes react rapidly to transient voltage spikes, absorbing high-energy surges like lightning or electrostatic discharge to safeguard sensitive components. Your choice between Zener and TVS diodes depends on whether you need continuous voltage regulation or robust transient surge protection.
Selection Criteria for Circuit Protection
When selecting between a Zener diode and a TVS diode for circuit protection, consider the maximum transient voltage and response time requirements; TVS diodes excel in fast response to transient surges, ideal for protecting sensitive electronics. Zener diodes are better suited for voltage regulation and clamping at specific voltage levels due to their precise breakdown characteristics. Assess your circuit's voltage tolerance and transient conditions carefully to choose the diode that optimally shields your components from damage.
Summary: Choosing Between Zener and TVS Diodes
Zener diodes provide voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage in low-power applications, while TVS diodes are designed for high-speed transient voltage suppression and protection against voltage spikes. Your choice depends on the application's need for precise voltage control or robust surge protection. Understanding the specific electrical characteristics, such as breakdown voltage and power dissipation, ensures optimal performance and reliability in your circuit design.
Zener Diode vs TVS Diode Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com